Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Engineering information management
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
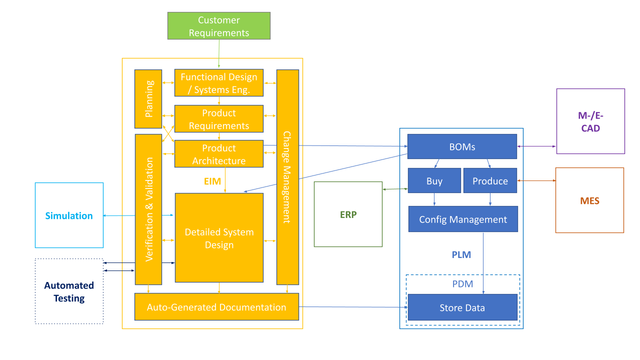
Engineering information management (EIM) is the business function within product development and specifically systems engineering that allows engineers to collaborate on a single source of truth of engineering data.
Contrary to product data management (PDM) and product lifecycle management (PLM), its main purpose is not storage of CAD-related drawings and files, but rather the full execution of the V-model for hardware development, complementing and integrating to the above mentioned systems.
Remove ads
Scope
EIM systems enable collaboration on all important aspects of the engineering lifecycle, such as:
- Requirements management
- Functional design
- Product architecture
- Detailed systems design and simulation
- Verification and validation
- Documentation
EIM systems implement the activities on both sides of the engineering V-model. Instead of being purely a data storage, it focuses also on the human interaction with the models and data,[1] thus enabling concurrent engineering.[2]
EIM therefore enables the optimization of products and engineering processes, where traditional methodologies have become ineffective in keeping up with rising product and process complexity.[3]
Remove ads
Interactions with the other engineering management systems
EIM systems do directly and indirectly interact with other tools in the engineering information infrastructure, such as:
- Computer simulation tools
- Automated hardware testing tools
- Product lifecycle and product data management systems[4]
- Enterprise resource planning tools
- Manufacturing execution systems
- Computer-aided design (MCAD) and electronic design automation (ECAD) tools
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads