Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Lithium iodide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
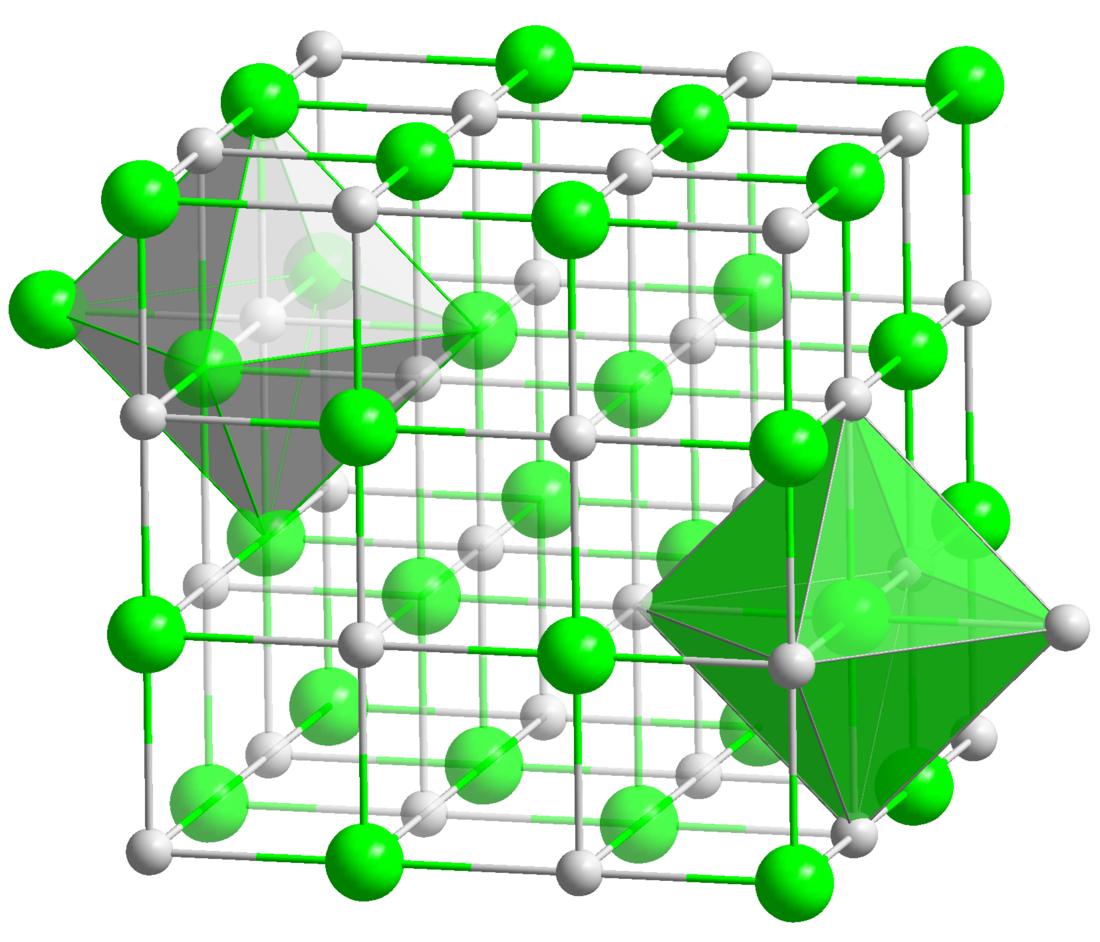
Lithium iodide, or LiI, is a compound of lithium and iodine. When exposed to air, it becomes yellow in color, due to the oxidation of iodide to iodine.[2] It crystallizes in the NaCl motif.[3] It can participate in various hydrates.[4]
Remove ads
Applications

Lithium iodide is used as a solid-state electrolyte for high-temperature batteries. It is also the standard electrolyte in artificial pacemakers[6] due to the long cycle life it enables.[7] The solid is used as a phosphor for neutron detection.[8] It is also used, in a complex with Iodine, in the electrolyte of dye-sensitized solar cells.
In organic synthesis, LiI is useful for cleaving C-O bonds. For example, it can be used to convert methyl esters to carboxylic acids:[9]
- RCO2CH3 + LiI → RCO2Li + CH3I
Similar reactions apply to epoxides and aziridines.
Lithium iodide was used as a radiocontrast agent for CT scans. Its use was discontinued due to renal toxicity. Inorganic iodine solutions suffered from hyperosmolarity and high viscosities. Current iodinated contrast agents are organoiodine compounds.[10]
It is also useful in MALDI imaging mass spectrometry of lipids by adding lithium salts to the matrix solution.[11]
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads