Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
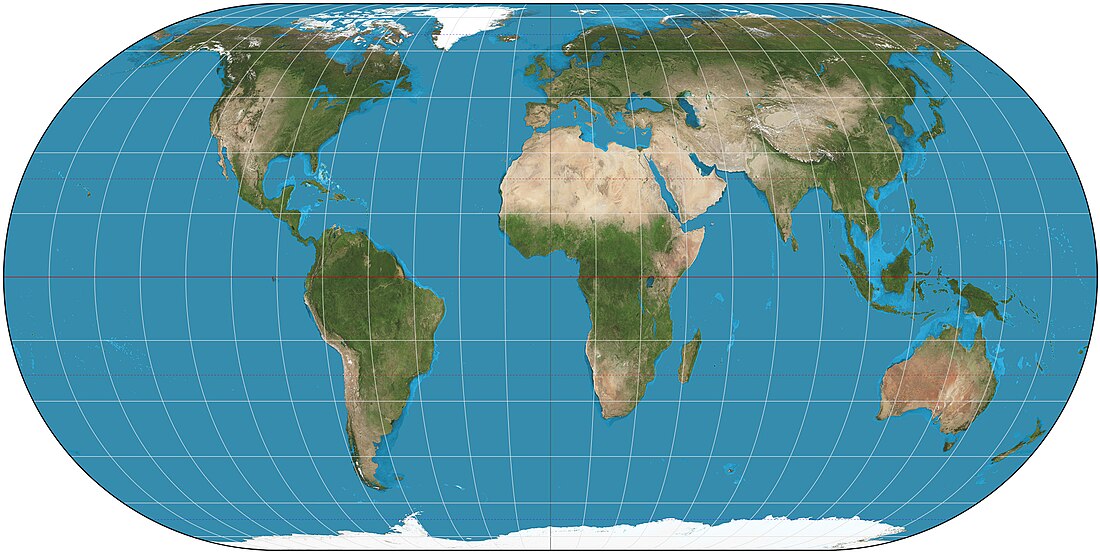
Eckert IV projection
Pseudocylindrical equal-area map projection From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Eckert IV projection is an equal-area pseudocylindrical map projection. The length of the polar lines is half that of the equator, and lines of longitude are semiellipses, or portions of ellipses. It was first described by Max Eckert in 1906 as one of a series of three pairs of pseudocylindrical projections. Within each pair, meridians are the same whereas parallels differ. Odd-numbered projections have parallels spaced equally, whereas even-numbered projections have parallels spaced to preserve area. Eckert IV is paired with Eckert III.[1]


Remove ads
Formulas
Summarize
Perspective
Forward formulae
Given a sphere of radius R, central meridian λ0 and a point with geographical latitude φ and longitude λ, plane coordinates x and y can be computed using the following formulas:
where
θ can be solved for numerically using Newton's method.[2]
Inverse formulae
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}x&={\frac {2}{\sqrt {4\pi +\pi ^{2}}}}R\,(\lambda -\lambda _{0})(1+\cos \theta )\approx 0.422\,2382\,R\,(\lambda -\lambda _{0})(1+\cos \theta ),\\[8pt]y&=2{\sqrt {\frac {\pi }{4+\pi }}}R\sin \theta \approx 1.326\,5004\,R\sin \theta ,\end{aligned}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f23e7d33107851d02f860589a7fb5a4eee05f749)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\theta &=\arcsin \left[y{\frac {\sqrt {4+\pi }}{2{\sqrt {\pi }}R}}\right]\approx \arcsin \left[{\frac {y}{1.326\,5004\,R}}\right]\\[8pt]\varphi &=\arcsin \left[{\frac {\theta +\sin \theta \cos \theta +2\sin \theta }{2+{\frac {\pi }{2}}}}\right]\\[8pt]\lambda &=\lambda _{0}+x{\frac {\sqrt {4\pi +\pi ^{2}}}{2R(1+\cos \theta )}}\approx \lambda _{0}+{\frac {x}{0.422\,2382\,R\,(1+\cos \theta )}}\end{aligned}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4dc58f1e467ea9369202d3b0a67c7e3f2e8a9842)