Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
List of Unix systems
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
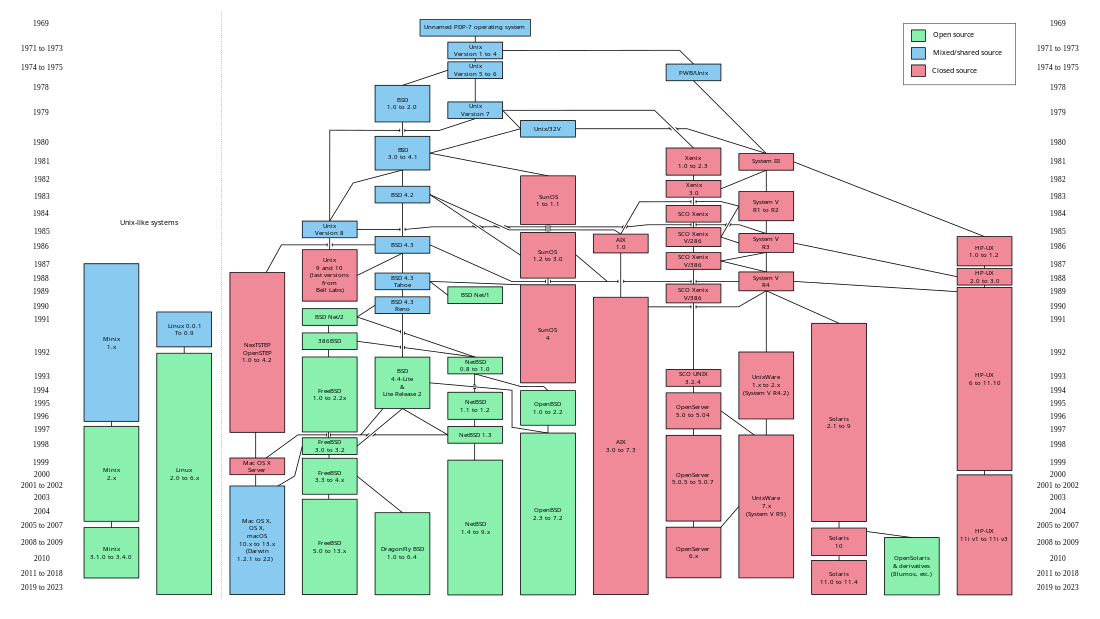
Each version of the UNIX Time-Sharing System evolved from the version before, with version one evolving from the prototypal Unix. Not all variants and descendants are displayed.
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Remove ads
Research Unix Systems and descendants
Summarize
Perspective
- UNIX Time-Sharing System v6 (1975)
- UNIX Time-Sharing System v7 (1979)
- UNIX Time-Sharing System v8 (1985)
- UNIX Time-Sharing System v9 (1986)
- UNIX Time-Sharing System v10 (1989)
- IX Multilevel-Secure UNIX System (1992)
The versions leading to v7 are also sometimes called Ancient UNIX. After the release of Version 10, the Unix research team at Bell Labs turned its focus to Plan 9 from Bell Labs, a distinct operating system released in 1993, and later on Inferno. All versions of BSD from its inception up to 4.3BSD-Reno are based on Research Unix, with versions starting with 4.4 BSD and Net/2 instead becoming Unix-like. Furthermore, 8th Edition Research Unix and on-wards had a close relationship to BSD. This began by using 4.1cBSD as the basis for the 8th Edition. In a Usenet post from 2000, Dennis Ritchie described these later versions of Research Unix as being closer to BSD than they were to UNIX System V,[1] which also included some BSD code:[2]
Research Unix 8th Edition started from (I think) BSD 4.1c, but with enormous amounts scooped out and replaced by our own stuff. This continued with 9th and 10th. The ordinary user command-set was, I guess, a bit more BSD-flavored than SysVish, but it was pretty eclectic.
Remove ads
Commercial AT&T Unix Systems and descendants
Each of the systems in this list is evolved from the version before, with Unix System III evolving from both the UNIX Time-Sharing System v7 and the descendants of the UNIX Time-Sharing System v6.
- UNIX System III (1981)
- UNIX System IV (1982)
- UNIX System V (1983)
- UNIX System V Release 2 (1984)
- UNIX System V Release 3.0 (1986)
- UNIX System V Release 3.2 (1987)
- UNIX System V Release 4 (1988)
- UnixWare 1.0 (System V Release 4.2) (1992)
- UnixWare 2.0 (System V Release 4.2MP) (1995)
- UnixWare 7 (System V Release 5) (1998)
- OpenServer 6.0 (System V Release 5) (2005)
Forks and ports
Remove ads
Other Unix operating systems
Below are other certified Unix operating systems:[4]
- macOS: Heavily based on BSD, macOS is registered as certified Unix 03 brand on both versions (Intel and Apple silicon-based).
- SCO OpenServer: Another operating system by SCO. Registered as Unix 93 “single and Multi-processor Industry Standard Intel architecture platform”.
- z/OS: z/OS by IBM is listed as two different operating systems, z/OS and z/OS V2R1. Both are Unix 95.
Unix-like operating systems
See also
Notes
- Two of the distros are certified UNIX brands, Inspur K-UX and EulerOS.[5]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads