Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
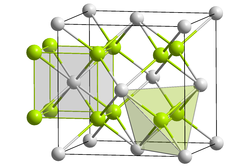
Lead(II) fluoride
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Lead(II) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula PbF2. It is a white solid. The compound is polymorphic, at ambient temperatures it exists in orthorhombic (PbCl2 type) form, while at high temperatures it is cubic (Fluorite type).[2]
Remove ads
Preparation
Lead(II) fluoride can be prepared by treating lead(II) hydroxide or lead(II) carbonate with hydrofluoric acid:[3]
- Pb(OH)2 + 2 HF → PbF2 + 2 H2O
Alternatively, it is precipitated by adding hydrofluoric acid to a lead(II) salt solution, or by adding a fluoride salt to a lead salt, such as potassium fluoride to a lead(II) nitrate solution,[4]
- 2 KF + Pb(NO3)2 → PbF2 + 2 KNO3
or sodium fluoride to a lead(II) acetate solution.
- 2 NaF + Pb(CH3COO)2 → PbF2 + 2 NaCH3COO
Remove ads
Uses

2 scintillator crystals used in the Muon g−2 experiment.
Lead(II) fluoride is used in low melting glasses, in glass coatings to reflect infrared rays, in phosphors for television-tube screens, and as a catalyst for the manufacture of picoline.[3] The Muon g−2 experiment uses PbF
2 crystals in conjunction with silicon photomultipliers. High energy charged particles create Cerenkov light as they pass through the crystals, which is measured by the silicon photomultipliers.[7][8]
It also serves as an oxygen scavenger in high-temperature fluorine chemistry, as plumbous oxide is relatively volatile.[9]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads