Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
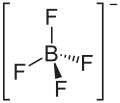
Lithium tetrafluoroborate
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Lithium tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with the formula LiBF4. It is a white crystalline powder. It has been extensively tested for use in commercial secondary batteries, an application that exploits its high solubility in nonpolar solvents.[2]
Remove ads
Applications
Although BF4− has high ionic mobility, solutions of its Li+ salt are less conductive than other less associated salts.[2] As an electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries, LiBF4 offers some advantages relative to the more common LiPF6. It exhibits greater thermal stability[3] and moisture tolerance.[4] For example, LiBF4 can tolerate a moisture content up to 620 ppm at room temperature whereas LiPF6 readily hydrolyzes into toxic POF3 and HF gases, often destroying the battery's electrode materials. Disadvantages of the electrolyte include a relatively low conductivity and difficulties forming a stable solid electrolyte interface with graphite electrodes.
Remove ads
Thermal stability
Because LiBF4 and other alkali-metal salts thermally decompose to evolve boron trifluoride, the salt is commonly used as a convenient source of the chemical at the laboratory scale:[5]
Production
LiBF4 is a byproduct in the industrial synthesis of diborane:[5][6]
LiBF4 can also be synthesized from LiF and BF3 in an appropriate solvent that is resistant to fluorination by BF3 (e.g. HF, BrF3, or liquified SO2):[5]
- LiF + BF3 → LiBF4
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads