Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Grosso mogul
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Grosso mogul, also Il grosso mogul, or capitalised [Il] Grosso Mogul ([The] Great Moghul), RV 208, is a violin concerto in D major by Antonio Vivaldi.[1][2][3] The concerto, in three movements, is an early work by the Venetian composer.[4] Around the mid-1710s Johann Sebastian Bach transcribed the concerto for organ, BWV 594, in C major.[5] A simplified version of the violin concerto, RV 208a, without the elaborated cadenzas that appear in manuscript versions of RV 208, and with a different middle movement, was published around 1720 in Amsterdam as concerto #11 of Vivaldi's Op. 7.[4]

Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Vivaldi's violin concerto in D major, RV 208, survives in three manuscripts:[6][7]
- Vivaldi's autograph score, conserved in Turin.
- A copy of the parts, conserved in the Landesbibliothek Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Günther Uecker in Schwerin.[3][4]
- Another copy of the parts conserved in Cividale del Friuli.[4]
The Grosso Mogul title appears on the Schwerin manuscript, which was written before 1717.[3][4][7][8] According to Michael Talbot, the name of the concerto can possibly be linked to Domenico Lalli's Il gran Mogol opera libretto, a setting of which had been presented in Naples in 1713.[4][9][10] Later settings of this libretto include Giovanni Porta's, staged in Venice in 1717, and Vivaldi's RV 697 (1730).[11][12][13][14]
The Schwerin and Cividale del Friuli copies of the concerto contain two variants of extended cadenzas for unaccompanied violin, in the first and last movements of the concerto.[4][5][8] The autograph version indicates where such cadenzas can be inserted in these movements, but does not contain the cadenzas.[8] A manuscript with the written-out cadenzas must have been circulating before c. 1713–1714 when Bach transcribed such versions for solo organ (BWV 594).[5][7][8]
An earlier version of the concerto, RV 208a, was probably composed by c. 1712–1713.[7] This version has a different middle movement than the RV 208 version.[7][8] Vivaldi seems to have had no supervision over the Op. 7 collection, published around 1720 in Amsterdam by the Roger firm, in which the older RV 208a version of the concerto was retained.[7] This version of the concerto does not contain the extended cadenzas, nor an indication where such cadenzas could be inserted.[15]
Remove ads
Movements
The concerto has been transmitted in a version for violin soloist, strings (two violin parts and one viola part), and basso continuo.[3] It has three movements:[3]
- Allegro,
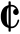 , D major
, D major - Recitative: Grave,
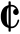 , B minor – this movement is performed by the violin soloist exclusively accompanied by the thoroughbass.
, B minor – this movement is performed by the violin soloist exclusively accompanied by the thoroughbass. - Allegro, 3
4, D major
First movement
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2018) |
The first movement, in D Major is in Ritornello form. The first solo episode consists of sixteenth notes, with double stops on every beat. [citation needed]
Second movement
The second movement, in B Minor is for the solo violin and basso continuo. There are strange rhythms, like improvisation.
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (November 2019) |
Third movement
The third movement, in D Major, is in Ritornello form, and is the most virtuosic of the 3 movements.
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (November 2019) |
Remove ads
Reception
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (June 2018) |
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
