Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
List of chiropterans
Animals in mammal order Chiroptera From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
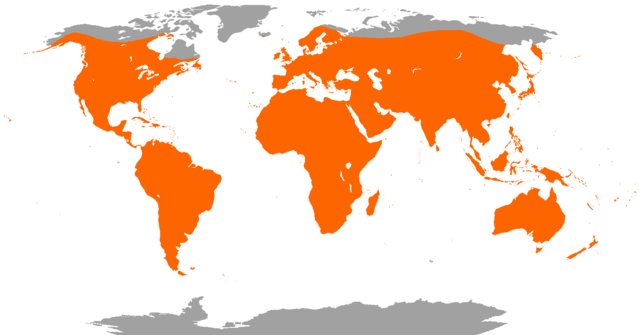
Chiroptera is an order of flying placental mammals. Members of this order are called chiropterans, or bats. The order comprises 1318 extant species, which are grouped into 226 genera. The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all mammal species worldwide. The majority of bats live in South and Central America, Africa, and southern and Southeast Asia, but the order can be found in most of the world outside of Antarctica and the arctic. They live in a variety of habitats, particularly forests and caves but also grasslands, savannas, shrublands, wetlands, deserts, and rocky areas. With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of sustained flight. They range in length from Kitti's hog-nosed bat, at 2 cm (1 in), to the great flying fox, at 37 cm (15 in). Bat wings are relatively proportionate to their size, with the large flying fox having the largest overall wingspan, up to 1.7 m (5.6 ft).[1]

Chiroptera is divided into two suborders: Yangochiroptera and Yinpterochiroptera. The suborders are further subdivided into clades and families. Yangochiroptera contains fourteen families grouped into three superfamilies: Emballonuroidea, containing the sheath-tailed and slit-faced bats; Noctilionoidea, containing the smoky, mustached, short-tailed, sucker-footed, bulldog, leaf-nosed, and disk-winged bats; and Vespertilionoidea, consisting of the wing-gland, bent-winged, free-tailed, funnel-eared, and vesper bats. Yinpterochiroptera includes seven families grouped into two superfamilies: Pteropodoidea, consisting of the fruit bats, and Rhinolophoidea, containing the hog-nosed, Old World leaf-nosed, false vampire, horseshoe, trident, and mouse-tailed bats.[2][3] The exact organization of the species is not fixed, with many recent proposals made based on molecular phylogenetic analysis. Nine species have been recorded as going extinct since 1500 CE.
Remove ads
Conventions
The author citation for the species or genus is given after the scientific name; parentheses around the author citation indicate that this was not the original taxonomic placement. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the collective range of species in that genera is provided. Ranges are based on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species unless otherwise noted. All extinct genera or species listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†".
Remove ads
Classification
Summarize
Perspective
The order Chiroptera consists of 1318 extant species belonging to 226 genera. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species. Modern molecular studies indicate that the 226 genera can be grouped into 21 families; these families are divided between two named suborders and are grouped in those suborders into named clades, and some of these families are subdivided into named subfamilies. An additional nine species have been recorded as going extinct since 1500 CE: three in the family Vespertilionidae, and six in the family Pteropodidae.
Suborder Yangochiroptera
- Superfamily Emballonuroidea
- Family Emballonuridae (sheath-tailed bats)
- Subfamily Emballonurinae (sheath-tailed, sac-winged, and ghost bats): 12 genera, 36 species
- Subfamily Taphozoinae (pouched and tomb bats): 2 genera, 18 species
- Family Nycteridae (slit-faced bats): 1 genus, 16 species
- Family Emballonuridae (sheath-tailed bats)
- Superfamily Noctilionoidea
- Family Furipteridae (smoky and thumbless bats): 2 genera, 2 species
- Family Mormoopidae (ghost-faced, naked-backed, and mustached bats): 2 genera, 11 species
- Family Mystacinidae (New Zealand short-tailed bats): 1 genus, 2 species
- Family Myzopodidae (sucker-footed bats): 1 genus, 2 species
- Family Noctilionidae (bulldog bats): 1 genus, 2 species
- Family Phyllostomidae (leaf-nosed bats)
- Subfamily Carolliinae (short-tailed bats): 1 genus, 8 species
- Subfamily Desmodontinae (vampire bats): 3 genera, 2 species
- Subfamily Glossophaginae (long-tongued bats): 16 genera, 37 species
- Subfamily Glyphonycterinae (big-eared bats): 3 genera, 5 species
- Subfamily Lonchophyllinae (nectar bats): 2 genera, 16 species
- Subfamily Lonchorhininae (sword-nosed bats): 1 genus, 5 species
- Subfamily Macrotinae (leaf-nosed bats): 1 genus, 2 species
- Subfamily Micronycterinae (big-eared bats): 2 genera, 12 species
- Subfamily Phyllostominae (round-eared and spear-nosed bats): 10 genera, 22 species
- Subfamily Rhinophyllinae (little fruit bats): 1 genus, 3 species
- Subfamily Stenodermatinae (yellow-shouldered and neotropical fruit bats): 20 genera, 90 species
- Family Thyropteridae (disk-winged bats): 1 genus, 5 species
- Superfamily Vespertilionoidea
- Family Cistugidae (wing-gland bats): 1 genus, 2 species
- Family Miniopteridae (bent-winged and long-fingered bats): 1 genus, 31 species
- Family Molossidae (free-tailed bats)
- Subfamily Molossinae (free-tailed bats): 18 genera, 119 species
- Subfamily Tomopeatinae (blunt-eared bat): 1 genus, 1 species
- Family Natalidae (funnel-eared bats): 3 genera, 11 species
- Family Vespertilionidae (vesper bats)
- Subfamily Kerivoulinae (woolly bats): 2 genera, 30 species
- Subfamily Murininae (tube-nosed bats): 3 genera, 35 species
- Subfamily Myotinae (mouse-eared bats): 3 genera, 121 species
- Subfamily Vespertilioninae (pipistrelles and serotines): 45 genera, 278 species (3 extinct)
Suborder Yinpterochiroptera
- Superfamily Pteropodoidea
- Family Pteropodidae (fruit bats)
- Subfamily Cynopterinae (short-nosed and tailless fruit bats): 15 genera, 28 species
- Subfamily Eidolinae (palm bats): 1 genera, 2 species
- Subfamily Harpyionycterinae (naked-backed fruit bats): 4 genera, 18 species
- Subfamily Nyctimeninae (tube-nosed fruit bats): 2 genera, 18 species
- Subfamily Pteropodinae (flying foxes): 7 genera, 81 species (6 extinct)
- Subfamily Rousettinae (rousettes and epauletted fruit bats): 13 genera, 41 species
- Subfamily Macroglossusinae (blossom bats): 5 genera, 10 species
- Family Pteropodidae (fruit bats)
- Superfamily Rhinolophoidea
- Family Craseonycteridae (Kitti's hog-nosed bat): 1 genus, 1 species
- Family Hipposideridae (Old World leaf-nosed bats): 7 genera, 86 species
- Family Megadermatidae (false vampire bats): 6 genera, 6 species
- Family Rhinolophidae (horseshoe bats): 1 genus, 92 species
- Family Rhinonycteridae (trident bats): 4 genera, 9 species
- Family Rhinopomatidae (mouse-tailed bats): 1 genus, 6 species
Remove ads
Chiropterans
Summarize
Perspective
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis, as supported by both the IUCN and the American Society of Mammalogists.[2][3]
Suborder Yangochiroptera
Superfamily Emballonuroidea
Family Emballonuridae
Main article: List of emballonurids
Members of the Emballonuridae family are called emballonurids, and include sheath-tailed bats, sac-winged bats, ghost bats, pouched bats, and tomb bats. They are all insectivorous and eat a variety of insects and spiders, and occasionally fruit.[5] Emballonuridae comprises 54 extant species, divided into 14 genera. These genera are grouped into two subfamilies: Emballonurinae, containing sheath-tailed, sac-winged, ghost, and other bat species, and Taphozoinae, containing pouched and tomb bats.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Balantiopteryx (sac-winged bat) |
Peters, 1867
Three species
|
Mexico, Central America, and northwestern South America | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (Ecuadorian sac-winged bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (gray sac-winged bat)[6] Habitats: Caves, shrubland, and forest[7] |
| Centronycteris (shaggy bat) |
Gray, 1838
Two species
|
Mexico, Central America, and northern and eastern South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (Thomas's shaggy bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (shaggy bat)[6] Habitat: Forest[8] |
| Coleura (sheath-tailed bat) |
Peters, 1867
Three species
|
Africa | Size range: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 in) tail (multiple)[6] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, caves, savanna, inland wetlands, and desert[9] |
| Cormura | Peters, 1867
One species
|
Central America and northern South America |
Size: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 in) tail[6] Habitat: Forest[10] |
| Cyttarops | Thomas, 1913
One species
|
Central America and northern South America |
Size: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in) tail[6] Habitat: Forest[11] |
| Diclidurus (ghost bat) |
Wied-Neuwied, 1820
Four species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (lesser ghost bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 8 cm (3 in) tail (northern ghost bat)[6] Habitat: Forest[12] |
| Emballonura (sheath-tailed bat) |
Temminck, 1838
Eight species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (Beccari's sheath-tailed bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (greater sheath-tailed bat)[6] Habitats: Rocky areas, caves, and forest[13] |
| Mosia | Gray, 1843
One species
|
Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands |
Size: 3–5 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 in) tail[6] Habitats: Forest, rocky areas, and caves[14] |
| Paremballonura (false sheath-tailed bat) |
Goodman, Puechmaille, Friedli-Weyeneth, Gerlach, Ruedi, Schoeman, Stanley, & Teeling, 2012
Two species
|
Madagascar | Size range: 4–5 cm (2 in), plus 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 in) tail (multiple)[6] Habitats: Caves and forest[15] |
| Peropteryx (dog-like bat) |
Peters, 1867
Five species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (lesser dog-like bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (greater dog-like bat)[6] Habitats: Caves, shrubland, and forest[16] |
| Rhynchonycteris | Peters, 1867
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America |
Size: 3–5 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 in) tail[6] Habitats: Forest and caves[17] |
| Saccopteryx (sac-winged bat) |
Illiger, 1811
Five species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (Amazonian sac-winged bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (greater sac-winged bat)[6] Habitats: Caves and forest[18] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saccolaimus (pouched bat) |
Temminck, 1838
Four species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia, Australia, and western and central Africa | Size range: 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Papuan sheath-tailed bat) to 14 cm (6 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (Pel's pouched bat)[6] Habitats: Savanna, caves, shrubland, and forest[19] |
| Taphozous (tomb bat) |
Geoffroy, 1818
Fourteen species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia, Australia, and Africa | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (black-bearded tomb bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (naked-rumped tomb bat)[6] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, coastal marine, rocky areas, savanna, caves, inland wetlands, and desert (some species unknown)[20] |
Close
Family Nycteridae
Main article: List of nycterids
Members of the Nycteridae family are called nycterids, or colloquially slit-faced bats. Nycteridae comprises 16 extant species in a single genus. They are all insectivorous, though the large slit-faced bat also regularly eats fish, frogs, birds, and bats.[21]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nycteris (slit-faced bat) |
Geoffroy & Cuvier, 1795
Sixteen species
|
Africa, western Arabian Peninsula, and southeastern Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (dwarf slit-faced bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 9 cm (4 in) tail (large slit-faced bat)[22] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, rocky areas, savanna, caves, and desert[23] |
Close
Superfamily Noctilionoidea
Family Furipteridae
Members of the Furipteridae family are called furipterids, and include two extant species, each in their own genus. They are both insectivorous.[24]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amorphochilus | Peters, 1877
One species
|
Western South America |
Size range: 3–5 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[25] Habitat: Forest[26] |
| Furipterus | Bonaparte, 1837
One species
|
Central America and South America |
Size range: 3–5 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[25] Habitats: Forest and caves[27] |
Close
Family Mormoopidae
Main article: List of mormoopids
Members of the Mormoopidae family are called mormoopids, and include ghost-faced bats, naked-backed bats, and mustached bats. Mormoopidae comprises eleven extant species, divided into two genera. They are all insectivorous.[28]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mormoops (ghost-faced bat) |
Leach, 1821
Two species
|
Southern North America, Central America, and northern South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Antillean ghost-faced bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (ghost-faced bat)[29] Habitats: Caves and forest[30] |
| Pteronotus (mustached bat) |
Gray, 1838
Nine species
|
Mexico, Caribbean, Central America, and northern and central South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Macleay's mustached bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Mesoamerican common mustached bat)[29] Habitats: Savanna, caves, and forest[31] |
Close
Family Mystacinidae
Members of the Mystacinidae family are called mystacinids, or colloquially New Zealand short-tailed bats, and include two extant species in a single genus. They are both omnivorous, eating insects, fruit, carrion, pollen, and nectar.[32]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mystacina (New Zealand short-tailed bat) |
Gray, 1843
Two species
|
New Zealand |
Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (New Zealand lesser short-tailed bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (New Zealand greater short-tailed bat)[33] Habitat: Forest[34] |
Close
Family Myzopodidae
Members of the Myzopodidae family are called myzopodids, or colloquially sucker-footed bats, and include two extant species in a single genus. They are both insectivorous.[35]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Myzopoda (sucker-footed bat) |
Milne-Edwards & A. Grandidier, 1878
Two species
|
Madagascar | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (western sucker-footed bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (Madagascar sucker-footed bat)[36] Habitats: Forest, inland wetlands, and caves[37] |
Close
Family Noctilionidae
Members of the Noctilionidae family are called noctilionids, or colloquially bulldog bats, and include two extant species in a single genus. They are both insectivorous, but the greater bulldog bat primarily eats fish.[38]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noctilio (bulldog bat) |
Linnaeus, 1766
Two species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (lesser bulldog bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (greater bulldog bat)[39] Habitats: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and caves[40] |
Close
Family Phyllostomidae
Main article: List of phyllostomids
Members of the Phyllostomidae family are called phyllostomids, or colloquially leaf-nosed bats, and include vampire bats, long-tongued bats, big-eared bats, broad-nosed bats, and yellow-shouldered bats. They primarily eat a variety of insects, fruit, nectar, and pollen, though a few will also eat birds, bats, and small mammals, and the three vampire bat species of the subfamily Desmodontinae solely consume blood.[41] Phyllostomidae comprises 203 extant species, divided into 60 genera. These genera are grouped into eleven subfamilies: Carolliinae, Desmodontinae, Glossophaginae, Glyphonycterinae, Lonchophyllinae, Lonchorhininae, Macrotinae, Micronycterinae, Phyllostominae, Rhinophyllinae, and Stenodermatinae.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carollia (short-tailed bat) |
Gray, 1838
Eight species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (chestnut short-tailed bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (gray short-tailed bat)[42] Habitats: Caves, savanna, and forest (some species unknown)[43] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desmodus | Wied-Neuwied, 1826
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America |
Size: 6–10 cm (2–4 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitats: Rocky areas and caves[44] |
| Diaemus | Miller, 1906
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and northern South America |
Size: 8–9 cm (3–4 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitats: Forest and caves[45] |
| Diphylla | Spix, 1823
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and northern South America |
Size: 6–10 cm (2–4 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitats: Forest, grassland, and caves[46] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anoura (tailless bat) |
Gray, 1838
Nine species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (tailed tailless bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, with no tail (Tschudi's tailless bat)[42] Habitats: Caves, shrubland, and forest[47] |
| Brachyphylla (fruit-eating bat) |
Gray, 1834
Two species
|
Caribbean | Size range: 7 cm (3 in) long, with no tail (Cuban fruit-eating bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, with no tail (Antillean fruit-eating bat)[42] Habitats: Caves and forest[48] |
| Choeroniscus (long-tailed bat) |
Thomas, 1928
Three species
|
Mexico, Central America, and northern South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (Godman's long-tailed bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (greater long-tailed bat)[42] Habitats: Inland wetlands and forest[49] |
| Choeronycteris | Tschudi, 1844
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and southern United States |
Size: 8–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 0.5–2 cm (0.2–0.8 in) tail[42] Habitats: Forest, caves, and desert[50] |
| Dryadonycteris | Nogueira, Lima, Peracchi, & Simmons, 2012
One species
|
Eastern Brazil |
Size: 5–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 0–1 cm (0.0–0.4 in) tail[42] Habitat: Forest[51] |
| Erophylla (flower bat) |
Miller, 1906
Two species
|
Caribbean | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0 in) tail (buffy flower bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (brown flower bat)[42] Habitat: Caves[52] |
| Glossophaga (long-tongued bat) |
Geoffroy, 1818
Five species
|
Mexico, Central America, and Southern Mexico | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (Commissaris's long-tongued bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Miller's long-tongued bat)[42] Habitats: Caves, shrubland, savanna, and forest[53] |
| Hylonycteris | Thomas, 1903
One species
|
Southern Mexico and Central America |
Size: 3–6 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 0–1 cm (0.0–0.4 in) tail[42] Habitats: Forest and caves[54] |
| Leptonycteris (long-nosed bat) |
Lydekker, 1891
Three species
|
Mexico, Central America, and northern South America | Size range: 7–9 cm (3–4 in) long, with no tail (multiple)[42] Habitats: Desert, caves, and forest[55] |
| Lichonycteris (little long-tongued bat) |
Thomas, 1895
Two species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 0.5–1 cm (0–0 in) tail (multiple)[42] Habitat: Forest[56] |
| Monophyllus (single leaf bat) |
Leach, 1821
Two species
|
Caribbean | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (Leach's single leaf bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (insular single leaf bat)[42] Habitat: Caves[57] |
| Musonycteris | Schaldach & McLaughlin, 1960
One species
|
Southern Mexico |
Size: 8–9 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 0.5–2 cm (0.2–0.8 in) tail[42] Habitats: Forest and caves[58] |
| Phyllonycteris (flower bats) |
Gundlach, 1860
Two species
|
Caribbean and Jamaica | Size range: 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (Jamaican flower bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Cuban flower bat)[42] Habitats: Caves and forest[59] |
| Platalina | Thomas, 1928
One species
|
Western South America |
Size: 6–8 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 0.5–1 cm (0.2–0.4 in) tail[42] Habitats: Savanna and caves[60] |
| Scleronycteris | Thomas, 1912
One species
|
Northern South America |
Size: 5–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 0.5–1 cm (0.2–0.4 in) tail[42] Habitat: Forest[61] |
| Xeronycteris | Gregorin & Ditchfield, 2005
One species
|
Eastern South America |
Size: Unknown[42] Habitats: Forest and savanna[62] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glyphonycteris (big-eared bat) |
Thomas, 1896
Three species
|
Central America and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (tricolored big-eared bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Davies's big-eared bat)[42] Habitats: Savanna, caves, and forest[63] |
| Neonycteris | Sanborn, 1949
One species
|
Northern South America | Size: Unknown[42] Habitat: Forest[64] |
| Trinycteris | Sanborn, 1949
One species
|
Central America and northern and eastern South America |
Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 0.5–2 cm (0.2–0.8 in) tail[42] Habitat: Forest[65] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lionycteris | Thomas, 1913
One species
|
Central America and northern South America |
Size: 4–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 0.5–1 cm (0.2–0.4 in) tail[42] Habitats: Forest, savanna, and caves[66] |
| Lonchophylla (nectar bat) |
Thomas, 1903
Fifteen species
|
Central America and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (Dekeyser's nectar bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (Handley's nectar bat)[42] Habitats: Savanna, caves, and forest[67] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lonchorhina (sword-nosed bat) |
Tomes, 1863
Five species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (Orinoco sword-nosed bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (Marinkelle's sword-nosed bat)[42] Habitats: Forest, grassland, rocky areas, savanna, and caves[68] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Macrotus (leaf-nosed bat) |
Gray, 1843
Two species
|
Western United States, Mexico, Central America, and Caribbean | Size range: 8–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail (multiple)[42] Habitats: Caves, shrubland, and forest[69] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lampronycteris | Sanborn, 1949
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America |
Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 0.5–2 cm (0.2–0.8 in) tail[42] Habitats: Forest and caves[70] |
| Micronycteris (big-eared bat) |
Gray, 1866
Eleven species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (little big-eared bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (hairy big-eared bat)[42] Habitats: Caves, savanna, and forest (some species unknown)[71] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chrotopterus | Peters, 1865
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America |
Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 0.5–2 cm (0.2–0.8 in) tail[42] Habitats: Forest and caves[72] |
| Gardnerycteris (hairy-nosed bat) |
Hurtado & Pacheco, 2014
Two species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Koepcke's hairy-nosed bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (striped hairy-nosed bat)[42] Habitats: Savanna and forest[73] |
| Lophostoma (round-eared bat) |
d'Orbigny, 1836
Seven species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (Davis's round-eared bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (white-throated round-eared bat)[42] Habitats: Savanna and forest[74] |
| Macrophyllum | Gray, 1838
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America |
Size: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[42] Habitat: Forest[75] |
| Mimon (golden bat) |
Gray, 1847
Two species
|
Northern and southeastern South America and Mexico, Central America, and northwestern South America | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (golden bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Cozumelan golden bat)[42] Habitats: Caves, savanna, and forest[76] |
| Phylloderma | Peters, 1865
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America |
Size: 8–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail[42] Habitats: Forest, savanna, and inland wetlands[77] |
| Phyllostomus (spear-nosed bat) |
Lacépède, 1799
Four species
|
South America, Northern South America, Mexico, Central America, and South America, and Central America and South America | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (lesser spear-nosed bat) to 13 cm (5 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (greater spear-nosed bat)[42] Habitats: Savanna, caves, and forest[78] |
| Tonatia (round-eared bat) |
Gray, 1827
Two species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America and Eastern South America | Size range: 6–9 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 in) tail (multiple)[42] Habitat: Forest[79] |
| Trachops | Gray, 1847
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America |
Size: 8–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 in) tail[42] Habitats: Forest and caves[80] |
| Vampyrum | Rafinesque, 1815
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America |
Size: 12–16 cm (5–6 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[81] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhinophylla (little fruit bat) |
Peters, 1865
Three species
|
Northern South America | Size range: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, with no tail (multiple)[42] Habitat: Forest[82] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ametrida | Gray, 1847
One species
|
Central America and northern South America |
Size: 3–6 cm (1–2 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[83] |
| Ardops | Miller, 1906
One species
|
Caribbean |
Size: 6–7 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[84] |
| Ariteus | Gray, 1838
One species
|
Jamaica |
Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[85] |
| Artibeus (neotropical fruit bat) |
Leach, 1821
Twelve species
|
Mexico, Caribbean, Central America, and northern South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (brown fruit-eating bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long (great fruit-eating bat)[42] Habitats: Rocky areas, savanna, caves, and forest[86] |
| Centurio | Gray, 1842
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and northern South America |
Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[87] |
| Chiroderma (big-eyed bat) |
Peters, 1860
Five species
|
Mexico, Central America, Caribbean, and northern South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (hairy big-eyed bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long (Guadeloupe big-eyed bat)[42] Habitats: Caves, savanna, and forest[88] |
| Dermanura (fruit-eating bat) |
Gervais, 1856
Eleven species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (Andersen's fruit-eating bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long (Aztec fruit-eating bat)[42] Habitats: Savanna, caves, and forest[89] |
| Ectophylla | H. Allen, 1892
One species
|
Central America |
Size: 3–5 cm (1–2 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[90] |
| Enchisthenes | K. Andersen, 1906
One species
|
Mexico, Central America, and northern South America |
Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[91] |
| Mesophylla | Thomas, 1901
One species
|
Central America and northern South America |
Size: 4–5 cm (2–2 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[92] |
| Phyllops | Peters, 1865
One species
|
Caribbean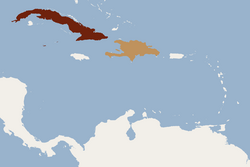 |
Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[93] |
| Platyrrhinus (broad-nosed bat) |
Saussure, 1860
Eighteen species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (brown-bellied broad-nosed bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long (buffy broad-nosed bat)[42] Habitats: Caves, savanna, and forest[94] |
| Pygoderma | Peters, 1863
One species
|
Central and eastern South America |
Size: Unknown[42] Habitat: Forest[95] |
| Sphaeronycteris | Peters, 1882
One species
|
Northern South America |
Size: 5–9 cm (2–4 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[96] |
| Stenoderma | E. Geoffroy, 1818
One species
|
Caribbean |
Size: 6–7 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[42] Habitat: Forest[97] |
| Sturnira (yellow-shouldered bat) |
Gray, 1842
23 species
|
Mexico, Central America, Caribbean, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (lesser yellow-shouldered bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long (Aratathomas's yellow-shouldered bat)[42] Habitat: Forest[98] |
| Uroderma (tent-making bat) |
Peters, 1865
Two species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (brown tent-making bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long (tent-making bat)[42] Habitats: Savanna and forest[99] |
| Vampyressa (little yellow-eared bat) |
Thomas, 1900
Three species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (northern little yellow-eared bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long (Melissa's yellow-eared bat)[42] Habitat: Forest[100] |
| Vampyriscus (yellow-eared bat) |
Thomas, 1900
Three species
|
Central America and northern South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (Brock's yellow-eared bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long (striped yellow-eared bat)[42] Habitat: Forest[101] |
| Vampyrodes (stripe-faced bat) |
Thomas, 1900
Two species
|
Central America and northern South America |
Size range: 7 cm (3 in) long, with no tail (great stripe-faced bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long (greater stripe-faced bat)[42] Habitat: Forest[102] |
Close
Family Thyropteridae
Members of the Thyropteridae family are called thyropterids, or colloquially disk-winged bats, and include five extant species in a single genus. They are all insectivorous.[103]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroptera (disk-winged bat) |
Miller, 1907
Five species
|
Central America and South America | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (De Vivo's disk-winged bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (LaVal's disk-winged bat)[104] Habitats: Forest and savanna[105] |
Close
Superfamily Vespertilionoidea
Family Cistugidae
Members of the Cistugidae family are called cistugids, or colloquially wing-gland bats, and include two extant species in a single genus. They are both insectivorous.[106]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cistugo (wing-gland bat) |
Thomas, 1912
Two species
|
Southern Africa | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Angolan hairy bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Lesueur's hairy bat)[107] Habitats: Rocky areas, shrubland, grassland, and desert[108] |
Close
Family Miniopteridae
Main article: List of miniopterids
Members of the Miniopteridae family are called miniopterids, and include bent-winged bats, or long-fingered bats. They are all insectivorous.[109] Miniopteridae comprises 31 extant species in a single genus.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Miniopterus | Bonaparte, 1837
31 species
|
Europe, Africa, and western, southeastern, and eastern Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (little bent-wing bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (great bent-winged bat)[110] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, rocky areas, caves, savanna, inland wetlands, and desert[111] |
Close
Family Molossidae
Main article: List of molossids
Members of the Molossidae family are called molossids, or colloquially free-tailed bats. They are all insectivorous.[112] Miniopteridae comprises 120 extant species, divided into 19 genera. These genera are grouped into two subfamilies: Molossinae, containing 119 species, and Tomopeatinae, which consists of a single species.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austronomus (Australasian free-tailed bat) |
Troughton, 1944
Two species
|
Australia and New Guinea | Size range: 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (New Guinea free-tailed bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (white-striped free-tailed bat)[113] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, savanna, and desert[114] |
| Cheiromeles (naked bat) |
Horsfield, 1824
Two species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (lesser naked bat) to 18 cm (7 in) long, plus 8 cm (3 in) tail (hairless bat)[113] Habitats: Caves and forest[115] |
| Cynomops (dog-faced bat) |
Thomas, 1920
Six species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Greenhall's dog-faced bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (cinnamon dog-faced bat)[113] Habitat: Forest[116] |
| Eumops (bonneted bat) |
Miller, 1906
Fifteen species
|
Southern North America, Central America, and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (northern dwarf bonneted bat) to 13 cm (5 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (Colombian bonneted bat)[113] Habitats: Forest, coastal marine, rocky areas, savanna, caves, and desert[117] |
| Micronomus | Gray, 1839
One species
|
Eastern Australia | Size: 5–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[113] Habitats: Forest and shrubland[118] |
| Molossops (dog-faced bat) |
Peters, 1865
Four species
|
South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (dwarf dog-faced bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (rufous dog-faced bat)[113] Habitats: Rocky areas, and forest (some species unknown)[119] |
| Molossus (velvety free-tailed bat) |
Geoffroy, 1805
Nine species
|
Mexico, Caribbean, Central America, and South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Aztec mastiff bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Alvarez's mastiff bat)[113] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, savanna, and caves[120] |
| Mops (free-tailed bat) |
Lesson, 1842
36 species
|
Africa and eastern and southeastern Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (little free-tailed bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (Medje free-tailed bat)[113] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, coastal marine, rocky areas, savanna, caves, and desert[121] |
| Mormopterus (little mastiff bat) |
Peters, 1865
Seven species
|
Western South America, Cuba, Madagascar and nearby islands, and island of Sumatra in Indonesia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Kalinowski's mastiff bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (Peters's wrinkle-lipped bat)[113] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, rocky areas, and caves[122] |
| Myopterus (African free-tailed bat) |
Geoffroy, 1818
Two species
|
Western and central Africa | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Bini free-tailed bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Daubenton's free-tailed bat)[113] Habitats: Savanna and forest[123] |
| Nyctinomops (free-tailed bat) |
Miller, 1865
Four species
|
North and South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (broad-eared bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (big free-tailed bat)[113] Habitats: Rocky areas, caves, and forest[124] |
| Otomops (mastiff bat) |
Thomas, 1913
Eight species
|
Africa, southern Arabian Peninsula, and southern and southeastern Asia | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (big-eared mastiff bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (Harrison's large-eared giant mastiff bat)[113] Habitats: Savanna, caves, and forest[125] |
| Ozimops (Australian free-tailed bat) |
Reardon, McKenzie, & Adams, 2014
Nine species
|
Australia, southeastern Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Cape York free-tailed bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (Beccari's free-tailed bat)[113] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, savanna, caves, inland wetlands, and desert[126] |
| Platymops | Thomas, 1906
One species
|
Eastern Africa | Size: 5–8 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[113] Habitats: Savanna and rocky areas[127] |
| Promops (mastiff bat) |
Gervais, 1856
Three species
|
Southern Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 5–10 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail (big crested mastiff bat)[113] Habitats: Forest (some species unknown)[128] |
| Sauromys | Peterson, 1965
One species
|
Southern Africa | Size: 6–9 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[113] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, and rocky areas[129] |
| Setirostris | Reardon, McKenzie, Cooper, Appleton, Carthew, & Adams, 2014
One species
|
Australia |
Size: 4–5 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[113] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, and rocky areas[130] |
| Tadarida (guano bat) |
Rafinesque, 1814
Eight species
|
North America, South America, Africa, Eastern Asia, southern Europe, and western, eastern, and southeastern Asia and Madagascar | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Mexican free-tailed bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (African giant free-tailed bat)[113] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, coastal marine, rocky areas, savanna, caves, and desert[131] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tomopeas | Miller, 1900
One species
|
Peru |
Size: 3–5 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[113] Habitat: Caves[132] |
Close
Family Natalidae
Main article: List of natalids
Members of the Natalidae family are called natalids, or colloquially funnel-eared bats. They are all insectivorous.[133] Natalidae comprises eleven extant species, divided into three genera.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chilonatalus (lesser funnel-eared bat) |
Miller, 1898
Three species
|
Caribbean | Size range: Unknown[134] Habitats: Caves and forest[135] |
| Natalus (greater funnel-eared bat) |
Gray, 1838
Seven species
|
Central America, South America, and Caribbean | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (Mexican greater funnel-eared bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (Jamaican greater funnel-eared bat)[134] Habitats: Caves and forest[136] |
| Nyctiellus | Gervais, 1855
One species
|
Cuba and The Bahamas |
Size: Unknown[134] Habitats: Forest and caves[137] |
Close
Family Vespertilionidae
Main articles: List of kerivoulines, List of murinines, List of myotines, and List of vespertilionines
Members of the Vespertilionidae family are called vespertilionids, or colloquially vesper bats, and include woolly bats, tube-nosed bats, mouse-eared bats, pipistrelles and serotines. They are all insectivorous, though one species also eats small birds.[106] Vespertilionidae comprises 461 extant species, divided into 53 genera. These genera are grouped into four subfamilies: Kerivoulinae, or woolly bats; Murininae, or tube-nosed bats; Myotinae, or mouse-eared bats; and Vespertilioninae, which includes pipistrelles, serotines, and other bat species. Vespertilioninae additionally contins three species which have been made extinct since 1500 CE.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kerivoula (woolly bat) |
Gray, 1842
26 species
|
Africa and southeastern Asia | Size range: 2 cm (1 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Least woolly bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (Kachin woolly bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, forest, caves, and grassland (some species unknown)[139] |
| Phoniscus (trumpet-eared bat) |
Miller, 1905
Four species
|
Papua New Guinea and eastern Australia, Southeastern Asia, and Possibly southeastern Africa | Size range: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail (multiple)[138] Habitats: Forest and inland wetlands[140] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Harpiocephalus | Gray, 1842
One species
|
Southeastern Asia |
Size: 5–8 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 4–5 cm (2–2 in) tail[138] Habitat: Forest[141] |
| Harpiola (tube-nosed bat) |
Thomas, 1915
Two species
|
India and Taiwan | Size range: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail (multiple)[138] Habitats: Forest, inland wetlands, and caves[142] |
| Murina (tube-nosed bat) |
Gray, 1842
32 species
|
Southern, southeastern, and eastern Asia, and Northern Australia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Annam tube-nosed bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (brown tube-nosed bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, forest, and caves (some species unknown)[143] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eudiscopus | Conisbee, 1953
One species
|
Southeastern Asia |
Size: 4–5 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitat: Forest[144] |
| Myotis (mouse-eared bat) |
Kaup, 1829
Many species
|
North America, South America, Europe, Africa, southern, southeastern, and eastern Asia, and Australia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Alcathoe bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (large myotis)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, desert, neritic marine, rocky areas, grassland, and inland wetlands (some species unknown)[145] |
| Submyotodon | Ziegler, 2003
One species
|
Taiwan | Size: 3–4 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 3–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitat: Forest[146] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antrozous | H. Allen, 1862
One species
|
Western North America and Cuba |
Size: 5–9 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest, rocky areas, and caves[147] |
| Arielulus (gilded sprite) |
Hill & Harrison, 1987
Four species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (bronze sprite) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (necklace sprite)[138] Habitats: Forest and inland wetlands[148] |
| Baeodon (yellow bat) |
Miller, 1906
Two species
|
Southern Mexico | Size range: 4–5 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail (multiple)[138] Habitat: Forest[149] |
| Barbastella (barbastelle) |
Gray, 1821
Four species
|
Europe, northern Africa, and western, southern, and eastern Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (eastern barbastelle) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Beijing barbastelle)[138] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, caves, and rocky areas[150] |
| Bauerus | Van Gelder, 1959
One species
|
Southern Mexico and Central America |
Size: 5–8 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2–2 in) tail[138] Habitat: Forest[151] |
| Chalinolobus (wattled bat) |
Peters, 1866
Seven species
|
New Zealand, Australia, and New Caledonia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (chocolate wattled bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Gould's wattled bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, and grassland[152] |
| Corynorhinus (American lump-nosed bat) |
H. Allen, 1865
Three species
|
North America | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (Rafinesque's big-eared bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (Mexican big-eared bat)[138] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, and caves[153] |
| Eptesicus (serotine bat) |
Rafinesque, 1820
26 species
|
North America, South America, Africa, Europe, and Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Argentine brown bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (big brown bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, desert, rocky areas, grassland, and inland wetlands[154] |
| Euderma | H. Allen, 1892
One species
|
Western North America |
Size: 6–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 4–5 cm (2–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest, caves, and desert[155] |
| Falsistrellus (false pipistrelle) |
Troughton, 1943
Two species
|
Australia | Size range: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2–2 in) tail (multiple)[138] Habitat: Forest[156] |
| Glauconycteris (butterfly bat) |
Dobson, 1875
Twelve species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Allen's spotted bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (pied butterfly bat)[138] Habitats: Shrubland, savanna, and forest[157] |
| Glischropus (thick-thumbed bat) |
Dobson, 1875
Three species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (common thick-thumbed bat) to 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Indochinese thick-thumbed bat)[138] Habitat: Forest[158] |
| Hesperoptenus (false serotine) |
Peters, 1868
Five species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Blanford's bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (Tickell's bat)[138] Habitats: Forest and caves[159] |
| Histiotus (big-eared brown bat) |
Gervais, 1856
Seven species
|
South America | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (big-eared brown bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (tropical big-eared brown bat)[138] Habitats: Forest and caves (some species unknown)[160] |
| Hypsugo (Asian pipistrelle) |
Kolenati, 1856
Eighteen species
|
Europe, northern Africa, and Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Alashanian pipistrelle) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Anthony's pipistrelle)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, desert, grassland, rocky areas, and inland wetlands[161] |
| Ia | Thomas, 1902
One species
|
Eastern Asia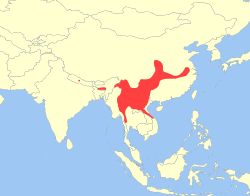 |
Size: 8–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 4–9 cm (2–4 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest and caves[162] |
| Idionycteris | Anthony, 1923
One species
|
Western United States and Mexico |
Size: About 7 cm (3 in), plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest, caves, and desert[163] |
| Laephotis (African long-eared bat) |
Thomas, 1901
Four species
|
Africa | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Angolan long-eared bat) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (De Winton's long-eared bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, desert, grassland, and inland wetlands[164] |
| Lasionycteris | Peters, 1866
One species
|
North America |
Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest, rocky areas, and caves[165] |
| Lasiurus (red bat) |
Gray, 1831
Seventeen species
|
North and South America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (minor red bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 9 cm (4 in) tail (Cuban yellow bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, and caves[166] |
| Mimetillus | Thomas, 1904
One species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest and savanna[167] |
| Neoromicia (serotine) |
Roberts, 1926
Sixteen species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Heller's serotine) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (cape serotine)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, desert, grassland, and inland wetlands[168] |
| Nyctalus (noctule bat) |
Bowdich, 1825
Eight species
|
Europe, northern Africa, and Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Lesser noctule) to 11 cm (4 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (Birdlike noctule)[138] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, caves, rocky areas, and inland wetlands[169] |
| Nycticeinops | Hill & Harrison, 1987
One species
|
Africa | Size: 3–5 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, and desert[170] |
| Nycticeius (evening bat) |
Rafinesque, 1819
Three species
|
Western Cuba, South America, and southern North America | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Temminck's mysterious bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (evening bat)[138] Habitat: Forest[171] |
| Nyctophilus (Australian big-eared bat) |
Leach, 1821
Seventeen species (one extinct)
|
Australia and southeastern Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (eastern long-eared bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (greater long-eared bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, grassland, and inland wetlands[172] |
| Otonycteris (long-eared bat) |
Peters, 1859
Two species
|
Western Asia and northern Africa | Size range: 5–9 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail (desert long-eared bat)[138] Habitats: Grassland, shrubland, rocky areas, and desert[173] |
| Parastrellus | Hoofer, Van Den Bussche, & Horáček, 2006
One species
|
Western United States and Mexico (in red) |
Size: 3–6 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest, grassland, rocky areas, caves, and desert[174] |
| Perimyotis | Menu, 1984
One species
|
Eastern North America (in yellow) |
Size: 4–5 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest, rocky areas, and caves[175] |
| Pharotis | Thomas, 1914
One species
|
Papua New Guinea |
Size: 4–5 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 4–5 cm (2–2 in) tail[138] Habitat: Forest[176] |
| Philetor | Thomas, 1902
One species
|
Southeastern Asia |
Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 3–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest and grassland[177] |
| Pipistrellus (pipistrelle) |
Kaup, 1829
33 species (2 extinct)
|
Australia, Africa, Europe, Japan, and western, southern, and southeastern Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Angulate pipistrelle) to 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Kelaart's pipistrelle)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, desert, rocky areas, grassland, intertidal marine, and inland wetlands[178] |
| Plecotus (lump-nosed bat) |
Geoffroy, 1818
Sixteen species
|
Europe, Asia, and northern Africa | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (brown long-eared bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (alpine long-eared bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, desert, grassland, and rocky areas[179] |
| Rhogeessa (yellow bat) |
H. Allen, 1866
Eleven species
|
Mexico, Central America, and South America | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (black-winged little yellow bat) to 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (Bickham's little yellow bat)[138] Habitats: Shrubland and forest[180] |
| Rhyneptesicus | Bianchi, 1917
One species
|
Western Asia | Size: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest, savanna, caves, and desert[181] |
| Scoteanax | Troughton, 1944
One species
|
Eastern Mexico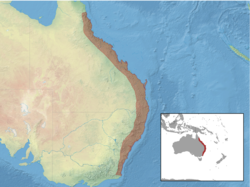 |
Size: 6–8 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2–2 in) tail[138] Habitat: Forest[182] |
| Scotoecus (lesser house bat) |
Thomas, 1901
Five species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa and southern Asia | Size range: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail (multiple)[138] Habitats: Shrubland, savanna, and forest[183] |
| Scotomanes | Dobson, 1875
One species
|
Eastern and southeastern Asia |
Size: 6–9 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest and caves[184] |
| Scotophilus (Old World yellow bat) |
Leach, 1821
Eighteen species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (lesser Asiatic yellow bat) to 13 cm (5 in) long, plus 10 cm (4 in) tail (Schreber's yellow bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, desert, and grassland (some species unknown)[185] |
| Scotorepens (broad-nosed bat) |
Troughton, 1943
Four species
|
Australia, Timor-Leste, and Papua New Guinea | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (little broad-nosed bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (eastern broad-nosed bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, desert, and grassland[186] |
| Scotozous | Dobson, 1875
One species
|
Southern Asia | Size: 3–6 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail[138] Habitats: Forest, shrubland, and desert[187] |
| Thainycteris | Kock & Storch, 1996
One species
|
Laos and Thailand | Size: 6–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2–2 in) tail[138] Habitat: Forest[188] |
| Tylonycteris (bamboo bat) |
Peters, 1872
Three species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 2 cm (1 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (pygmy bamboo bat) to 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (greater bamboo bat)[138] Habitat: Forest[189] |
| Vespadelus (forest bat) |
Troughton, 1943
Nine species
|
Australia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (eastern cave bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (large forest bat)[138] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, desert, and grassland[190] |
| Vespertilio (parti-coloured bat) |
Linnaeus, 1758
Two species
|
Europe and Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (parti-coloured bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 6 cm (2 in) tail (Asian particolored bat)[138] Habitats: Shrubland, coastal marine, forest, caves, desert, rocky areas, grassland, and inland wetlands[191] |
Close
Suborder Yinpterochiroptera
Superfamily Pteropodoidea
Family Pteropodidae
Main article: List of pteropodids
Members of the Pteropodidae family are called pteropodids, or colloquially fruit bats, flying foxes, or megabats. Most species primarily or exclusively eat fruit, though the species of the subfamily Macroglossusinae primarily eat pollen and nectar and many of the species of the subfamily Nyctimeninae sometimes eat insects.[1] Pteropodidae comprises 193 extant species, divided into 46 genera. These genera are grouped into seven subfamilies: Eidolinae, Harpyionycterinae, Nyctimeninae, Pteropodinae, Rousettinae, and Macroglossusinae. Pteropodinae additionally contins six species which have been made extinct since 1500 CE.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aethalops (sooty bat) |
Thomas, 1923
Two species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (Borneo fruit bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, with no tail (pygmy fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[193] |
| Alionycteris | Kock, 1969
One species
|
Philippines |
Size: 6–8 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitat: Forest[194] |
| Balionycteris (spotted-winged fruit bat) |
Matschie, 1899
Two species
|
Southeastern Asia and Malaysia | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (Malayan spotted-winged fruit bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, with no tail (spotted-winged fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[195] |
| Chironax | K. Andersen, 1912
One species
|
Southeastern Asia |
Size: 5–8 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[196] |
| Cynopterus (short-nosed fruit bat) |
F. Cuvier, 1824
Seven species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia | Size range: 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (lesser short-nosed fruit bat) to 13 cm (5 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (Indonesian short-nosed fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[197] |
| Dyacopterus (dyak fruit bat) |
K. Andersen, 1912
Three species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (dayak fruit bat) to 15 cm (6 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Rickart's dyak fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[198] |
| Haplonycteris | Lawrence, 1939
One species
|
Philippines |
Size: 6–8 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitat: Forest[199] |
| Latidens | Thonglongya, 1972
One species
|
Southern India |
Size: 10–11 cm (4–4 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[200] |
| Megaerops (tailless fruit bat) |
Peters, 1865
Four species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (Javan tailless fruit bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, with no tail (Ratanaworabhan's fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[201] |
| Otopteropus | Kock, 1969
One species
|
Philippines |
Size: 6–8 cm (2–3 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitat: Forest[202] |
| Penthetor | K. Andersen, 1912
One species
|
Southeastern Asia |
Size: 7–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 0.5–2 cm (0.2–0.8 in) tail[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[203] |
| Ptenochirus (musky fruit bat) |
Peters, 1861
Two species
|
Philippines | Size range: 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (lesser musky fruit bat) to 13 cm (5 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (greater musky fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[204] |
| Sphaerias | Miller, 1906
One species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia |
Size: 7–9 cm (3–4 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitat: Forest[205] |
| Thoopterus (swift fruit bat) |
Matschie, 1899
Two species
|
Indonesia | Size range: 8 cm (3 in) long, with no tail (Suhaniah fruit bat) to 12 cm (5 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (swift fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[206] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eidolon | Rafinesque, 1815
Two species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa and western Arabian Peninsula | Size range: 15 cm (6 in) long, with no tail (straw-coloured fruit bat) to 21 cm (8 in) long, with no tail (Madagascan fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Savanna, forest, and caves[207] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aproteles | Menzies, 1977
One species
|
New Guinea |
Size: About 25 cm (10 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[208] |
| Boneia | Jentink, 1879
One species
|
Indonesia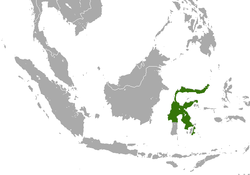 |
Size: About 19 cm (7 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[209] |
| Dobsonia (naked-backed fruit bat) |
Palmer, 1898
Fourteen species
|
Southeastern Asia and northern Australia | Size range: 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 0.5 cm (0.2 in) tail (lesser naked-backed fruit bat) to 25 cm (10 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (bare-backed fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Rocky areas, forest, and caves[210] |
| Harpyionycteris (harpy fruit bat) |
Thomas, 1896
Two species
|
Indonesia and Philippines | Size range: 11 cm (4 in) long, with no tail (Sulawesi harpy fruit bat) to 16 cm (6 in) long, with no tail (harpy fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Forest[211] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nyctimene (tube-nosed fruit bat) |
Borkhausen, 1797
Sixteen species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (Keast's tube-nosed fruit bat) to 15 cm (6 in) long, with no tail (broad-striped tube-nosed fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Savanna, forest, and inland wetlands[212] |
| Paranyctimene (lesser tube-nosed fruit bat) |
Tate, 1942
Two species
|
New Guinea and Indonesia | Size range: 6–10 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail (multiple)[192] Habitat: Forest[213] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acerodon (sharp-toothed flying fox) |
Jourdan, 1837
Five species
|
Indonesia and Philippines | Size range: 19 cm (7 in) long, with no tail (Sulawesi flying fox) to 30 cm (12 in) long, with no tail (Giant golden-crowned flying fox)[192] Habitat: Forest[214] |
| Desmalopex (white-winged flying fox) |
Miller, 1907
Two species
|
Philippines | Size range: 13 cm (5 in) long, with no tail (small white-winged flying fox) to 24 cm (9 in) long, with no tail (white-winged flying fox)[192] Habitats: Grassland and forest[215] |
| Mirimiri | Helgen, 2005
One species
|
Fiji |
Size: 17–20 cm (7–8 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitat: Forest[216] |
| Neopteryx | Hayman, 1946
One species
|
Indonesia |
Size: About 16 cm (6 in), with no tail[192] Habitat: Forest[217] |
| Pteralopex (monkey-faced bat) |
Thomas, 1888
Five species
|
Solomon Islands | Size range: 16 cm (6 in) long, with no tail (montane monkey-faced bat) to 28 cm (11 in) long (Bougainville monkey-faced bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[218] |
| Pteropus (flying fox) |
Brisson, 1762
65 species (6 extinct)
|
Southern, southeastern, and eastern Asia, Australia, and Madagascar and nearby islands |
Size range: 9 cm (4 in) long, with no tail (dwarf flying fox) to 37 cm (15 in) long, with no tail (great flying fox)[192] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, and inland wetlands[219] |
| Styloctenium (stripe-faced fruit bat) |
Matschie, 1899
Two species
|
Indonesia and Philippines (in red) | Size range: 14 cm (6 in) long, with no tail (Mindoro stripe-faced fruit bat) to 20 cm (8 in) long, with no tail (Sulawesi stripe-faced fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[220] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casinycteris (short-palated bat) |
Thomas, 1910
Two species
|
Central Africa | Size range: 7–10 cm (3–4 in) long, with no tail (short-palated fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[221] |
| Eonycteris (dawn bat) |
Dobson, 1873
Three species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia | Size range: 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (cave nectar bat) to 13 cm (5 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (greater nectar bat)[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[222] |
| Epomophorus (epauletted bat) |
Bennett, 1836
Twelve species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (Peters's dwarf epauletted fruit bat) to 19 cm (7 in) long, plus 0.1 cm (0.04 in) tail (Dobson's epauletted fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, grassland, and rocky areas[223] |
| Epomops (epauletted fruit bat) |
Gray, 1870
Two species
|
Central and western Africa | Size range: 10–20 cm (4–8 in) long, with no tail (Buettikofer's epauletted fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Shrubland, savanna, and forest[224] |
| Hypsignathus | H. Allen, 1861
One species
|
Western and central Africa |
Size: 16–30 cm (6–12 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitats: Forest and savanna[225] |
| Megaloglossus (long-tongued fruit bat) |
Pagenstecher, 1885
Two species
|
Western and central Africa | Size range: 6 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (Woermann's fruit bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, with no tail (Azagnyi fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[226] |
| Myonycteris (collared fruit bat) |
Matschie, 1899
Five species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | Size range: 8 cm (3 in) long, with no tail (little collared fruit bat) to 14 cm (6 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Angolan rousette)[192] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, grassland, and rocky areas[227] |
| Nanonycteris | Matschie, 1899
One species
|
Western Africa |
Size: 6–9 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 0.1–0.5 cm (0.04–0.20 in) tail[192] Habitats: Forest and savanna[228] |
| Pilonycteris | Nesi, Tsang, Simmons, McGowen, & Rossiter, 2021
One species
|
Indonesia |
Size: 8–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in) tail[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[229] |
| Plerotes | K. Andersen, 1910
One species
|
Southern Africa |
Size: 7–10 cm (3–4 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitats: Forest and savanna[230] |
| Rousettus (rousette) |
Gray, 1821
Seven species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia and Africa | Size range: 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (Leschenault's rousette) to 20 cm (8 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Egyptian fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, desert, grassland, and rocky areas[231] |
| Scotonycteris (tear-drop bat) |
Matschie, 1894
Three species
|
Western Africa and Western and central Africa | Size range: 6–9 cm (2–4 in) long, with no tail (multiple)[192] Habitat: Forest[232] |
| Stenonycteris | Thomas, 1906
One species
|
Eastern Africa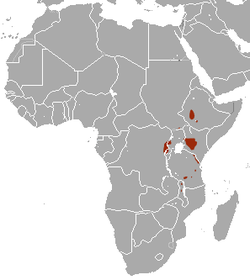 |
Size: 11–18 cm (4–7 in) long, plus 0.5–3 cm (0.2–1.2 in) tail[192] Habitats: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[233] |
Close
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Macroglossus (long-tongued fruit bat) |
F. Cuvier, 1824
Two species
|
Southeastern Asia and northern Australia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (long-tongued nectar bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (long-tongued fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[234] |
| Melonycteris | Dobson, 1877
One species
|
Papua New Guinea |
Size: 7–11 cm (3–4 in) long, with no tail[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[235] |
| Nesonycteris (Solomon Islands blossom bat) |
Thomas, 1887
Two species
|
Solomon Islands | Size range: 8 cm (3 in) long, with no tail (Fardoulis's blossom bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long, with no tail (Woodford's fruit bat)[192] Habitat: Forest[236] |
| Notopteris (long-tailed blossom bat) |
Gray, 1859
Two species
|
Fiji, Vanuatu and New Caledonia | Size range: 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (New Caledonia blossom bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (long-tailed fruit bat)[192] Habitats: Forest and caves[237] |
| Syconycteris (blossom bat) |
Matschie, 1899
Three species
|
Southeastern Asia and northern Australia | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (common blossom bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, with no tail (Halmahera blossom bat)[192] Habitats: Shrubland, savanna, and forest[238] |
Close
Superfamily Rhinolophoidea
Family Craseonycteridae
Members of the Craseonycteridae family are called craseonycterids. The family contains a single insectivorous species.[239]
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Craseonycteris | Hill, 1974
One species
|
Thailand and Myanmar |
Size range: 2–4 cm (1–2 in) long, with no tail[240] Habitats: Forest and caves[241] |
Close
Family Hipposideridae
Main article: List of hipposiderids
Members of the Hipposideridae family are called hipposiderids, or colloquially Old World leaf-nosed bats. They are all insectivorous.[242] Hipposideridae comprises 86 extant species, divided into 7 genera.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthops | Thomas, 1888
One species
|
Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands |
Size: 4–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 0.3–1 cm (0.1–0.4 in) tail[243] Habitats: Forest and caves[244] |
| Asellia (trident bat) |
Gray, 1838
Four species
|
Northern and eastern Africa and Western Asia | Size range: 4 cm (2 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (Patrizi's trident leaf-nosed bat) to 6 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (multiple)[243] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, savanna, caves, and desert[245] |
| Aselliscus (trident bats) |
Tate, 1941
Three species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 1 cm (0 in) tail (Temminck's trident bat) to 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Stoliczka's trident bat)[243] Habitats: Caves and forest[246] |
| Coelops (tailless leaf-nosed bat) |
Blyth, 1848
Two species
|
Southeastern Asia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, with no tail (Malayan tailless leaf-nosed bat) to 5 cm (2 in) long, with no tail (East Asian tailless leaf-nosed bat)[243] Habitats: Caves and forest[247] |
| Doryrhina (roundleaf bat) |
Peters, 1871
Two species
|
Central and western Africa | Size range: 7 cm (3 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (cyclops roundleaf bat) to 10 cm (4 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (greater roundleaf bat)[243] Habitats: Savanna and forest[248] |
| Hipposideros (roundleaf bat) |
Gray, 1831
70 species
|
Southern, southeastern, and eastern Asia, Africa, southern Arabian Peninsula, and Northern Australia | Size range: 3 cm (1 in) long, plus 1 cm (0.4 in) tail (dusky leaf-nosed bat) to 11 cm (4 in) long, plus 7 cm (3 in) tail (fierce roundleaf bat)[243] Habitats: Shrubland, forest, grassland, rocky areas, savanna, caves, and inland wetlands (some species unknown)[249] |
| Macronycteris (leaf-nosed bat) |
Gray, 1866
Four species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | Size range: 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail (giant roundleaf bat) to 13 cm (5 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (striped leaf-nosed bat)[243] Habitats: Rocky areas, caves, savanna, and forest[250] |
Close
Family Megadermatidae
Members of the Megadermatidae family are called megadermatids, or colloquially false vampire bats. They are primarily insectivorous, but will also eat a wide range of small vertebrates.[21] Megadermatidae comprises six extant species, each in their own genus.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardioderma | Peters, 1873
One species
|
Eastern Africa |
Size range: 7–8 cm (3–3 in) long, with no tail[251] Habitats: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[252] |
| Eudiscoderma | Soisook, Prajakjitr, Sunate Karapan, Francis, & Bates, 2015
One species
|
Thailand |
Size range: 7–8 cm (3–3 in) long, with no tail[251] Habitat: Forest[253] |
| Lavia | Gray, 1838
One species
|
Sub-Saharan Africa |
Size range: 6–9 cm (2–4 in) long, with no tail[251] Habitats: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[254] |
| Lyroderma | Lacépède, 1799
One species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia |
Size range: 7–10 cm (3–4 in) long, with no tail[251] Habitats: Forest, shrubland, rocky areas, and caves[255] |
| Macroderma | Miller, 1906
One species
|
Northern Australia |
Size range: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, with no tail[251] Habitats: Forest, savanna, shrubland, rocky areas, and caves[256] |
| Megaderma | (Geoffroy, 1810)
One species
|
Southern and southeastern Asia |
Size range: 5–9 cm (2–4 in) long, with no tail[251] Habitats: Savanna, shrubland, forest, caves, desert, grassland, rocky areas, and inland wetlands[257] |
Close
Family Rhinolophidae
Main article: List of rhinolophids
Members of the Rhinolophidae family are called rhinolophids, or colloquially horseshoe bats. They are all insectivorous.[258] Rhinolophidae comprises 92 extant species in a single genus.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
Close
Family Rhinonycteridae
Members of the Rhinonycteridae family are called rhinonycterids, or colloquially trident bats. They are all insectivorous.[258] Rhinolophidae comprises nine extant species in four genera.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloeotis | Thomas, 1901
One species
|
Southern Africa |
Size range: 3–5 cm (1–2 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0–2 in) tail[261] Habitats: Forest, savanna, and caves[262] |
| Paratriaenops (Madagascar trident bat) |
Benda & Vallo, 1847
Three species
|
Madagascar |
Size range: 4–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0–1 in) tail (Grandidier's trident bat)[261] Habitats: Forest, caves, and rocky areas[263] |
| Rhinonicteris | Gray, 1847
One species
|
Northern Australia |
Size range: 4–6 cm (2–2 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in) tail[261] Habitats: Savanna and caves[264] |
| Triaenops (trident bat) |
Dobson, 1871
Four species
|
Africa and western Asia |
Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail (Yemeni trident leaf-nosed bat) to 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail (multiple)[261] Habitats: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and caves[265] |
Close
Family Rhinopomatidae
Members of the Rhinopomatidae family are called rhinopomatids, or colloquially mouse-tailed bats. They are all insectivorous.[266] Rhinopomatidae comprises ninsixe extant species in a single genus.
More information Name, Authority and species ...
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhinolophus (mouse-tailed bat) |
Geoffroy, 1818
Six species
|
Northern and eastern Africa and western and southern Asia | Size range: 5 cm (2 in) long, plus 5 cm (2.0 in) tail (Egyptian mouse-tailed bat) to 9 cm (4 in) long, plus 9 cm (4 in) tail (greater mouse-tailed bat)[267] Habitats: Grassland, shrubland, rocky areas, caves, forest, and desert[268] |
Close
Remove ads
References
Sources
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
Remove ads