Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Link domain
Protein domain From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
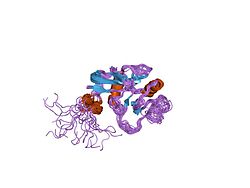
A Link domain or Link module, also known as Xlink domain (X for extracellular), is a protein domain that binds to hyaluronic acid.[1] It is important in blood cell migration and apoptosis.[2] The link domain is found in some extracellular proteins in vertebrates such as the hyalectans.[3] It appears to be involved in extracellular matrix assembly and stability, cell adhesion, and migration.[3][4]
Remove ads
Structure
The structure has been shown to consist of two alpha helices and two antiparallel beta sheets arranged around a large hydrophobic core similar to that of C-type lectin.[5] This domain contains four conserved cysteines involved in two disulphide bonds. The link domain has also been termed HABM (hyaluronic acid binding module)[4] and PTR (proteoglycan tandem repeat).[6]
Link domain proteins
Proteins which contain the link domain include:
- the hyalectans (a family of proteoglycans): aggrecan, brevican, neurocan and versican, which are expressed in the CNS;
- the cartilage link protein (LP), a proteoglycan that together with HA and aggrecan forms multimolecular aggregates;
- Tumour necrosis factor-inducible protein 6 (TSG-6), which may be involved in cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions during inflammation and tumourigenesis;
- CD44 antigen, the main cell surface receptor for HA.
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads