Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Jia Xian
Chinese mathematician From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
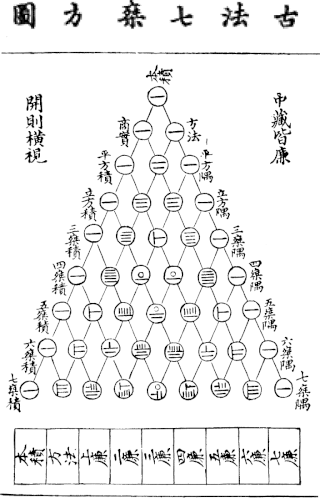
Jia Xian (simplified Chinese: 贾宪; traditional Chinese: 賈憲; pinyin: Jiǎ Xiàn; Wade–Giles: Chia Hsien; ca. 1010–1070) was a Chinese mathematician from Kaifeng of the Song dynasty. He described Pascal's triangle during the 11th century.


Remove ads
Biography
According to the history of the Song dynasty, Jia was a palace eunuch of the Left Duty Group. He studied under the mathematician Chu Yan, and was well versed in mathematics, writing many books on the subject. Jia Xian described the Pascal's triangle (Jia Xian triangle) around the middle of the 11th century, about six centuries before Pascal. Jia used it as a tool for extracting square and cubic roots. The original book by Jia entitled Shi Suo Suan Shu was lost; however, Jia's method was expounded in detail by Yang Hui, who explicitly acknowledged his source: "My method of finding square and cubic roots was based on the Jia Xian method in Shi Suo Suan Shu."[1] A page from the Yongle Encyclopedia preserved this historic fact.
Jia Xian's additive-multiplicative method implemented the "Horner" rule.[2]
Remove ads
Additive-multiplicative method of square-root extraction
Additive-multiplicative method of cubic-root extraction
References
Bibliography
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads