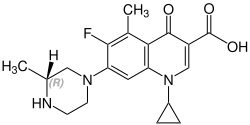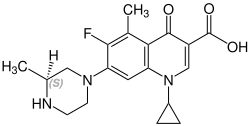Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Grepafloxacin
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Grepafloxacin (trade name Raxar, Glaxo Wellcome) was an oral broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent used to treat bacterial infections. Grepafloxacin was withdrawn worldwide from markets in 1999,[1][2] due to the drug's potential to cause a potentially fatal cardiac arrhythmia.[3]
Remove ads
Clinical uses
Grepafloxacin was used for treating exacerbations of chronic bronchitis caused by susceptible bacteria (e.g. Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis),[4][5][6] community-acquired pneumonia (including those, in addition to the above germs, caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae)[7][8] gonorrhea and non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis (for example caused by Chlamydia trachomatis or Ureaplasma urealyticum).[9][10]
Remove ads
Synthesis
Summarize
Perspective
The preparation of quinolones bearing a substituent at position 5 is complicated by the greater electrophilic character of the 8 position. One scheme for resolving the problem consists in blocking access to position 8 by first adding a readily removable group to that center.

The scheme starts with the conversion of the carboxylic acid in (1) to its dimethyloxazoline derivative (3) by reaction with the aminomethyl propanol (2). Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) then removes a proton from the 8 position; treatment of that anion with trimethylsilyl iodide leads to the silylated intermediate (4). A second round of LDA then generates a carbanion at the only open position; reaction with methyl iodide leads to the corresponding 5 methyl derivative (5). Treatment of that product with cesium fluoride breaks the carbon–silicon bond, removing the silyl group; aqueous acid then hydrolyzes the oxazoline to afford the free acid (6). This last intermediate is then taken on to the quinolone (9) [13] by essentially the same scheme as that used to prepare difloxacin, with the difference that the chain elongation is by means of Grignard reagent of ethyl bromoacetate. Treatment of (9) with 2-methylpiperazine proceeds by reaction at the less hindered of the two amino groups; saponification then affords grepafloxacin (10).
Remove ads
Stereochemistry
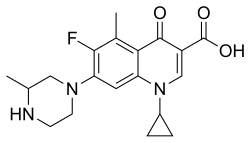
Grepafloxacin contains a stereocenter and consists of two enantiomers. This is a racemate, ie a 1: 1 mixture of (R)- and the (S)-forms:
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads