Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Junkers EF 126
German experimental pulsejet fighter From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
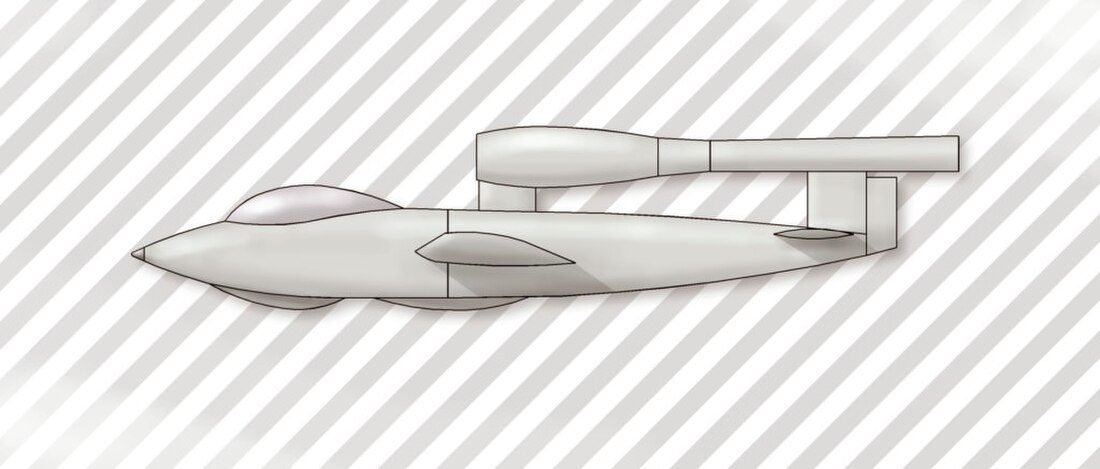
The Junkers EF 126 was an experimental fighter proposed by the German Miniaturjägerprogramm of 1944–1945, for a cheap and simple fighter powered by a pulsejet engine. No examples were built during the war, but the Soviet Union completed both unpowered and powered prototypes.
The design of the Ju EF 126 was developed into the Junkers EF 127, a rocket-powered version.
Remove ads
Miniaturjäger
During 1944, the Miniaturjäger programme for the simplest, cheapest fighter possible was launched by the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM), the German Ministry of Aviation. In order to minimise cost and complexity, it was to be powered by a pulse jet, as used by the V-1 flying bomb and its manned version, the Fieseler Fi 103R (Reichenberg).[1] Designs were produced by Heinkel, with a pulse jet powered version of their Heinkel He 162, Blohm & Voss (the P213) and Junkers.[2]
Remove ads
EF 126
Junker's design, the EF 126, was of similar layout to the V-1, with the single Argus 109-044, rated at 4.9 kilonewtons (1,100 lbf), mounted above the aft fuselage and fin. The fuselage was of metal construction, while the wings were wooden. A retractable nosewheel undercarriage was to be fitted. As the pulse-jet's power would reduce at altitude, the aircraft was intended for low-altitude use and had a secondary ground-attack role. Armament consisted of two 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon, and up to 400 kg (880 lb) of bombs could be carried under the wings.[3]
Remove ads
Variants
- EF 126 V1
First prototype, towed into the air by a captured Junkers Ju 88G-6 in the post war period. Later, it crashed.
- EF 126 V2
Second prototype, also constructed but never completed.
- EF 126 V3,V5
Complete prototypes with Argus pulse jet.
- EF 126 V4
Completed and tested by the Soviets in 1947, with a running engine.
Specifications (Ju EF 126)
Data from German Aircraft of the Second World War.[3]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 8.46 m (27 ft 9 in)
- Wingspan: 6.65 m (21 ft 10 in)
- Height: 1.9 m (6 ft 3 in)
- Wing area: 8.9 m2 (189 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 1,100 kg (2,420 lb)
- Gross weight: 2,800 kg (6,160 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 1,100kg
- Powerplant: 1 × Argus 109-044 Pulse jet, 4.9 kN (1,100 lbf) thrust
Performance
- Maximum speed: 780 km/h (485 mph, 421 kn)
- Range: 350 km (218 mi, 189 nmi) 60% power
- Endurance: 45 min
- Rate of climb: 8.0 m/s (1,575 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 314 kg/m2 (32.6 lb/sq ft)
- Endurance: 23 mins (100% speed)
Armament
- Guns: 2× 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon
- Bombs: 400 kg (880 lb) external weapons
Remove ads
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads