Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
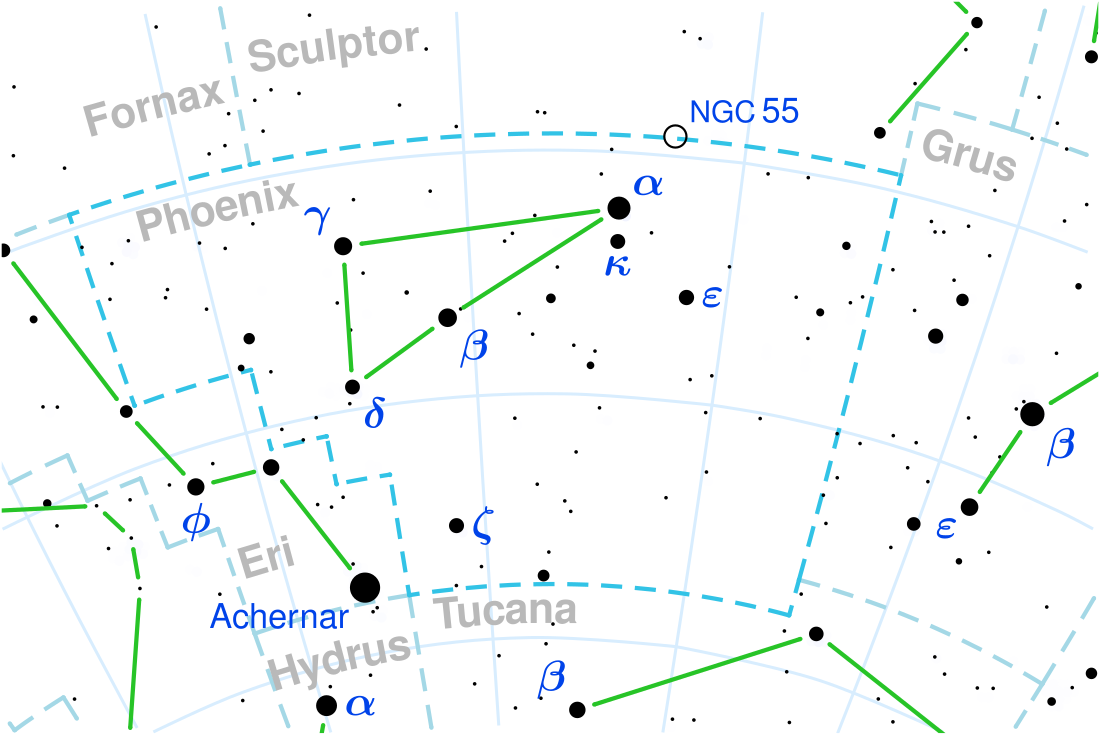
Epsilon Phoenicis
Star in the constellation Phoenix From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Epsilon Phoenicis is a star in the southern constellation of Phoenix. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.87.[2] The distance to this star is approximately 144 light years based on parallax measurements, but it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −9.2 km/s.[5]
This is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of K0III,[4] a star that has used up its core hydrogen and has expanded. It is a red clump star, indicating that it has passed the red-giant branch, undergone a helium flash and is currently on the core helium-fusing horizontal branch.[3] Epsilon Phoenicis is about two times more massive than the Sun, and expanded to ten times its radius. It radiates 50 the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere[7] at an effective temperature of 4,862 K. Based on the elemental abundance of iron in the stellar atmosphere, the metallicity of Epsilon Phoenicis is similar to that of the Sun.[8]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads