Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
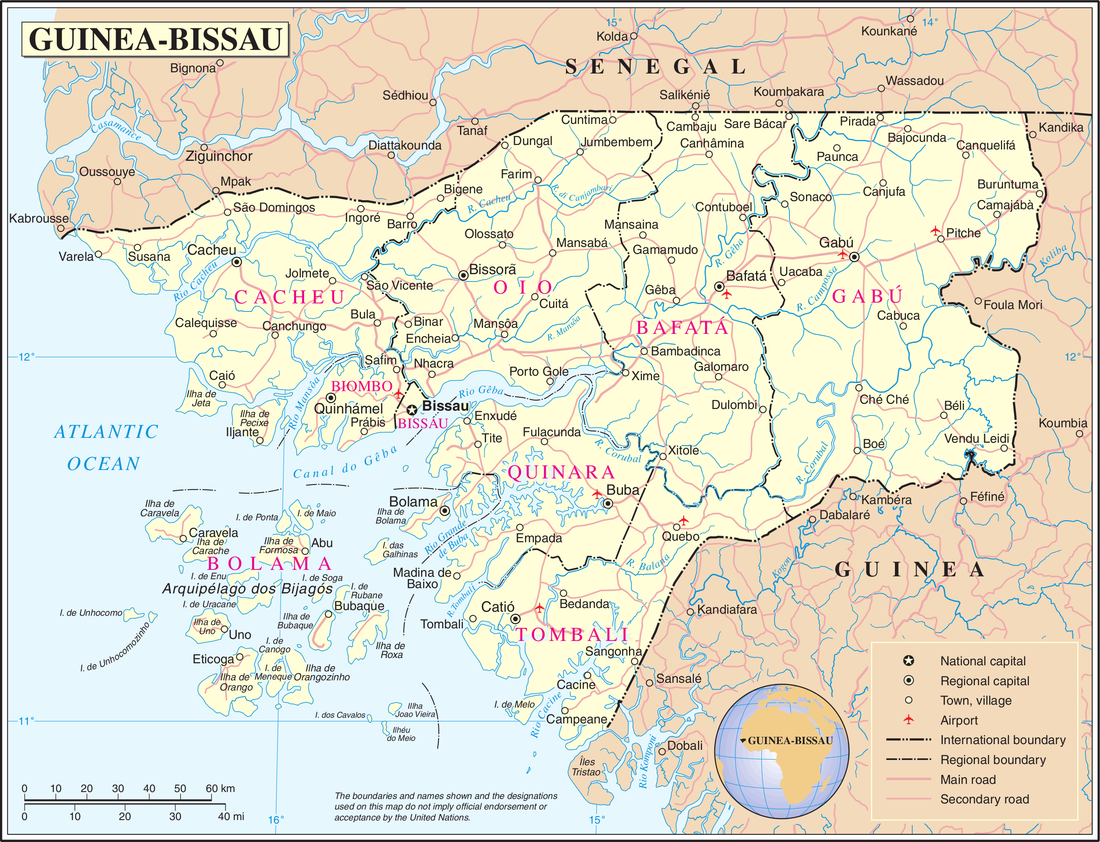
Geography of Guinea-Bissau
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The geography of Guinea-Bissau is that of low coastal plains bordering the Atlantic Ocean. The country borders Senegal in the north and Guinea in the southeast.
Terrain and ecology
Summarize
Perspective

The terrain of Guinea-Bissau is mostly low coastal plain with swamps of Guinean mangroves rising to Guinean forest-savanna mosaic in the east.[1] A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 1,203km² of tidal flats in Guinea-Bissau, making it the 28th ranked country in terms of tidal flat area. [2]
Around 66 million years ago, an asteroid impact occurred 400 km of the west-African coast. The 2022 discovered Nadir buried Crater has a diameter of 9 km. The impact caused an earthquake of 6.5 magnitude and created a 1 km high tsunami. The combined forces could be an explanation for the extremely scarred coastline of Guinea-Bissau.
The lowest point on Guinea-Bissau is at sea level at the Atlantic Ocean.[1] The highest point in Guinea-Bissau is Dongol Ronde with an elevation of 277 m (909 ft).[1] The Conservation Atlas of Tropical Forests: Africa authored in 1992 cites Fouta Djallon at 262 m (860 ft) as the highest.[3]
Natural resources found in Guinea-Bissau include fish, timber, phosphates, bauxite, clay, granite, limestone and unexploited deposits of petroleum.[1] 10.67% of the land is arable and 235.6 square kilometres are irrigated.[1]
Natural hazards include a hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze that may reduce visibility during the dry season and brush fires.[1] Severe environmental issues include deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing and overfishing.[1]
Near the Senegal border there have been historic sightings of the painted hunting dog, Lycaon pictus, but that endangered canid may now be extirpated in that locale.[4]
Remove ads
Climate
Summarize
Perspective
Guinea-Bissau's climate is tropical. This means it is generally hot and humid. It has a monsoonal-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds and a dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds.[1]

Guinea-Bissau is warm all year around and there is little temperature fluctuation; it averages 26.3 °C (79.3 °F). The average rainfall for the capital city Bissau is 2,024 millimetres (79.7 in) although this is almost entirely accounted for during the rainy season which falls between June and September/October. From December through April, the country receives very little rainfall.

Remove ads
Bissagos Islands
Information from the CIA World Factbook




- Location
- Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea and Senegal
- Geographic coordinates
- 12°00′N 15°00′W
- Map references
- Area
-
- Total: 36,125 km²
- country rank in the world: 134th
- Land: 28,120 km²
- Water: 8,005 km²
- Total: 36,125 km²
- Area comparative
- Australia comparative: slightly more than 1/2 the size of Tasmania
- Canada comparative: approximately 1/2 the size of New Brunswick
- United Kingdom comparative: approximately 3/5 larger than Wales
- United States comparative: approximately 1/8 larger than Maryland
- EU comparative: slightly more than 1/2 the size of Ireland
- Land boundaries
- Coastline
- 350 km
- Maritime claims
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
- Terrain
- Mostly low coastal plain rising to savanna in east
- Elevation extremes
-
- Lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
- Natural resources
- Fish, timber, phosphates, bauxite, unexploited deposits of petroleum
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 10.67%
- Permanent crops: 8.89%
- Other: 80.44% (2012 est.)
- Irrigated land
- 223.6 km2 (2003)
- Total renewable water resources
- 31 km3
- Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
-
- Total: 0.18 km3/yr (18%/6%/76%)
- Per capita: 135.7 m3/yr (2005)
- Natural hazards
- Hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze may reduce visibility during dry season; brush fires
- Environment—current issues
- Deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; overfishing
- Environment—international agreements
-
- Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: None of the selected agreements[1]
Remove ads
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Guinea-Bissau, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point – the northern section of the border with Senegal*
- Easternmost point – unnamed location on the border with Guinea immediately south-west of the Guinean village of Sofan, Gabú Region
- Southernmost point – unnamed headland on Ilha Cataque, Tombali Region
- Westernmost point - Cape Roxo at the point where the border with Senegal enters the Atlantic Ocean, Cacheu Region
- *Note: Guinea-Bissau does not have a northernmost point, the border here being formed by a parallel of latitude.
Remove ads
See also
Line notes
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads