Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
FlmA-FlmB toxin-antitoxin system
RNA family From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
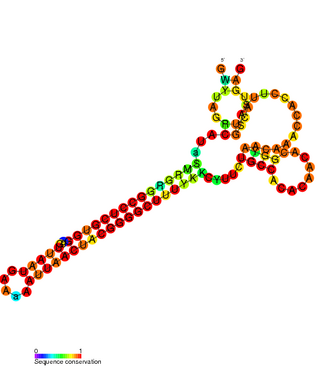
The FlmA-FlmB toxin-antitoxin system consists of FlmB RNA (F leading-region maintenance B), a family of non-coding RNAs and the protein toxin FlmA. The FlmB RNA transcript is 100 nucleotides in length and is homologous to sok RNA from the hok/sok system and fulfills the identical function as a post-segregational killing (PSK) mechanism.[1][2]
flmB is found on the F-plasmid of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. It is responsible for stabilising the plasmid. If the plasmid is not inherited, long-lived FlmA mRNA and protein will be highly toxic to the cell, possibly to the point of causing cell death.[2] Daughter cells which inherit the plasmid inherit the FlmB gene, coding for FlmB RNA which binds the leader sequence of FlmA mRNA and represses its translation.[1]
Remove ads
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads