Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
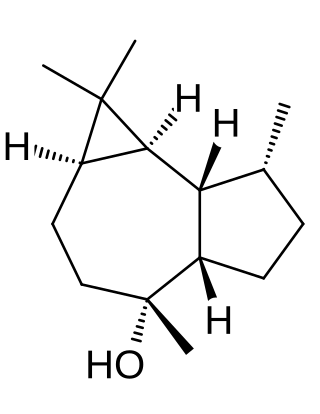
Ledol
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Ledol is a poisonous sesquiterpene that can cause cramps, paralysis, and delirium.[citation needed] Caucasian peasants used Rhododendron plants for these effects in shamanistic rituals.[1] Ledol resides in the essential oils of certain plants and when crushed, these oils are released. One of the plants with the highest concentration of these essential oils is Rhododendron tomentosum.[2]
The word "ledol" comes from the Greek word "ledos" meaning "robe". This likely comes from the "wooly" appearance of the plant, which has hair-like stalks stemming from the flower.[3]
Remove ads
Historical and traditional uses
The earliest known written record of Rhododendron plant toxicity dates back to 401 B.C. in China.[4] Despite their toxicity, Rhododendron species have been documented in traditional medicinal practices across various cultures, including Chinese, Ayurvedic, European, and North American practices.
The accounts of Rhododendron from around the world describe numerous health benefits and treatments to various ailments.
R. tomentosum is highly recorded with various uses, like treating rheumatism, coughs, colds, and insect bites. Some common names it has are "wild rosemary", "marsh tea", and "marsh rosemary". Scientists have studied R. tomentosum's shoots, due to the shoots having the highest concentration of essential oils, for potential antidiabetic, antimicrobial, and antioxidant purposes.[5]
Remove ads
Mechanism of action

Although the ledol mechanism of action is quite under-studied, ledol is a sesquiterpenoid and studies on similar sesquiterpenoids, such as picrotoxinin, have shown that these molecules often target GABA receptors.[6] These sesquiterpenoids act as GABA antagonists on GABA post-synaptic receptors. GABA-A receptors, in particular, function as chloride channels that facilitate the flow of chloride ions across cell membranes.[7]
When GABA is deficient, symptoms can include respiratory difficulty, seizures, delirium, vomiting, nausea, gastrointestinal issues, headaches, increased blood pressure, and muscle cramps.[8] This pattern reflects how known GABA-A receptor antagonists, such as picrotoxinin, affect the body.[9] Ledol has similar—if not identical—effects in the body, albeit milder than those of known GABA-A antagonists, according to sources.[10]
Another sesquiterpenoid, Nootkatone, was proven to exhibit similar effects in insects.[11]
Remove ads
Metabolism
Even though the metabolism of ledol has yet to be elucidated, a 2023 article involving sesquiterpene lactones, such as parthenolide, showed the sesquiterpenes reacting to human liver microsomes.[12] This demonstrates the reactivity with the liver's CYP3A4 enzyme. Through relation, the metabolism is possibly facilitated through the liver if ingested.
Sources
Summarize
Perspective
Ledol is found in labrador tea,[13] an herbal tea (not a true tea) made from three closely related species:
- Rhododendron tomentosum – Northern Labrador tea, previously Ledum palustre
- Rhododendron groenlandicum – Bog Labrador tea, previously Ledum groenlandicum or Ledum latifolium
- Rhododendron columbianum – Western Labrador tea, or trapper's tea, previously Ledum glandulosum
Ledol is also found in the essential oil of priprioca at a concentration of around 4%.[14]
Ledol is also found to varying concentrations in the following plants:[15]
- Cistus ladaniferus
- Corymbia maculata
- Eucalyptus albens
- Eucalyptus astringens
- Eucalyptus blakelyi
- Eucalyptus bosistoana
- Eucalyptus botryoides
- Eucalyptus camaldulensis
- Eucalyptus citriodora
- Eucalyptus cladocalyx
- Eucalyptus dealbata
- Eucalyptus diversicolor
- Eucalyptus globulus
- Eucalyptus maidenii
- Eucalyptus melliodora
- Eucalyptus moluccana
- Eucalyptus nova-anglica
- Eucalyptus occidentalis
- Eucalyptus oviformis
- Eucalyptus paniculata
- Eucalyptus polyanthemos
- Eucalyptus punctata
- Eucalyptus saligna
- Eucalyptus siderophloia
- Eucalyptus sideroxylon
- Eucalyptus tereticornis
- Humulus lupulus
- Hyssopus officinalis
- Mentha × piperita
- Panax quinquefolius
- Peumus boldus
- Pimenta dioica
- Piper cubeba
- Salvia officinalis
- Satureja obovata
- Syzygium aromaticum
- Teucrium arduini
- Teucrium gnaphalodes
- Teucrium polium
- Valeriana officinalis
- Vitex agnus-castus
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads