Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
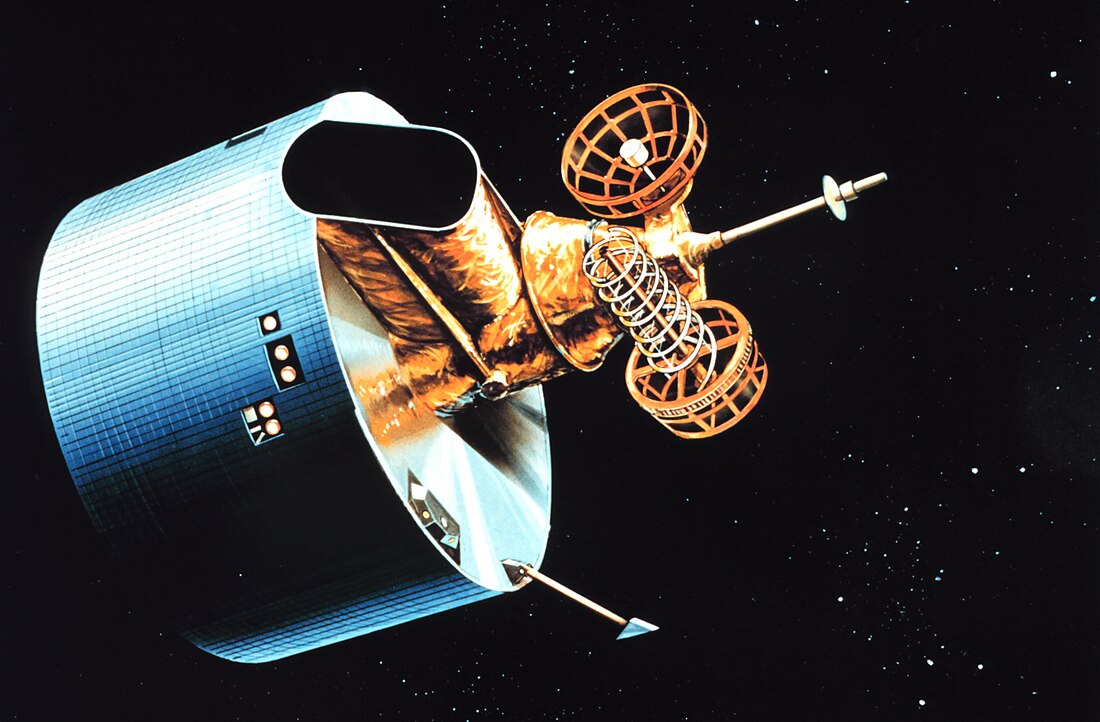
GOES 6
NOAA weather satellite From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
GOES-6, known as GOES-F before becoming operational, was a geostationary weather satellite which was operated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system.[1] Launched in 1983, it was used for weather forecasting in the United States.
GOES-6 was built by Hughes Space and Communications, and was based on the HS-371 satellite bus. At launch it had a mass of 660 kilograms (1,460 lb),[2] with an expected operational lifespan of around seven years.
Remove ads
Launch
GOES-F was launched using a Delta 3914 carrier rocket[3] flying from Launch Complex 17A at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.[4] The launch occurred at 22:26 GMT on 28 April 1983.[5]
Orbit
The launch successfully placed GOES-F into a geosynchronous transfer orbit, from which it raised itself to geostationary orbit by means of an onboard Star 27 apogee motor, with insertion occurring on 9 May 1983.[6]
Following insertion into geosynchronous orbit, GOES-6 was positioned at 135° West. In 1984 it was moved, initially to 97° West, and later to 108° West to cover for the failure of the Visible Infrared Spin-Scan Radiometer on GOES-5. After GOES-7 replaced GOES-5 in 1987, GOES-6 was returned to 135° West, where it remained for the rest of its operational life.[4] Its imager had failed on 21 January 1989,[1] leaving GOES-7 as the only operational GOES satellite for over five years, until the launch of GOES-8 in 1994. Following this failure, it remained operational as a relay satellite until it was retired to a graveyard orbit on 19 May 1992.[1][6]

Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads