Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Labyrinthine artery
Artery of the internal ear From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
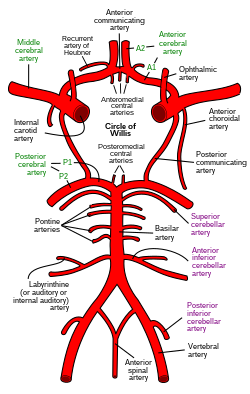
The labyrinthine artery (auditory artery, internal auditory artery) is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery or the basilar artery. It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus. It supplies blood to the internal ear.
Remove ads
Structure
The labyrinthine artery is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) or the basilar artery.[1][2] It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus.[1] It divides into a cochlear branch and a labyrinthine (or anterior vestibular) branch.[1]
Function
The labyrinthine artery supplies blood to the inner ear.[1][3] It also supplies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) along its length.[3]
Clinical significance
The labyrinthine artery may become occluded.[3] This can cause loss of hearing and balance on the affected side.[3]
History
The labyrinthine artery may also be known as the internal auditory artery or the auditory artery.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads