Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Hungarian diaspora
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Hungarian diaspora or Magyar diaspora refers to ethnic Hungarians (Magyars) living outside the borders of present-day Hungary. The diaspora can be divided into two main groups: the first group includes those who are autochthonous to their homeland, living in parts of neighbouring regions that were part of Hungary prior to the World War I Treaty of Trianon of 1920.[2][note 1] As a consequence, 3.3 million Hungarians found themselves outside the new borders. The other main group is the emigrants who have left Hungary at various times, and their descendants. Migrations increased during certain pivotal events, notably the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 and the Fall of the Berlin Wall. There has been some emigration since Hungary joined the EU in 2004, especially to countries such as Germany and the United Kingdom,[3] but those patterns have been less extensive than for certain other countries of Central and Eastern Europe, such as Poland and Bulgaria. Additionally, there is the Magyarab people, a small community in Nubia resulting from a historical migration of Magyars, likely during the Ottoman period in Hungary.[4]

Hungary
+1,000,000
+100,000
+10,000
+1,000

Remove ads
Distribution by country
Summarize
Perspective




Hungarian immigration patterns to Western Europe increased in the 1990s and especially since 2004, after Hungary's admission in the European Union. Thousands of Hungarians from Hungary sought available work through guest-worker contracts in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Finland, Sweden, Spain, and Portugal.
Remove ads
Hungarian citizenship
Summarize
Perspective

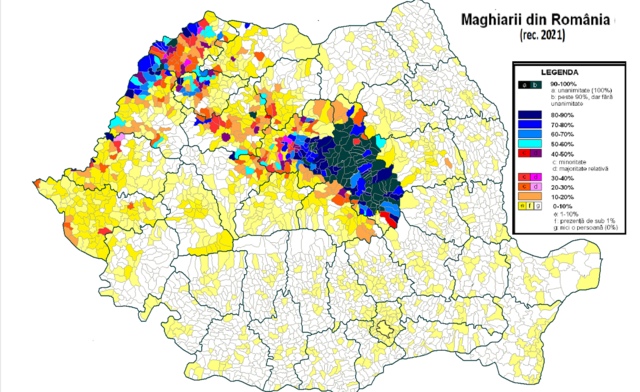
A proposal supported by the DAHR to grant Hungarian citizenship to Hungarians living in Romania but without meeting Hungarian-law residency requirements was narrowly defeated at a 2004 referendum in Hungary.[37] The referendum was invalid because of not enough participants. After the failure of the 2004 referendum, the leaders of the Hungarian ethnic parties in the neighboring countries formed the HTMSZF organization in January 2005, as an instrument lobbying for preferential treatment in the granting of Hungarian citizenship.[38]
In 2010, some amendments were passed in Hungarian law facilitating an accelerated naturalization process for ethnic Hungarians living abroad; among other changes, the residency-in-Hungary requirement was waived.[39] In May 2010, Slovakia announced it would strip Slovak citizenship from anyone applying for Hungarian citizenship.[40] Romania's President Traian Băsescu declared in October 2010: "We have no objections to the adoption by the Hungarian government and parliament of a law making it easier to grant Hungarian citizenship to ethnic Hungarians living abroad."[41]
The new citizenship law took effect on 1 January 2011. It did not grant the right to vote, even in national elections, to Hungarian citizens unless they also resided in Hungary on a permanent basis.[42] In February 2011, the Fidesz government announced that it intended to grant the right to vote to its new citizens.[43] Between 2011 and 2012, 200,000 applicants took advantage of the new, accelerated naturalization process;[44] there were another 100,000 applications pending in the summer of 2012.[45] As of February 2013, the Hungarian government had granted citizenship to almost 400,000 Hungarians ‘beyond the borders’.[46] In June 2013, Deputy Prime Minister Zsolt Semjén announced that he expected the number to reach about half a million by the end of the year.[47]
Hungarian citizens abroad have been able to participate in the parliamentary elections without Hungarian residency starting from the 2014 Hungarian parliamentary election, however, they cannot vote for a candidate running for the seat in a single-seat constituency, but for a party list.
Remove ads
Famous people of Hungarian descent
Remove ads
Politics
Since the Hungarian diaspora could start voting in elections in Hungary from 2012,[70] they have overwhelmingly supported the ruling Fidesz. In the 2014 Hungarian parliamentary election, Fidesz won over 95% of the vote,[71] in the 2018 Hungarian parliamentary election, over 96%, while in the 2019 European Parliament election in Hungary, Fidesz received 96%.[72]
In the 2022 Hungarian parliamentary election, over 93%, while in the 2024 European Parliament election in Hungary, Fidesz received 90%.
Minority interest parties
In several Eastern European countries, parties that represent the interests of Hungarian minorities have emerged.
Remove ads
Gallery
- John von Neumann (1903–1957), Hungarian-American mathematician and physicist of Hungarian descent.
- Mickey Hargitay was a Hungarian-American actor and 1955 Mr. Universe.
See also
Notes
- Before entering World War II, Hungary regained some areas, but later lost after the 1947 Treaty of Paris.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


