Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Jhankaradhvani
Nineteenth raga in the Melakarta From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Jhankaradhvani or Jhankaradhwani (pronounced jhankāradhvani) is a ragam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is the 19th Melakarta rāgam in the 72 melakarta rāgam system of Carnatic music.
It is called Jhankārabhramari in the Muthuswami Dikshitar school of Carnatic music.[1][2][3]
Remove ads
Structure and Lakshana
Summarize
Perspective
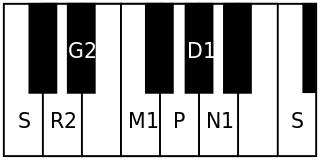
It is the 1st rāgam in the 4th chakra Veda. The mnemonic name is Veda-Pa. The mnemonic phrase is sa ri gi ma pa dha na.[2] Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see swaras in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms):
(the notes in this scale are chathusruthi rishabham, sadharana gandharam, shuddha madhyamam, shuddha dhaivatham, shuddha nishadham)
As it is a melakarta rāgam, by definition it is a sampoorna rāgam (has all seven notes in ascending and descending scale). It is the shuddha madhyamam equivalent of Shamalangi, which is the 55th melakarta.
Remove ads
Asampurna Melakarta
Summarize
Perspective
Jhankārabhramari is the 19th Melakarta in the original list compiled by Venkatamakhin. The notes used in the scale are the same, but the zig-zag usage of notes in both ascending and descending scle (vakra prayoga) is the difference.[1]
Remove ads
Janya rāgams
Jhankaradhvani has a few minor janya rāgams (derived scales) associated with it. See List of janya rāgams for full list of rāgams associated with Jhankaradhvani.
Compositions
A couple of compositions set to this musical scale are:
- Phanipati sayee by Thyagaraja
- Varam tharum by Koteeswara Iyer
- Jhasha Kethana Pitaram by Dr. M. Balamuralikrishna
- Himachala kumarim bhaja by Muthuswami Dikshitar is set to Raga Jhankārabhramari.
Related rāgams
This section covers the theoretical and scientific aspect of this rāgam.
Jhankaradhvani's notes when shifted using Graha bhedam, yields 2 other minor melakarta rāgams, namely, Ratnangi and Gamanashrama. Graha bhedam is the step taken in keeping the relative note frequencies same, while shifting the shadjam to the next note in the rāgam. For further details and an illustration refer Graha bhedam on Ratnangi.
Remove ads
Notes
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
