Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
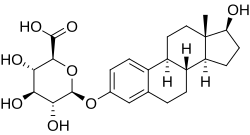
Estradiol 3-glucuronide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Estradiol 3-glucuronide (E2-3G), also known as 17β-estradiol 3-(β-D-glucuronide), is a naturally occurring and endogenous estrogen conjugate.[1] It is specifically the C3 glucuronide conjugate of estradiol, the major estrogen in the body.[1] It is formed from estradiol in the liver by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in urine and bile.[2][3] Similarly to estrogen sulfates like estrone sulfate, estrogen glucuronides have much higher water solubility than do unconjugated estrogens like estradiol.[3]
Estrogen glucuronides can be deconjugated into the corresponding free estrogens by β-glucuronidase in tissues that express this enzyme, such as the mammary gland.[2] As a result, estrogen glucuronides have estrogenic activity via conversion into estrogens.[2]
Estradiol 3-glucuronide is a positional isomer of estradiol 17β-glucuronide.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads