Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
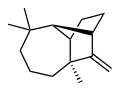
Longifolene
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Longifolene is a common sesquiterpene. It is an oily liquid hydrocarbon found primarily in the high-boiling fraction of certain pine resins. The name is derived from that of a pine species from which the compound was isolated.[1] It is a tricyclic chiral molecule. The enantiomer commonly found in pines and other higher plants exhibits a positive optical rotation of +42.73°. The other enantiomer (optical rotation −42.73°) is found in small amounts in certain fungi and liverworts.
Remove ads
Occurrence
Terpentine obtained from Pinus longifolia (obsolete name for Pinus roxburghii Sarg.) contains as much as 20% of longifolene.[2]
Longifolene is also one of two most abundant aroma constituents of lapsang souchong tea, because the tea is smoked over pinewood fires.[3]
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of longifolene begins with farnesyl diphosphate (1) (also called farnesyl pyrophosphate) by means of a cationic polycyclization cascade. Loss of the pyrophosphate group and cyclization by the distal alkene gives intermediate 3, which by means of a 1,3-hydride shift gives intermediate 4. After two additional cyclizations, intermediate 6 produces longifolene by a 1,2-alkyl migration.

Remove ads
Synthesis and related chemistry
The laboratory characterization and synthesis of longifolene has long attracted attention.[4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11]
 |
| Longifolene total synthesis by Corey |
|---|
It reacts with borane to give the derivative dilongifolylborane, which is a chiral hydroborating agent.[12]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads