Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Griko language
Dialect of Italiot Greek From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Griko (endonym: Griko/Γκρίκο), sometimes spelled Grico, is one of the two dialects of Italiot Greek (the other being Calabrian Greek or Grecanico), spoken by Griko people in Salento, province of Lecce, Italy.[2][3][4][5][6] Some Greek linguists consider it to be a Modern Greek dialect and often call it Katoitaliótika (Greek: Κατωιταλιώτικα, lit. 'Southern Italian') or Grekanika (Γραικάνικα). Griko and Standard Modern Greek are partially mutually intelligible.[7]
This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: Article contradicts itself. (February 2023) |
Remove ads
Classification
The most popular hypothesis on the origin of Griko is the one by Gerhard Rohlfs[8] and Georgios Hatzidakis, that Griko's roots go as far back in history as the time of the ancient Greek colonies in Southern Italy and Sicily in the eighth century BC. The Southern Italian dialect is thus considered to be the last living trace of the Greek elements that once formed Magna Graecia.
There are, however, competing hypotheses according to which Griko may have preserved some Doric elements, but its structure is otherwise mostly based on Koine Greek, like almost all other Modern Greek dialects.[9] Thus, Griko should rather be described as a Doric-influenced descendant of Medieval Greek spoken by those who fled the Byzantine Empire to Italy to escape the Turks. The idea of Southern Italy's Greek dialects being historically derived from Medieval Greek was proposed for the first time in the 19th century by Giuseppe Morosi.[10]
Remove ads
Geographic distribution
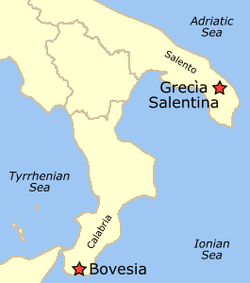
Two small Italiot Greek-speaking communities survive today in the Italian regions of Calabria (Metropolitan city of Reggio Calabria)[11] and Puglia (Province of Lecce).[12]
The Italiot Greek-speaking area of Puglia is called Grecìa Salentina and includes seven villages where Griko is still spoken – Calimera, Castrignano dei Greci, Corigliano d’Otranto, Martano, Martignano, Sternatia and Zollino – in addition to four villages – Carpignano Salentino, Cutrofiano, Melpignano and Soleto – where Griko has not been spoken for one or two centuries.[13][14] The total population of Grecia Salentina is around 40,000.[15]
The Calabrian Greek region also consists of nine villages in Bovesia, (including Bova Superiore, Roghudi, Gallicianò, Chorìo di Roghudi and Bova Marina)[16] and four districts in the city of Reggio Calabria, but its population is significantly smaller, with around only 2000 inhabitants.[17]
Remove ads
Official status
By Law 482 of 1999, the Italian parliament recognized the Griko communities of Reggio Calabria and Salento as a Greek ethnic and linguistic minority. It states that the Republic protects the language and culture of its Albanian, Catalan, Germanic, Greek, Slovene and Croat populations and of those who speak French, Franco-Provençal, Friulian, Ladin, Occitan and Sardinian.[18] According to UNESCO data from 2011, the two dialects of Griko are classified as severely endangered languages.[19]
Culture
Summarize
Perspective
There is rich oral tradition and Griko folklore. Griko songs, music and poetry are particularly popular in Italy and Greece. Famous music groups from Salento include Ghetonia, Aramirè, and Canzoniere Grecanico Salentino. Also, influential Greek artists such as Dionysis Savvopoulos and Maria Farantouri have performed in Griko. The Greek musical ensemble Encardia focuses on Griko songs as well as on the musical tradition of Southern Italy at large.[20][21]
Samples
Sample text from Καληνύφτα – Kalinifta ("Good night") and Andramu pai, popular Griko songs:
Remove ads
Phonology
- Nasal+stop clusters [ᵐb, ⁿd, ᵑɡ] along with voiceless equivalents [ᵐp, ⁿt, ᵑk] also are heard.
- The cacuminal /ɖ/ may also be realized as an affricate [ɖːʐ], and consonant sequences /tr/ and /tːr/ may be pronounced as [ʈʂ] and [ʈːʂ] among speakers.
- [z] is heard as a realization of /s/ when before a voiced consonant.
- A few cases of a palatal lateral [ʎ] can be heard, possibly as a result of the influence of Standard Italian.
- Vowels /i, u/ are heard as homorganic glides [j, w] when following consonants and preceding other vowels.[24]
Remove ads
Grammar
In many aspects, its grammar is similar to that of Modern Greek. The language has three genders, masculine, feminine, and neuter. All nouns and adjectives are declined according to number and case. There are four cases, just like in Modern Greek: nominative, genitive, accusative, and vocative. Verbs are conjugated according to person, number, tense, mood, and aspect. The table below shows the personal pronouns of the Griko language:
Remove ads
See also
Notes and references
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads