| Image |
Nebula |
Maximum dimension
(in light-years/parsecs) |
Type |
Notes |
|---|
|
Abell 3391/3395 ICM[3] |
49,000,000 ly (15,000,000 pc)[3] |
Intracluster medium (ICM) |
Continuous warm-hot emission filament between two galaxy clusters. |
|
Abell 1659S ICM[4] |
2,413,000 ly (740,000 pc)[4] |
Intracluster medium (ICM) |
One of the gas clumps of the Abell 1659 galaxy cluster. |
|
Abell 1659N ICM[4] |
1,618,000 ly (496,000 pc)[4] |
Intracluster medium (ICM) |
One of the gas clumps of the Abell 1659 galaxy cluster. |
 |
Slug Nebula[5] |
1,500,000 ly (460,000 pc)[6] |
Enormous Lyα nebula (ELAN) |
Around the quasar UM287 at around z=2.3. Cosmic filament illuminated by the quasar. |
|
MAMMOTH-1 |
1,441,000 ly (442,000 pc)[7] |
Enormous Lyα nebula (ELAN) |
The nebula is associated with the galaxy overdensity BOSS1441,[7] which is a protocluster at z=2.3. The nebula represents the circumgalactic medium. Its emission is powered by starburst and an obscured AGN. One of the most extended ELAN discovered as of 2019.[8] |
 |
NGC 262 Halo Cloud |
1,300,000 ly (400,000 pc)[9] |
H I region |
Spiral nebula surrounding NGC 262, which is one of the largest known galaxies. |
 |
Ivory Nebula |
1,190,500 ly (365,000 pc)[2] |
Enormous Lyα nebula (ELAN) |
Also called MLAN1 at z=2.31. Another ELAN, called MLAN 10 is nearby. |
 |
Q0042−2627 nebula |
1,040,000 ly (320,000 pc)[5] |
Enormous Lyα nebula (ELAN) |
Around the quasar LBQS 0042-2627, at z=3.280 |
|
Jackpot Nebula[10] |
1,010,000 ly (310,000 pc)[11] |
Enormous Lyα nebula (ELAN) |
Four quasars embedded in the nebula. Likely progenitor of a massive galaxy cluster at z=2.05. |
 |
Fabulous Nebula[12] |
969,000 ly (297,000 pc)[13] |
Enormous Lyα nebula (ELAN) |
Also called SDSS J1020+1040 nebula, after the central quasar (aka 4C 10.29), located at z=3.164. Inspiraling material.[13] Will likely evolve into an elliptical galaxy.[12] |
 |
Leo Ring |
650,000 ly (200,000 pc)[14] |
HVC |
A large ring of cold gas that formed from a collision of two galaxies.[15] |
 |
Magellanic Stream |
600,000 ly (180,000 pc)[16] |
complex of HVCs |
Connects the Large and Small Magellanic clouds; extends across 180° of the sky. |
 |
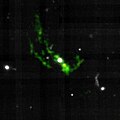
filament near TXS 0206-048 |
391,000 ly (120,000 pc)[17] |
[O II] nebula |
Longest cool filament near a quasar as of 2022. Quasar is located at z=1.13. Filament is accreted into the galaxy and subsequently to the quasar. |
 |
EELR of 3C 458 |
363,000 ly (111,000 pc)[18] |
emission line nebula |
The size is likely larger. The paper only describes the maximal distance to the nucleus and not the entire size. |
 |
nebula around the Teacup galaxy |
363,000 ly (111,000 pc)[19] |
ionized nebula |
part of the circumgalactic medium around the Teacup galaxy, illuminated by the AGN |
 |
Lyman-alpha blob 1 |
300,000 ly (92,000 pc)[20] |
LαB |
Largest blob in the LAB Giant Concentration[citation needed] |
 |
Himiko Gas Cloud |
55,000 ly (17,000 pc)[21] |
Intergalactic cloud
(possible LαB) |
One of the most massive lyman-alpha blobs known |
|
HVC 127-41-330 |
20,000 ly (6,100 pc)[22] |
HVC |
 |
Smith's Cloud |
9,800 ly (3,000 pc)[23] |
HVC |
Extends about 20° of the sky |
 |
Tarantula Nebula |
1,895 ly (581 pc)[24][a] |
H II region |
Most active starburst region in the Local Group |
 |
NGC 604 |
1,520 ly (470 pc)[25][26][b] |
H II region |
Largest H II region located in the Triangulum Galaxy |
 |
N44 |
1,000 ly (310 pc)[27] |
Emission nebula |
Contains a 250 light year wide superbubble that was probably formed from stellar winds.[28] |
 |
N11 |
1,000 ly (310 pc)[29] |
H II region |
N11 is the second largest star formation region in the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy. |
 |
NGC 2404 |
940 ly (290 pc) |
H II region |
Largest H II region located in the spiral galaxy NGC 2403 |
 |
NGC 595 |
880 ly (270 pc)[30] |
H II region |
Contains massive stars that have strong stellar winds. |
 |
Ring Nebula (NGC 6822) |
838 ly (257 pc) |
H II region |
The Ring Nebula is located in the lower right of the image |
 |
Gum Nebula |
809–950 ly (248–291 pc)[31][32] |
Emission nebula |
Extends about 36° of the sky |
 |
Bubble Nebula (NGC 6822) |
758 ly (232 pc)[33][34][35] |
H II region |
The Bubble Nebula is located in the upper left of the image |
 |
NGC 6188 |
600 ly (180 pc)[36] |
Emission nebula |
|
 |
NGC 592 |
580 ly (180 pc)[37][38] |
H II region |
Located in the Triangulum Galaxy |
 |
Cygnus X |
560 ly (170 pc) |
radio and infrared emission nebula[39] |
Cygnus X is relative nearby, but hidden behind dark clouds, dimensions on the sky are 7° x 7°[40] and distance is 1400 pc[39] |
 |
Sh2-310 |
531–681 ly (163–209 pc)[41][c] |
H II region |
Nebula surrounding VY Canis Majoris, which is one of largest known stars. |
 |
Carina Nebula |
460 ly (140 pc)[42] |
H II region |
Nearest giant H II region to Earth |
 |
Dragonfish Nebula |
450 ly (140 pc)[43] |
Emission nebula |
|
 |
N119 |
430–570 ly (131–175 pc)[44] |
H II region |
Peculiar S-shape |
 |
RCW 49 |
350 ly (110 pc)[45] |
H II region |
|
 |
Soul Nebula |
330 ly (100 pc)[46] |
H II region |
|
 |
Heart Nebula |
330 ly (100 pc)[47] |
H II region |
Has been named the “Heart nebula” because of its resemblance to a human heart. |
 |
Henize 70 (N70 or DEM L301)[48] |
300 ly (92 pc)[49] |
H II region |
The N 70 Nebula, in the Large Magellanic Cloud has a shell structure and is really a bubble in space. It is a "Super Bubble". |
 |
Barnard's Loop |
300 ly (92 pc)[50][51] |
H II region |
Supernova over the last 4 million years probably carved cavities in gas clouds forming the semi circle shape of Barnard's loop. |
 |
Sh2-54 |
252 ly (77 pc)[52][53] |
H II region |
|
 |
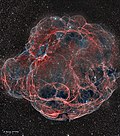
Prawn Nebula |
250 ly (77 pc)[54] |
H II region |
|
 |
Simeis 147 |
160 ly (49 pc)[55] |
Supernova remnant |
|
 |
NGC 7822 |
150 ly (46 pc)[56] |
Emission nebula |
|
 |
IC 2944 |
142 ly (44 pc)[57][58] |
Emission nebula |
|
 |
Eagle Nebula |
140 ly (43 pc)[59] |
H II region |
Part of another diffuse nebula IC 4703. |
 |
Rosette Nebula |
130 ly (40 pc)[60] |
H II region |
Only 36 stars were known to be in this nebula but the Chandra telescope increased the number of known stars to 160. |
 |
Lagoon Nebula |
110 ly (34 pc)[61] |
H II region |
|
 |
Veil Nebula |
100–130 ly (31–40 pc)[62] |
Supernova remnant |
Located in the Cygnus Loop |
 |
NGC 3576 |
100 ly (31 pc)[63] |
Emission nebula |
|
 |
N41 |
100 ly (31 pc)[64] |
Emission nebula |
|
|
The following well-known nebulae are listed for the purpose of comparison. |
 |
Orion Nebula |
20 ly (6.132 pc)[65] |
Diffuse Nebula |
The closest major star formation region to Earth.[66] |
 |
Crab Nebula |
11 ly (3.4 pc)[67] |
Supernova remnant |
The remnant of a supernova that occurred in 1054 AD.[68] |
 |
Bubble Nebula |
6-10 ly (1.84-3.066 pc) |
Emission nebula |
|
 |
Helix Nebula |
5.74 ly (1.76 pc)[72] |
Emission nebula |
|
 |
Eightburst Nebula |
0.8 ly (0.2453 pc)[73] |
Emission nebula |
|
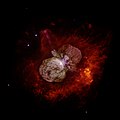 |
Homunculus Nebula |
0.58 ly (0.1778 pc) [74] |
Emission nebula |
Surrounds the star system Eta Carinae. |
 |
Stingray Nebula |
0.16 ly (0.049 pc)[75] |
Emission nebula |
One of the smallest nebulae. |



















































