Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
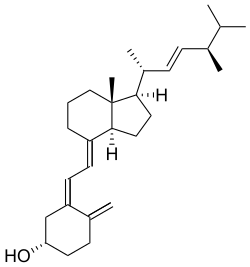
Ergocalciferol
Vitamin D2, a chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Ergocalciferol, also known as vitamin D2 and nonspecifically calciferol, is a type of vitamin D found in food. It is used as a dietary supplement[3] to prevent and treat vitamin D deficiency[4] due to poor absorption by the intestines or liver disease.[5] It may also be used for low blood calcium due to hypoparathyroidism.[5] It is taken by mouth or via injection into a muscle.[4][5]
Excessive doses can result in vitamin D toxicity causing increased urine production, high blood pressure, kidney stones, kidney failure, muscle weakness, and constipation.[6] If high doses are taken for a long period of time, tissue calcification may occur.[5] Normal doses are safe in pregnancy.[7] It works by increasing the amount of calcium absorbed by the intestines and reabsorbed by the kidneys.[6] Food in which it is found include some mushrooms.[8]
Ergocalciferol was first described in 1936.[9] Ergocalciferol is available as a generic medication and over the counter.[6] In 2023, it was the 48th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 13 million prescriptions.[10][11] Certain foods such as breakfast cereal and margarine have ergocalciferol added to them in some countries.[12][13] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[14]
Remove ads
Use

Ergocalciferol may be used as a vitamin D supplement, whereas cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) is produced naturally by the skin when exposed to ultraviolet light.[15] Ergocalciferol (D2) and cholecalciferol (D3) are considered to be equivalent for vitamin D production, as both forms appear to have similar efficacy in ameliorating rickets[16] and reducing the incidence of falls in elderly patients.[17] Conflicting reports exist, however, concerning the relative effectiveness, with some studies suggesting that ergocalciferol has less efficacy based on limitations in absorption, binding, and inactivation.[18] A meta-analysis concluded that evidence usually favors cholecalciferol in raising vitamin D levels in blood, although it stated more research is needed.[18]
Remove ads
Mechanism
Ergocalciferol is a secosteroid formed by a photochemical bond breaking of a steroid, specifically, by the action of ultraviolet light (UV-B or UV-C) on ergosterol, a form of provitamin D2.[19]
Like cholecalciferol, ergocalciferol is inactive by itself. It requires two hydroxylations to become active: the first in the liver by CYP2R1 to form 25-hydroxyergocalciferol (ercalcidiol or 25-OH D2[20]), and the second in the kidney by CYP27B1, to form the active 1,25-dihydroxyergocalciferol (ercalcitriol or 1,25-(OH)2D2), which activates the vitamin D receptor.[21] Unlike cholecalciferol, 25-hydroxylation is not performed by CYP27A1 for ergocalciferol.[22]
Ergocalciferol and metabolites have lower affinity to the vitamin D-binding protein compared to the D3 counterparts. The binding affinity of ercalcitriol to the vitamin D receptor is similar to that of calcitriol.[22] Ergocalciferol itself and metabolites can be deactivated by 24-hydroxylation.[23]
Remove ads
Sources
Summarize
Perspective
Fungus, from USDA nutrient database (per 100g), D2 + D3:[24][25]
- Mushrooms, Agaricus bisporus:
- raw portobello: 0.3 μg (10 IU); exposed to ultraviolet light: 11.2 μg (446 IU)
- raw crimini: 0.1 μg (3 IU); exposed to ultraviolet light: 31.9 μg (1276 IU)
- Mushrooms, shiitake:
- raw: Vitamin D (D2 + D3): 0.4 μg (18 IU)
- dried: Vitamin D (D2 + D3): 3.9 μg (154 IU)
Lichen
- Cladina arbuscula specimens grown under different natural conditions contain provitamin D2 and vitamin D2, ranges 89–146 and 0.22–0.55 μg/g dry matter respectively. They also contain vitamin D3 (range 0.67 to 2.04 μg/g) although provitamin D3 could not be detected. Vitamin D levels correlate positively with UV irradiation.[26]
Plantae
- Alfalfa (Medicago sativa subsp. sativa), shoot: 4.8 μg (192 IU) vitamin D2, 0.1 μg (4 IU) vitamin D3[27]
Biosynthesis
The vitamin D2 content in mushrooms and C. arbuscula increase with exposure to ultraviolet light.[26][28] Ergosterol (provitamin D2) found in these fungi is converted to previtamin D2 on UV exposure, which then turns into vitamin D2. As cultured mushrooms are generally grown in darkness, less vitamin D2 is found compared to those grown in the wild or dried in the sun.[19]
When fresh mushrooms or dried powders are purposely exposed to ultraviolet light, vitamin D2 levels can be concentrated to much higher levels.[29][30][31] The irradiation procedure does not cause significant discoloration, or whitening, of mushrooms.[32] Claims have been made that a normal serving (approx. 2 oz or 60 grams) of fresh mushrooms treated with ultraviolet light have increased vitamin D content to levels up to 80 micrograms or 3200 IU if exposed to just five minutes of UV light after being harvested.[30]
Button mushrooms with enhanced vitamin D2 content produced this way functions similarly to a vitamin D2 supplement; both effectively improves vitamin D status.[29][33] Vitamin D2 from UV-irradiated yeast baked into bread or mushrooms is bioavailable and increases blood levels of 25(OH)D.[29]
Remove ads
Names
Viosterol, the name given to early preparations of irradiated ergosterol, is essentially synonymous with ergocalciferol.[34][35] However, currently, Viosterol is also the brand name for cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) in some countries.[36][37]
Ergocalciferol is manufactured and sold under various brand names, including Deltalin (Eli Lilly and Company), Drisdol (Sanofi-Synthelabo), and Calcidol (Patrin Pharma).[citation needed]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads