Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
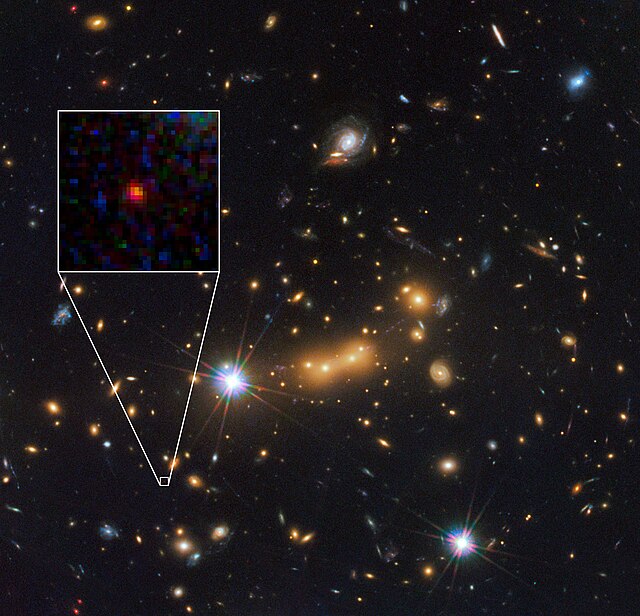
MACS0647-JD
One of the farthest known galaxies from the Earth in the constellation Camelopardalis From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
MACS0647-JD is a galaxy with a spectroscopic redshift of z = 10.17, equivalent to a light travel distance of 13.34 billion light-years (4 billion parsecs). It formed about 460 million years after the Big Bang.[2]
Remove ads
Details
Summarize
Perspective
JD refers to J-band Dropout – the galaxy was not detected in the so-called J-band (F125W), nor in 14 bluer Hubble filters. It only appeared in the two reddest filters (F140W and F160W).
It is less than 600 light-years wide, and contains roughly a billion stars.
The galaxy was discovered with the help of Cluster Lensing And Supernova survey with Hubble (CLASH), which uses massive galaxy clusters as cosmic telescopes to magnify distant galaxies behind them, an effect called gravitational lensing. Observations were recorded by the Wide Field Camera 3 on the Hubble Space Telescope,[4] with support from the Spitzer Space Telescope.[5]
The location of the galaxy is in the constellation Camelopardalis, which is also the location of the gravitational lensing cluster that helped discover this galaxy: MACSJ0647+7015 at z = 0.591.[6]
MACS0647-JD was announced in November 2012, but by the next month UDFj-39546284, which was previously thought to be z = 10.3, was said to be at z = 11.9,[7] although more recent analyses have suggested the latter is likely to be at a lower redshift.[8]
Infrared NIRCam imaging of MACS0647-JD by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in September 2022 determined a photometric redshift of 10.6±0.3, in agreement with the previous Hubble estimate. Additional spectroscopic observations by JWST will be needed to accurately confirm the redshift of MACS0647-JD.[1]

Remove ads
Spectroscopy by JWST
NIRCam and NIRSpec observations of MACS0647-JD were performed in 2023 by the James Webb space telescope.
The massive gravity of the MACS0647 galaxy cluster acts as a cosmic lens to bend and magnify the light from the more distant MACS0647-JD galactic system. Because of this gravitational lensing of the massive galaxy cluster MACS0647, the image of MACS0647-JD appears in three separate locations: JD1, JD2, and JD3. The three lensed images are magnified by factors of eight, five and two, respectively.
The NIRCam imaging observations were able to spatially resolve the galaxy MACS0647-JD into two components A and B.
Spectroscopy of component A yields a spectroscopic redshift of z = 10.17 based on 7 resolve emission lines in the rest-frame ultraviolet (UV) and blue optical: CIII] λλ 1907,1909, [O II] λ3727, [Ne III] λ3869, [Ne III] λ3968, Hδ λ4101, Hγ λ4340, et [O III] λ4363.[2]
The MACS0647-JD galaxy, given its spectral shift, is therefore observed just 460 million years after the Big Bang.
MACS0647-JD has a stellar mass log(M⋆/ M⊙) = 8.1 ± 0.3, which is equivalent to 126 million solar masses.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads