Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
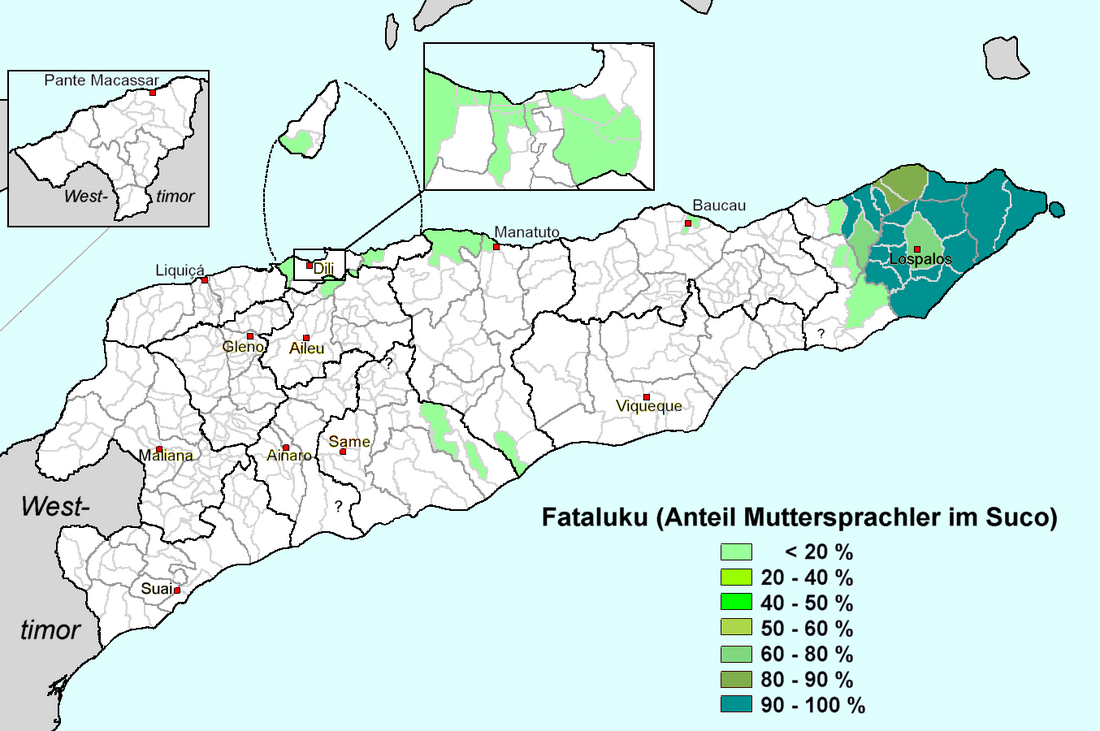
Fataluku language
Papuan language of East Timor From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Fataluku (also known as Dagaga, Dagoda', Dagada) is a Papuan language spoken by approximately 37,000 people of Fataluku ethnicity in the eastern areas of East Timor, especially around Lospalos. It is a member of the Timor-Alor-Pantar language family, which includes languages spoken both in East Timor and nearby regions of Indonesia.[2] Fataluku's closest relative is Oirata,[3] spoken on Kisar island, in the Moluccas of Indonesia.[4] Fataluku is given the status of a national language under the constitution. Speakers of Fataluku normally have a command of Tetum and/or Indonesian,[5] those speakers who are educated under Portuguese rule or from younger generation educated under Portuguese-language educational system during independence speak Portuguese.
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (July 2024) |
It has a considerable number of Austronesian loanwords, and it has borrowed elements of Sanskrit and Arabic vocabulary via Malay and elements of Portuguese.[3]
The five main Fataluku dialects are identified as follows: East Fataluku, South Fataluku, Central Fataluku, North Fataluku and Northwest Fataluku.[6] The differences that exist between these dialects, especially beyond phonology, are unclear and require more research. Dialects differ with respect to the phonetic realization of palatal obstruents, the presence of a glottal stop phoneme and a voicing distinction in stops, as well as aspects of the stress system.[7]
Remove ads
Phonology
Vowels
Consonants
Remove ads
Words and phrases
In the examples below, the letter 'c' and the letter combination 'tx' are pronounced as the 'ch' in the English word 'church'.
Rau ana kapare? / e nicha rau rau / maice ana umpe? "how are you?" Rau "good" Kapare "not good" Hó "yes" Xaparau "thank you" Tali even xaparau "thank you very much" nitawane "you're welcome" Favoruni "please" itu nae tini "excuse me" Ó lai'i "hello" mua toto, ia toto,purupale " take care" Kois ta niat ali fanuhene "see you later" Pronoun Possessive pronoun I : Aniri/Ana My: Ahani You : Eri (singular), Iri (plural) Your: Eheni(sing), Eheniere (plur) We : Iniri (excl), Afiri (inclusive) Our: Inihini (exc), Afihini: (incl) They : Tawari, Márafuri Their: Their Tavarhini, Marafurhini He/She : Tavai, marí, mármocoi His/Her: Tavahini, Marmokoihini It : Iví Its: Ivihini, Tavahini
Remove ads
Vaihoho Sung-Poems
Vaihoho is a sacred form of storytelling for the Fataluku people of Timor-Leste. Vaihoho or sung-stories has been the major form for continuing the Fataluku oral tradition. From 1999 to 2014, cultural leader Justino Valentim recorded a significant amount of Vaihoho material. Funded by the Modern Endangered Archives Program at the UCLA Library, a team from Many Hands International, led by in partnership with the University of Melbourne, digitized 17 field notebooks of sung-songs and five Fataluku language dictionaries collected by Valentim as well as notes, poems and photos involving the practice of Vaihoho.[8] This collection is available digitally through the UCLA library.[9]
See also
Notes
Further reading
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads