Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Kleverlandish
Low Franconian dialect group From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
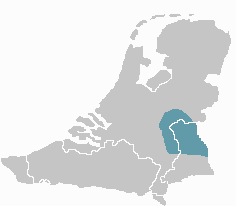
Kleverlandish (Dutch: Kleverlands; German: Kleverländisch) is a group of Low Franconian dialects spoken on both sides of the Dutch-German border along the Meuse and Rhine rivers.
Remove ads
Extent and terminology
Summarize
Perspective
Kleverlandish varieties are spoken in the Netherlands in the northernmost part of Dutch Limburg, in the northeasternmost part of North Brabant (Land van Cuijk), and in the southeastern part of Gelderland (around Nijmegen and around Zevenaar and 's-Heerenberg in the Liemers region), and in Germany in the districts of Cleves and Wesel in northwestern North Rhine-Westphalia. To the northeast, Kleverlandish borders on the Low Saxon speech area, its western border is the diphthongisation line.[1] Traditionally, its southern extent bordering on the South Low Franconian dialect group (commonly called "Limburgish" in Belgium and the Netherlands) is defined by the Uerdingen line (the ik-ich-isogloss),[1] but many Dutch and German scholars place the boundary further to the north based on wider criteria than the ik-ich-isogloss.[2][3][a]
Originally, the term Kleverländisch[b] referred only to the dialects in the German part of the speech area,[4] which are also called Niederrheinsch ('Low Rhenish') in traditional German dialectology.[c] The dialects on the Dutch side were first classified as a distinct group by te Winkel (1898) (as "Saxon-East Franconian") and Van Ginneken (1917) ("Guelderish-Limburgish"). The close affinity between these dialect areas had long been recognized by Dutch and German scholars;[d] but it was the Belgian dialectologist Jan Goossens who first extended the scope of the term "Kleverlandish" to include all varieties on both sides of the border.[5][4]
Remove ads
Characteristics
Kleverlandish is characterized by several conservative features, such as:[6]
- Retention of -al-/-ol- before consonants (e.g. Kleverlandish ald 'old'; in most Low Franconian dialects, -l- is vocalized in this environment (Standard Dutch oud), while Low Saxon dialects retains the -l- but merge the vowels to -o- (Low Saxon old))
- Retention of historically long high vowels (diphthongized in most Low Franconian dialects to the west, e.g. Kleverlandish is vs. Standard Dutch ijs < *īs).
A typical West Low Franconian feature is the fronting of /uː/ to /y(ː)/ (e.g. hüs 'house' < *hūs) which however did not fully radiate into the German area of Kleverlandish, where in many areas it affects only part of the vocabulary.[7]
Remove ads
Status
In much of the Kleverlandish speech area in both the Netherlands and Germany, speakers are shifting from Kleverlandish to regional colloquial forms of the respective national languages, Dutch and German, with a higher degree of decline of dialect usage in Germany than in the Netherlands.[8] In Dutch Limburg, Kleverlandish varieties spoken within the province are included in the official recognition of Limburgish as a regional language (even though they do not belong to Limburgish in a dialectological sense). Official recognition does not extend to other Dutch provinces, nor to Germany.[e]
Other classifications
In the widely reproduced dialect map by Jo Daan, Kleverlandish dialects in the Netherlands are included in the large central-southern dialect group, but divided over two subgroups: varieties in Gelderland are assigned to the South Guelderish subgroup (which also includes dialects spoken in the southwest of Gelderland which have taken part in the Hollandic-Brabantian diphthongisation), while Kleverlandish varieties in North Brabant and Limburg are included in the North Brabant–North Limburg subgroup.[9]
In Heeringa (2004), Kleverlandish dialects in the Netherlands are assigned to two different major dialects groups: the Gelderland varieties are included in the Central Dutch group, while varieties in the Land van Cuijk and northern Limburg are included in the Limburg group.[10]
Remove ads
Notes
- From German Kleverland 'Land of Cleves'.
- E.g. Wiesinger (2017), p. 351–352 (footnote 27): "Mit „Niederrheinisch“ bezeichnen wir im Anschluß an 49. WENKER den von südlich-ripuarischen Eigenheiten freien niederfränkischen Raum am deutschen Niederrhein, der als Teilgebiet des Gesamtniederfränkischen in der Regionalforschung vielfach als „Kleverländisch“ bezeichnet wird."
- E.g. Weijnen (1958), p. 363: "Tot het Noordlimburgs reken ik het gebied ten noorden van de Uerdinger- en mich-linie [...] Het sluit aan bij de dialecten van het Land van Cuyk, het Land van Nijmegen, de Over-Betuwe, de Lijmers en het Oostijsels [...] Ook is er sterke verwantschap met het Cleefs." ('I consider the area north of the Uerdingen and the mich line as North Limburgian [...] it agrees with the dialects of Land van Cuyk, Land van Nijmegen, Upper Betuwe, Lijmers and Oostijsel [...] there is also a strong affinity with the dialect of Cleves.')
- In Gelderland, efforts for official recognition have begun in 2023, see "Petitie voor behoud Kleverlands in Gelderland gestart", Interreg Deutschland-Nederland.
Remove ads
Citations
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads