Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
List of comparative firefighting ranks
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Fire department ranking systems derive from the military, with different systems existing in different parts of the world as a reflection of that region's military.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2021) |
Rank in the fire service is an important element of its structure due to the battle-like conditions found on emergency incidents. Positions of authority need to be clearly defined, as do the type and number of subordinates under a rank, and the ability to manage the number of personnel on an incident or emergency scene.
Remove ads
Australia
Summarize
Perspective
New South Wales
- Fire and Rescue New South Wales[1]
- Fire and Rescue New South Wales Retained firefighters
- New South Wales Rural Fire Service
Victoria
- Victoria Country Fire Authority
Western Australia
- Department of Fire and Emergency Services
Remove ads
Austria
Salzburg
- Volunteer fire departments
Remove ads
Belgium
New rank structure as of 2015:[2]
Obsolete ranks:
Brazil
- Officers
- NCO and enlisted grades
Remove ads
Canada
Summarize
Perspective

Ranking categories and insignia in the Canadian fire service is common across the country, with minor variations, often based on department size. Virtually every fire department in Canada has at least a fire chief, and usually captains.
Rank insignia is worn either on the collar, (colloquially called "collar dogs" or "collar brass"), or on epaulets, and in some cases, both. Also badges, which also denote rank, are worn in some regions.
Badge, stripe and trumpet colours are a further denotation, silver being non-Chief ranks, gold reserved for Chiefs.
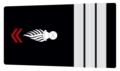
Like the United States, Canada uses speaking trumpets for rank indication - a reference to a megaphone-like device used in the early days of the fire service, for officer ranks. Typically, silver trumpets indicate lieutenant (1 trumpet) or captain (2 trumpets), and gold indicates Chief officer ranks, ranging 2 trumpets (Battalion or District Chief) up to 5 trumpets (Fire Chief).
Due to close ties and histories with Britain, there are also considerable ranking similarities to the United Kingdom, including the use of rank insignia on uniform epaulets.
Toronto
Montreal
Vancouver
Remove ads
Colombia


Chile
Ranks are divided between company officers and fire department officers, which can be subdivided between active officers (field officers) and administrative officers. The active officers are the captain, and three or four lieutenants, these four active officers are distinguished by red lines on their helmets.
China
Remove ads
Czech Republic
Cyprus
Denmark
Remove ads
France
Summarize
Perspective
Civilian fire fighters
Civilian fire services uses the following ranks. The chief fire officer of a departemental fire brigade can be a comptroller general, a colonel senior class or a colonel, depending on the size of the brigade.
Paris Fire Brigade

The Paris Fire Brigade belongs to the army and uses army ranks with the corps of engineers badge. The commanding officer has the rank of divisional general.
Marseille Naval Fire Battalion
The Marseille Naval Fire Battalion belongs to the navy and uses naval ranks. The commanding officer has the rank of rear admiral.
Germany
Summarize
Perspective
In Germany every federal state has its own civil protection laws thus they have different rank systems. In the professional fire brigades, the intermediate technical fire service requires basic fire fighter training for employment, advanced fire technical service requires a bachelor's degree from a fire college or promotion from the intermediate service, while higher technical fire service requires a master's degree from a university. Additionally, in the volunteer fire departments, there is a difference between a rank and an official position. This is founded on the military traditions of the fire departments. Every firefighter can hold a high rank without having an official position. A firefighter can be promoted by years of service, training skills and qualifications. Official positions are partly elected or given by capabilities. These conditions allow that older ordinary firefighters have higher ranks than their leaders. But through this ranks are no authorities given (brevet rank).
Rheinland-Pfalz
- Professional fire fighters (intermediate technical grades) of Rheinland-Pfalz
Completed vocational training in a technical occupation suitable for the fire service. Basic firefighter training.
 |
 | ||
| Brandmeister/-in während der Laufbahnausbildung |
Brandmeister | Oberbrandmeister | Hauptbrandmeister |
- Professional fire fighters (advanced technical grades) of Rheinland-Pfalz
Bachelor of engineering and two years departmental training
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| Brandinspektorenanwärter | Brandinspektor | Brandoberinspektor | Brandamtmann | Brandamtsrat | Brandoberamtsrat |
- Professional fire fighters (higher technical grades) of Rheinland-Pfalz
Master of engineering and two years of departmental training
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| Brandreferendar | Brandrat | Oberbrandrat | Branddirektor | Leitender Branddirektor Ministerialrat |
Leitender Ministerialrat | Landesfeuerwehrinspekteur |
- Helmet insignia of Rheinland-Pfalz
 |
 |
 |
| Company leaders | Upper technical grades, battalion chiefs | Higher technical grades, fire chiefs |
Saxony
- Ranks of the professional fire brigades in Saxony
- Which functions which ranks hold depends on the size of the fire brigade.
- Promoted from intermediate service.
- Ranks of the volunteer fire brigades in Saxony
Germany 1935-1945
Summarize
Perspective
The Feuerschutzpolizei was formed in 1938 as a branch of the Ordnungspolizei, formed in 1938 when the German municipal professional fire brigades were transferred to the national police. The previously red fire vehicles, blue uniforms and fire service ranks were replaced by green fire vehicles, green uniforms and police ranks.
Greece
Hungary
Officers
NCO and enlisted grades
India
In the Indian fire services, the ranks and hierarchy may vary slightly across different states and organizations. The specific rank names and their corresponding responsibilities may vary across different states and organizations in India. The following ranks are commonly found in indian fire departments.[10]
- Director general, fire and rescue services (head of the department) (IPS cadre officer in the rank of DGP)
- Director/additional director
- Regional fire officer/ divisional officer/joint director
- District fire officer
- Station officer, (in-charge of fire stations)
- Assistant station officer
- Senior fire and rescue officer/senior fireman/leading fireman
- Fire and rescue officer/fireman/ fireman (driver), (this is the entry-level position in the fire service.)
Indonesia
Summarize
Perspective
Firefighters in Indonesia form part of the civil service of local governments and wear variant forms of uniforms worn by civil servants and employees.
Iran
Summarize
Perspective

In Iran, every city has its own fire department, but ranks are the same in the whole country, and are as follows:
Ireland
Summarize
Perspective
Ireland's fire service is provided by its 31 local authorities. The four Dublin local authorities provide an unified fire service for County Dublin. Dublin Fire Brigade also provides an emergency ambulance service. Galway City Council and Galway County Council also provide a unified fire service. Whereas Cork City Council and Cork County Council provide separate fire services. The remaining local authorities provide a fire service for their respective county.[11] Ireland's ranks and insignia are similar across the country, with some differences in Dublin Fire Brigade.
Israel
- Officers
- Other Ranks
Italy
Japan
Summarize
Perspective
Municipal fire departments
The rank structure and insignia of the career municipal fire departments of Japan are dictated in regulations published by the Fire and Disaster Management Agency, the nation's coordinating body for fire and rescue services. In formal and station wear, rank is indicated by a small rectangular badge, normally worn on the left breast, consisting of varying numbers of lines and stars (the star used on the badge is the Firefighter's Emblem of Japan), whereas in operational wear rank is normally indicated by bands on the headwear of varying number and thickness according to rank.
Volunteer fire corps
The rank structure and insignia of the reserve volunteer fire corps of Japan are also dictated by the Fire and Disaster Management Agency. As with the career departments, in formal and station wear, rank is indicated by a small rectangular badge, normally worn on the left breast, consisting of varying numbers of lines and stars (the star used on the badge in this case is the Volunteer Fire Corps Emblem of Japan), whereas in operational wear rank is normally indicated by bands on the headwear of varying number and thickness according to rank.
Luxembourg
Malaysia
Netherlands
New Zealand
Summarize
Perspective
In New Zealand, rank is shown on epaulettes on firefighters' station uniform, and through colors and stripes on firefighter helmets. As the nation only has a single fire service, Fire and Emergency New Zealand, ranks are consistent through the country.
Nicaragua
Philippines
Commissioned officers
- Fire director (major general)
- Fire chief superintendent (brigadier general)
- Fire senior superintendent (colonel)
- Fire superintendent (lieutenant colonel)
- Fire chief inspector (major)
- Fire senior inspector (captain)
- Fire inspector (lieutenant)
Non-commissioned officers
- Senior fire officer 4 (executive master sergeant)
- Senior fire officer 3 (chief master sergeant)
- Senior fire officer 2 (senior master sergeant)
- Senior fire officer 1 (master sergeant)
- Fire officer 3 (staff sergeant)
- Fire officer 2 (corporal)
- Fire officer 1 (firefighter)
Peru
Cuerpo General de Bomberos Voluntarios del Perú
Poland
State Fire Service
| Strażak Firefighter Private |
Starszy strażak Senior firefighter Private |
Sekcyjny Section leader Private 1st class |
Starszy sekcyjny Senior section leader Specialist |
| Młodszy ogniomistrz Junior firemaster Corporal |
Ogniomistrz Firemaster Sergeant |
Starszy ogniomistrz Senior firemaster Staff sergeant | |
| Młodszy aspirant Junior aspirant Sergeant 1st class |
Aspirant Aspirant Master sergeant |
Starszy aspirant Senior aspirant Sergeant major |
Aspirant sztabowy Staff aspirant Command sergeant major |
| Młodszy kapitan Junior captain Second lieutenant |
Kapitan Captain First lieutenant |
Starszy kapitan Senior captain Captain |
Młodszy brygadier Junior brigadier Major |
| Brygadier Brigadier Lieutenant colonel |
Starszy brygadier Senior brigadier Colonel |
Nadbrygadier Chief brigadier Brigadier general |
Generał brygadier General brigadier Major general |
Volunteer Fire Services
- Local level
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Firefighter | Senior Firefighter | Team Commander | Deputy Section Commander | Section Commander | Deputy Platoon Commander | Platoon Commander |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Board Member | Member of the Audit Committee | Deputy Fire Chief | Vice President and Fire Chief | Chairman of the Audit Committee | President |
Fire Brigades 1941

Romania
- Officer ranks
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mareșal | General | General-locotenent | General-maior | General de brigadă | Colonel | Locotenent-colonel | Maior | Căpitan | Locotenent | Sublocotenent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Other ranks
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plutonier adjutant șef | Plutonier adjutant | Plutonier-major | Plutonier | Sergent-major | Sergent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Russian Federation
Summarize
Perspective
- Rank insignia
Personnel of the Russian State Fire Service use special ranks of internal service (apart from military personnel of the service who use military ranks).[19]
- Helmet insignia


Singapore
- Officers
- Warrant officers
- Other ranks
Soviet Union
Switzerland
- Officer grades
- Other grades
Taiwan
Tunisia
Tunisian firefighter's ranks are the same as the army, police and national guard.
Turkey
United Kingdom, Crown dependencies, British Overseas Territories
Contemporary
National Fire Service 1941–1948
United States
Summarize
Perspective

This ranking system is close to universal across all regions. There may be jurisdictions that do not utilize this rank structure, though they are rare.
In the United States, helmet colors often denote a fire fighter's rank or position. Generally, white helmets denote chief officers, (battalion chiefs, division chiefs, etc.), and red helmets denote company officers, (captains, lieutenants). While not universal, there are other commonalities, such as black for non-ranked firefighters, blue for EMS, and green for probationary firefighter.
There are some region specifics for helmet colors, though they have little to do with rank. For example, in San Francisco the SFFD paint their helmets based on a color system that denotes the apparatus they are assigned to.
Officer ranks are most commonly denoted by the number of speaking trumpets - a reference to a megaphone-like device used in the early days of the fire service, although currently and incorrectly called "bugles". , or by striping. Ranks proceed from one (lieutenant) to five (fire chief) trumpets.
The ranks of Deputy and Assistant Chief may differ based on region: one area may have the Assistant Chief as higher rank than Deputy, while another jurisdiction would be the opposite - Deputy out-ranking Assistant.
Typically, the captain is the ranking officer of a fire station, (which may include anywhere from one apparatus up to several apparatus), and the lieutenant is typically in charge of a single apparatus.
There are also both state (e.g. CalFire in California) and federal (e.g. U.S. Forest Service) rank structures. These align with the typical ranking of the rest of the North American fire service.
Some other U.S. fire departments such as the New York City Fire Department (FDNY) use military rank insignia (specifically sleeve insignia, though it is not an official part of the FDNY uniform code) in addition to the traditional bugles.
Vatican City
Venezuela
Summarize
Perspective
The firefighter units of the National Directorate for Civil Protection and Firefighting follow a rank system modeled more on the National Guard and the French Paris Fire Brigade. However, officer ranks follow US influence in the insignia.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads