Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
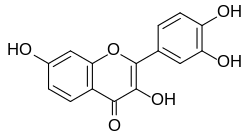
Fisetin
Plant chemical From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Fisetin (7,3′,4′-flavon-3-ol) is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols.[1] It occurs in many plants where it serves as a yellow pigment. It is found in many fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries, apples, persimmons, onions, and cucumbers.[2][3][4]
Its chemical formula was first described by Austrian chemist Josef Herzig in 1891.[5]
Remove ads
Sources
Summarize
Perspective
Fisetin is a flavonoid synthesized by many plants such as the trees and shrubs of Fabaceae, acacias Acacia greggii,[6] and Acacia berlandieri,[6] parrot tree (Butea frondosa), honey locust (Gleditsia triacanthos), members of the family Anacardiaceae such as the Quebracho colorado, and species of the genus Rhus, which contains the sumacs.[7] Along with myricetin, fisetin provides the color of the traditional yellow dye young fustic, an extract from the Eurasian smoketree (Rhus cotinus).
Many fruits and vegetables contain fisetin.[2] In one study, fisetin content was highest in strawberries, with content also observed in apples, grapes, onions, tomatoes, and cucumbers.[2] Fisetin can be extracted from fruit juices, wines,[8] and teas.[3] It is also present in Pinophyta species such as the yellow cypress (Callitropsis nootkatensis).
The average intake of fisetin from foods in Japan is about 0.4 mg per day.[1]
Remove ads
Research
Although fisetin has been under laboratory research over several decades for its potential role in senescence or anticancer properties, among other possible effects, there is no clinical evidence that it provides any benefit to human health, as of 2018.[1]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads