Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Fraser Stoddart
Scottish chemist (1942–2024) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Sir James Fraser Stoddart, FRS FRSE HonFRSC[4] (24 May 1942 – 30 December 2024) was a British-American chemist who was Chair Professor in Chemistry at the University of Hong Kong.[8] He was the Board of Trustees Professor of Chemistry and head of the Stoddart Mechanostereochemistry Group in the Department of Chemistry at Northwestern University in the United States.[9] He worked in the area of supramolecular chemistry and nanotechnology. Stoddart developed highly efficient syntheses of mechanically-interlocked molecular architectures such as molecular Borromean rings, catenanes and rotaxanes utilising molecular recognition and molecular self-assembly processes. He demonstrated that these topologies can be employed as molecular switches.[10] His group has even applied these structures in the fabrication of nanoelectronic devices and nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS).[11] His efforts were recognized by numerous awards, including the 2007 King Faisal International Prize in Science.[12][13][14] He shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry together with Ben Feringa and Jean-Pierre Sauvage in 2016 for the design and synthesis of molecular machines.[5][15][16][17][18]



Remove ads
Early life and education
Fraser Stoddart was born in Edinburgh, Scotland, on 24 May 1942,[1] the only child of Tom and Jean Stoddart.[19][20] He was brought up as a tenant farmer on Edgelaw Farm, a small community consisting of three families. Sir Fraser professed a passion for jigsaw puzzles and construction toys in his formative years, which he believed was the basis for his interest in molecular construction.[21]
Stoddart received early schooling at the local village school in Carrington, Midlothian, before going on to Melville College in Edinburgh.[22][23] He started at the University of Edinburgh in 1960 where he initially studied chemistry, physics and mathematics.[19] He was awarded a Bachelor of Science degree in Chemistry in 1964 followed by a Doctor of Philosophy in 1966[24] for research on natural gums in Acacias supervised by Sir Edmund Langley Hirst and D M W Anderson[6] from the University of Edinburgh.[25]
Remove ads
Career
Summarize
Perspective
In 1967, Stoddart went to Queen's University (Canada) as a National Research Council Postdoctoral Fellow. In 1970 he moved to the University of Sheffield as an Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) Research Fellow, before joining the academic staff as a lecturer in chemistry. In early 1978 he was a Science Research Council Senior Visiting Fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry. Later in 1978, he was transferred to the ICI Corporate Laboratory in Runcorn, England where he first started investigating the mechanically interlocked molecules that would eventually become molecular machines.[26] At the end of the three year secondment he returned to Sheffield[27] where he was promoted to a Readership in 1982.
Stoddart was awarded a Doctor of Science degree from the University of Edinburgh in 1980[28] for his research into stereochemistry beyond the molecule. In 1990, he moved to the Chair of Organic Chemistry at the University of Birmingham and was Head of the School of Chemistry there (1993–97) before moving to UCLA as the Saul Winstein Professor of Chemistry in 1997, succeeding Nobel laureate Donald Cram.[14][29]
In July 2002, Stoddart became the Acting Co-Director of the California NanoSystems Institute (CNSI). In May 2003, he became the Fred Kavli Chair of NanoSystems Sciences and served from then through August 2007 as the Director of the CNSI.[29]
In 2008, Stoddart established the Mechanostereochemistry Group and was named Board of Trustees Professor in Chemistry at Northwestern University.[30] He went on to be the Director of the Center for the Chemistry of Integrated Systems (CCIS) at Northwestern University in 2010.[31]
In 2017, Stoddart was appointed a part-time position at the University of New South Wales to establish his New Chemistry initiative at the UNSW School of Chemistry.[32]
In 2019, Stoddart introduced a skincare brand called Noble Panacea.[33]
In 2021, Stoddart co-founded a startup called H2MOF, dedicated to solving the challenges associated with hydrogen storage and transportation.[34]
In 2023, Stoddart joined the University of Hong Kong as Chair Professor of Chemistry.[8]
During 35 years, nearly 300 PhD students and postdoctoral researchers have been trained in his laboratories.[22]
Remove ads
Research
Summarize
Perspective
Stoddart is one of only a few chemists of the past quarter century to have pioneered a new field in organic chemistry. By establishing a new field where the main feature is mechanical bonds, he paved the way for molecular recognition, self-assembly processes for template-directed mechanically interlocked syntheses, molecular switches, and motor-molecules. These advances have formed the basis of the fields of nanoelectronic devices, nanoelectromechanical systems, and molecular machines.[35][5]
One of his major contributions to the development of mechanically-interlocked molecular architectures such as rotaxanes and catenanes was the establishment of efficient synthetic protocols based on the binding of cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) with electron-rich aromatic guests.[36] His group reported the synthesis of an advanced mechanically interlocked molecular architecture called molecular Borromean rings through the use of dynamic covalent chemistry.[37] The efficient procedures developed to synthesize these molecular architectures was applied to the construction of molecular switches that operate based on the movement of the various components with respect to one another. These interlocked molecules have potential uses as molecular sensors, actuators, amplifiers, and molecular switches, and can be controlled chemically, electrically, and optically.[38]
His work bridged the gap between chemistry and the scientific and engineering challenges of nanoelectromechanical systems."[39]
Stoddart pioneered the use of mechanically interlocked molecular architectures to create nanomechanical systems.[40][41] He has demonstrated that such devices can be fabricated using a combination of the bottom-up approach of molecular self-assembly and a top-down approach of lithography and microfabrication.[42]
The credit for making molecular machines attractive to chemists goes to Fraser Stoddart, (... who) had the vision to realise that these architectures gave you the possibility of large amplitude-controlled motions, and that that could be the basis of molecular machines.
Presentation style
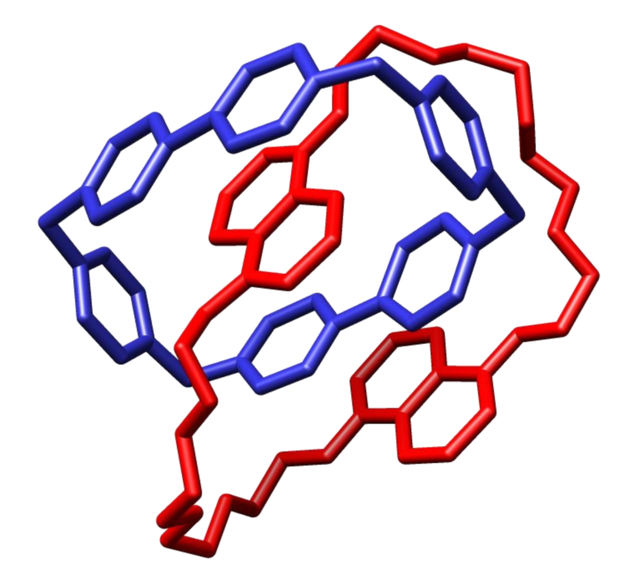
Stoddart's papers and other material are instantly recognizable due to a distinctive "cartoon"-style of representation he developed beginning in the late 1980s. A solid circle is often placed in the middle of the aromatic rings of the molecular structures he has reported, and different colours to highlight different parts of the molecules. The different colours usually correspond to the different parts of a cartoon representation of the molecule, but are also used to represent specific molecular properties (blue, for example, is used to represent electron-poor recognition units while red is used to represent the corresponding electron-rich recognition units). The distinctive colouring has led to coining the term 'little blue box' for the cyclophane cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene); an important π-acceptor used to synthesize mechanically bonded structures.[26] Stoddart maintains this standardized colour scheme across all of his publications and presentations, and his style has been adopted by other researchers reporting mechanically interlocked molecules based on his syntheses.[43][44]
ISI ratings
As of 2024[update] Stoddart had an h-index of 168.[45][46] As of 2023 he had published more than 1200 publications.[47]
Remove ads
Personal life and death
Stoddart was an American and British citizen. He was married to Norma Agnes Scholan from 1968[1][2][3] until her death in 2004 from cancer.[26] They had two daughters: Fiona Jane and Alison Margaret.[1] Norma Stoddart obtained a PhD in biochemistry and helped support the research efforts of her husband at the Universities of Sheffield, Birmingham, and California, Los Angeles.[48]
On 30 December 2024, Stoddart died from cardiac arrest at a hotel in Melbourne, Australia, where he was visiting his daughter, at the age of 82.[49][50][51][52][53]
Remove ads
Philanthropy
The Fraser and Norma Stoddart Prize for PhD students was established at their alma mater, the University of Edinburgh.[2] It was first awarded in 2013.[54]
Awards and honours
Summarize
Perspective
Stoddart was appointed a Knight Bachelor in the New Year's Honours December 2006, by Queen Elizabeth II for Services to Chemistry and Molecular Nanotechnology.[27][55]
In 2007, he received the Albert Einstein World Award of Science in recognition for his outstanding and pioneering work in molecular recognition and self-assembly, and the introduction of quick and efficient template-directed synthetic routes to mechanically interlocked molecular compounds, which have changed the way chemists think about molecular switches and machines.[56]
In 2016, he shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry together with Ben Feringa and Jean-Pierre Sauvage for the design and synthesis of molecular machines.[5][12]
Memberships
- 2014 Membership, National Academy of Sciences, US[57]
- 2012 Fellowship, American Academy of Arts and Sciences, US[58]
- 2011 Honorary Fellowship, Royal Society of Chemistry, UK[59]
- 2008 Honorary Fellowship, Royal Society of Edinburgh, UK[60]
- 2006 Appointed Knight Bachelor by HM Queen Elizabeth II, UK[55]
- 2006 Foreign membership, Science Division of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences[61]
- 2005 Fellowship, American Association for the Advancement of Science, US[62]
- 1999 Fellowship, Academy of Sciences Leopoldina, Germany[63]
- 1994 Elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of London, UK[4]
Other awards and honours
- 2018 Fray International Sustainability Award [64]
- 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- 2016 Haworth Memorial Lectureship, Royal Society of Chemistry[65][66]
- 2014 Centenary Prize Winner, Royal Society of Chemistry[67]
- 2012 Distinguished Citizen Award, Illinois Saint Andrew Society, Chicago, US
- 2010 Royal Medal of the Royal Society of Edinburgh presented by Duke of Edinburgh[68][69]
- 2008 Davy Medal of the Royal Society of London[39]
- 2008 American Chemical Society Arthur C. Cope Award[70]
- 2007 Feynman Prize in Nanotechnology (Experimental)[71]
- 2007 Albert Einstein World Award of Science[56]
- 2007 Tetrahedron Prize for Creativity in Organic Chemistry[72]
- 2007 King Faisal International Prize in Science[13][14]
- 2007 Jabir Ibn Hayyan (Geber) Medal (Saudi Chemical Society)
- 2005 University of Edinburgh Alumnus of the Year 2005 Award[73]
- 2004 Nagoya Gold Medal in Organic Chemistry[74]
- 1999 American Chemical Society Arthur C Cope Scholar Award[75]
- 1993 International Izatt-Christensen Award in Macrocyclic Chemistry[76]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


