Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Hiding in the Light
Episode of Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
"Hiding in the Light" is the fifth episode of the American documentary television series Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey. It premiered on April 6, 2014 on Fox and aired on April 7, 2014 on National Geographic Channel. The episode explores properties of light, cameras, the scientific method, and the composition of the universe. The episode includes a look at the contributions of the 10th century physicist Ibn al-Haytham, described as the "father of the modern scientific method".[1][2]
The episode was received positively by critics, with many remarking on the brilliant visuals of the end sequence completed with Rhapsody in Blue "showcasing the same image of New York City, viewed through the filters of various wavelengths of light: visible, infrared, ultraviolet, X-ray, gamma ray, microwave, and even a radio image".[3][4] The episode maintained the previous week's 18-49 rating/share of 1.5/4, with 3.98 million American viewers watching on Fox.[5]
Remove ads
Episode summary
Summarize
Perspective
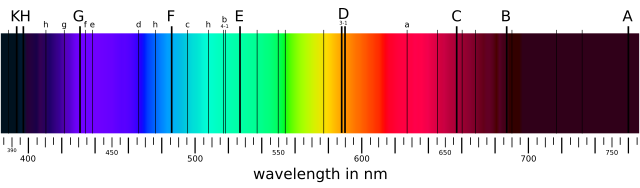
This episode explores the wave theory of light as studied by mankind, noting that light has played an important role in scientific progress, with such early experiments from over 2000 years ago involving the camera obscura by the Chinese philosopher Mozi. Tyson describes the work of the 11th century Arabic scientist Ibn al-Haytham, considered to be one of the first to postulate on the nature of light and optics leading to the concept of the telescope, as well as one of the first researchers to use the scientific method.
Tyson proceeds to discuss the nature of light as discovered by mankind. Work by Isaac Newton using refraction through prisms demonstrated that light was composed of the visible spectrum, while findings of William Herschel in the 19th century showed that light also consisted of infrared rays. Joseph von Fraunhofer would later come to discover that by magnifying the spectrum of visible light, gaps in the spectrum would be observed. These Fraunhofer lines would later be determined by Cecilia Payne and Annie Jump Cannon to be caused by the absorption of light by electrons in moving between atomic orbitals when it passed through atoms, with each atom having a characteristic signature due to the quantum nature of these orbitals. This since has led to the core of astronomical spectroscopy, allowing astronomers to make observations about the composition of stars, planets, and other stellar features through the spectral lines, as well as observing the motion and expansion of the universe, and the existence of dark matter.
Remove ads
Reception
Ratings
The episode's premiere on Fox brought a 1.5/4 in the 18-49 rating/share, with an audience of 3.98 million American viewers. It placed third and last in its timeslot behind Resurrection and Believe; and twelfth out of fifteenth for the night.[5]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads