Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
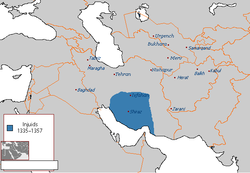
Injuids
Iranian dynasty of Persian origin From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Injuids (also Injus or House of Inju) were an Iranian[1] dynasty of Persian origin that came to rule over the cities of Shiraz and Isfahan during the 14th century. Its members became de facto independent rulers following the breakup of the Ilkhanate until their defeat in 1357 against the Muzaffarids.
Remove ads
Before the breakup of the Ilkhanate

The Injuids gained control of parts of Iran, mostly Fars, in 1304 at the beginning of the reign of the Ilkhan Öljeitü. The Ilkhan had given Sharaf al-Din Mahmud Shah control of the injü (or inji; the Mongol word for the royal estates). Before progressively gaining independence, the "Injuids" had been appointed initially by Öljeitü as "margrave", or local governors, for the area of Fars.[3]
Sharaf al-Din was reportedly descended from 'Abd-Allah Ansari, an 11th-century mystic of Herat. His son, Amir Ghiyas al-Din Kai-Khusrau, assisted another family, the Muzaffarids, in their takeover of Yazd. By 1325 Sharaf al-Din had gained nearly an absolute grip on the region. His power displeased Öljeitü's successor Abu Sa'id, who ordered Sharaf al-Din removed and sent a Sheikh Hussein ibn Juban to replace him. Kai-Khusrau, who ruled Shiraz for his father, resisted; and Sheikh Hussein was forced to return with an Ilkhan army. Also during Abu Sa'id's lifetime, Sharaf al-Din was imprisoned in Tabriz for a failed attempt to murder his successor.
Remove ads
Independence
Summarize
Perspective

With the death of Abu Sa'id in 1335, Arpa Ke'un took the throne. He had Sharaf al-Din executed; two of Sharaf's sons in the royal encampment (Amir Jalal al-Din Mas'ud Shah, who fled to Hasan Buzurg; Shaikh Abu Ishaq to Amir 'Ali Padishah) withdrew from the scene. Meanwhile, Kai-Khusrau was asserting his authority in Shiraz. When Arpa Ke'un was captured by rebels, he was sent to Mas'ud Shah, who killed him. Mas'ud Shah then served as vizier under the Jalayirid puppet Ilkhan Muhammed Khan; when the latter was killed, he made his way to Shiraz. The two brothers came into conflict, which was only settled when Kai-Khusrau's died (1338/9).
Mas'ud Shah was quickly faced with more challenges to his reign. A year after Kai Khusrau's death, a fourth son of Sharaf al-Din named Shams al-Din Muhammad escaped from his brother's prison of Qal'a-yi Saf'id, whereupon he joined the Chobanids. Shams al-Din, together with the Chobanid Pir Hosayn, marched to Shiraz, which they captured. Mas'ud Shah fled to Luristan. Pir Hosayn, however, murdered Shams al-Din; this act lost him support in the city, and he had to withdraw. Pir Hosayn reconquered the city in the next year, however. Mas'ud Shah attempted to take advantage of Chobanid infighting, and allied with Yagi Basti to take the city, which had in the meantime fallen into the hands of Abu Ishaq. He had been given Isfahan by Pir Hosayn, and he now took Shiraz as well. When Yagi Basti murdered Mas'ud Shah that same year, Abu Ishaq became the sole surviving son of Sharaf al-Din. He took Shiraz from Yagi Basti in March 1343.
Remove ads
Fall of the Injuids under Abu Ishaq
Summarize
Perspective

Jamal al-Din Abu Ishaq's goal was to conquer Kerman; he therefore undertook expeditions against the Muzaffarids, who were led by Mubariz al-Din Muhammad. The rivalry between the two heated up during a campaign against the Muzaffarid city of Yazd during 1350 and 1351. In retaliation, Mubariz al-Din invaded Fars in 1352. After defeating the Injuids in battle, he laid siege to Shiraz in 1353. Abu Ishaq, who grew increasingly paranoid, ordered the extermination of two-quarters of the city in order to root out traitors. The chief of another quarter, fearing for his people, gave the key for his gate to Mubariz al-Din's son Shah Shuja. Abu Ishaq was forced to surrender, but he escaped and made his way to Isfahan with the support of the Jalayirids. Mubariz al-Din, however, laid siege to that city also, and captured it in 1357. Abu Ishaq again surrendered, was sent to Shiraz, and was executed. The Injuid lands now fell into the hands of the Muzaffarids, who would hold them until the onslaught of Timur forty years later.
Arts of the book
The Injuids, having been appointed initially by Öljeitü as "margrave", or local governors, for the area of Fars, tried to assert their independence by the creation of a specific literature with elaborate illustrations. This efforts helped Shiraz become a recognized and admired center for the arts of the book throughout the 14th century.[3]
The Injuid school of Shiraz is characterized by a fairly consistent style, and many of the manuscripts are signed and dated. The paintings are very rich in color, using red, yellow ocher, or sometimes plain-paper backgrounds. The painting are quite original compared to others of the period, the style is rather vigorous, the action scenes are dynamic.[6]
The depiction of mountains in particular is quite characteristic, with strong symbolic peaks painted over yellow backgrounds, although this is probably derived from Mongol painting. Some of the faces tend to be Iranian, and derive from traditional Sassanid styles.[7]
- Samak-e Ayyar, Injuid, circa 1330
- Bahram Gur and Azadeh in hunting place, Istanbul Shahnameh, Shiraz 1331.[8]
- Shahnama, 1352 CE, Shiraz, Injuid
Remove ads
Architecture and decorative arts
Summarize
Perspective
The Khuda Khane ("House of God") in Shiraz, commissioned by the Injuids in 1351
Injuid period Mihrab, Imami Madrasa, Isfahan (1354–55 CE). Metropolitan Museum of Art.[9]
Various architectural creations are known from the Injuid period. A remarkable mihrab in mo'araq cut-tile mosaic dated to 755 AH (1354–55 CE), at the time the city was still under the control of the Injuids of Abu Ishaq, and just before the city fell to the Muzaffarids in 1356–57, was recovered from a madrasa in Isfahan, the Imami Madrasa.[9] The mihrab is considered as a masterpiece of mo'araq technique, a type of decorative technique started during the Ilkhanid period in the early 14th century in the cities of Sham, Tabriz and Sultaniyya.[9] From an architectural and stylistic standpoint, the Imami Madrasa itself is considered as belonging to the "Ilkhanid era".[10]
In Shiraz, the Khuda Khane ("House of God") kiosk at the center of the Atigh Jame' Mosque was commissioned by the Injuids in 1351, in order to store Qur'ans.[11][12] In Shiraz also, Abu Ishaq reportedly had a building constructed that reflected the Sasanian palace Taq-e Kasra at Ctesiphon. However, the construction was never finished and no remains of the building stand today.[13]
Remove ads
Injuid rulers
- Sharaf al-Din Mahmud Shah (1304–1335)
- Amir Ghiyas al-Din Kai-Khusrau (1336–1338/9)
- Amir Jalal al-Din Mas'ud Shah (in opposition to Kai-Khusrau) (c. 1338–1342)
- Shams al-Din Muhammad (in opposition to Mas'ud Shah) (1339)
- Shaikh Jamal al-Din Abu Ishaq (c. 1343–1357)
Genealogy of House of Inju
Remove ads
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads