Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
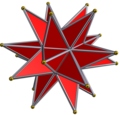
Great stellated dodecahedron
Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
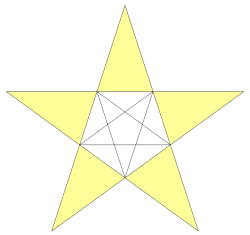
In geometry, the great stellated dodecahedron is a Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron, with Schläfli symbol {5/2,3}. It is one of four nonconvex regular polyhedra.
| Great stellated dodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron |
| Stellation core | regular dodecahedron |
| Elements | F = 12, E = 30 V = 20 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 12 { 5⁄2 } |
| Schläfli symbol | {5⁄2,3} |
| Face configuration | V(35)/2 |
| Wythoff symbol | 3 | 2 5⁄2 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Ih, H3, [5,3], (*532) |
| References | U52, C68, W22 |
| Properties | Regular nonconvex |
 (5⁄2)3 (Vertex figure) |
 Great icosahedron (dual polyhedron) |

It is composed of 12 intersecting pentagrammic faces, with three pentagrams meeting at each vertex.
It shares its vertex arrangement, although not its vertex figure or vertex configuration, with the regular dodecahedron, as well as being a stellation of a (smaller) dodecahedron. It is the only dodecahedral stellation with this property, apart from the dodecahedron itself. Its dual, the great icosahedron, is related in a similar fashion to the icosahedron.
Shaving the triangular pyramids off results in an icosahedron.
If the pentagrammic faces are broken into triangles, it is topologically related to the triakis icosahedron, with the same face connectivity, but much taller isosceles triangle faces. If the triangles are instead made to invert themselves and excavate the central icosahedron, the result is a great dodecahedron.
The great stellated dodecahedron can be constructed analogously to the pentagram, its two-dimensional analogue, by attempting to stellate the n-dimensional pentagonal polytope (which has pentagonal polytope faces and simplex vertex figures) until it can no longer be stellated; that is, it is its final stellation.
Remove ads
Images
Remove ads
Formulas
Summarize
Perspective
For a great stellated dodecahedron with edge length E (where E represents the length of any edge of the internal icosahedron),
Remove ads
Related polyhedra

A truncation process applied to the great stellated dodecahedron produces a series of uniform polyhedra. Truncating edges down to points produces the great icosidodecahedron as a rectified great stellated dodecahedron. The process completes as a birectification, reducing the original faces down to points, and producing the great icosahedron.
The truncated great stellated dodecahedron is a degenerate polyhedron, with 20 triangular faces from the truncated vertices, and 12 (hidden) pentagonal faces as truncations of the original pentagram faces, the latter forming a great dodecahedron inscribed within and sharing the edges of the icosahedron.
References
- Wenninger, Magnus (1974). Polyhedron Models. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-09859-9.
- Coxeter, Harold (1954). "Uniform Polyhedra". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences. 246 (916). Royal Society: 401–450. Bibcode:1954RSPTA.246..401C. doi:10.1098/rsta.1954.0003. JSTOR 91532. S2CID 202575183.
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads