Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Flavanol-anthocyanin adduct
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Flavanol-anthocyanin adducts are formed during wine ageing through reactions between anthocyanins and tannins present in grape, with yeast metabolites such as acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde-induced reactions yield ethyl-linked species such as malvidin glucoside-ethyl-catechin.[1][2]
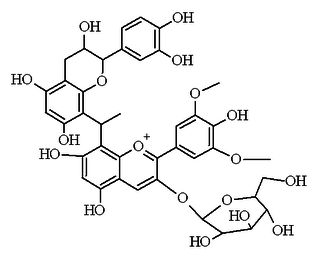
This type of compound has a better color stability at pH 5.5 than normal anthocyanins. When the pH was increased from 2.2 to 5.5, the solution of the pigment became progressively more violet (λmax = 560 nm at pH 5.5), whereas similar solutions of the anthocyanin were almost colorless at pH 4.0.[3]
Remove ads
References
See also
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
