Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
G Herculis
Star in the constellation Hercules From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
g Herculis is a binary star[12] system in the northern constellation of Hercules, which makes part of a wide triple star system. It has the Flamsteed designation 30 Herculis, while g Herculis is the Bayer designation. This system is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued point of light. Based upon a measured parallax of 9.2 mas, it is located around 354 light years away from the Sun. The system is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of 1.5 km/s.[6]
Remove ads
Characteristics
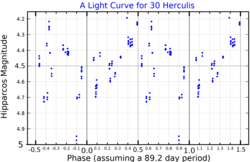
This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 2.310 years and an eccentricity of 0.37.[4] The visible component is an aging red giant on the asymptotic giant branch[4] with a stellar classification of M6− III.[5] According to Samus et al. (2017), it is a semiregular variable of subtype SRb, which ranges between visual magnitudes 4.3 and 6.3 over 89.2 days.[3][13] It displays cyclical periods of 62.3, 89.5, and 888.9 days.[4] The star is surrounded by a circumstellar dust shell that seems primarily composed of oxides of iron, magnesium, and aluminium, rather than silicates.[14]
In addition to the spectroscopic pair, there is a much wider star sharing similar proper motion and distance. It is a so-called proper motion companion. This star has a projected separation of 1,060 astronomical units from the inner pair. Its mass is estimated at 0.4 solar masses, and its apparent magnitude is much fainter than that of g Herculis.[15]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads