Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
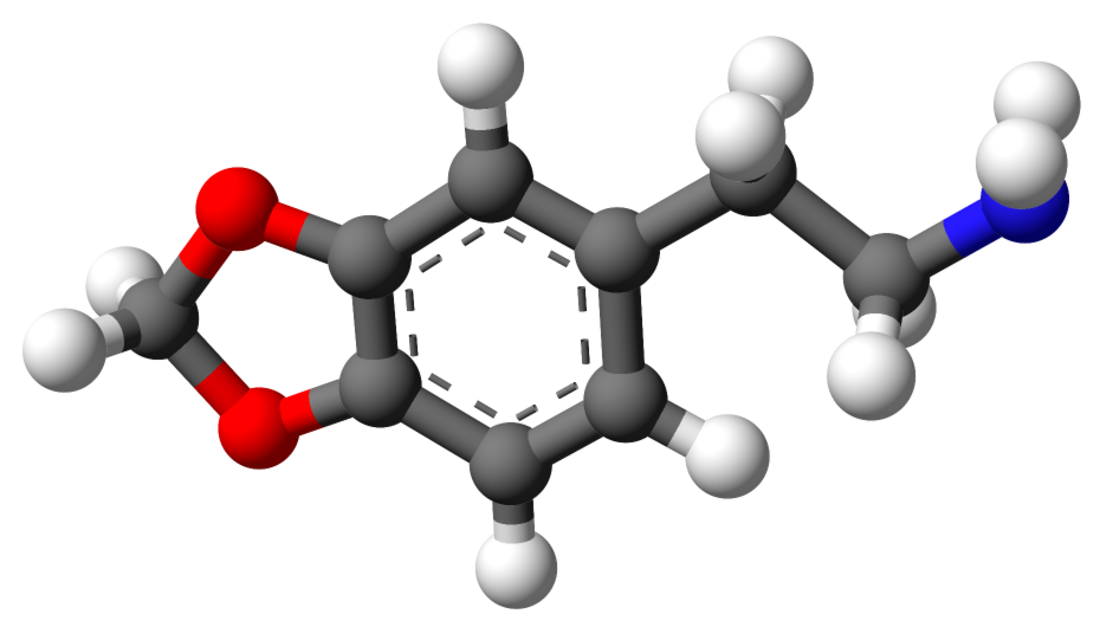
3,4-Methylenedioxyphenethylamine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
MDPEA, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxyphenethylamine or as homopiperonylamine, is a possible psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine and methylenedioxyphenethylamine families.[2] It is the 3,4-methylenedioxy derivative of phenethylamine (PEA).[2] The drug is structurally related to 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), but lacks the methyl group at the α carbon.[2] It is a key parent compound of a large group of compounds known as entactogens such as MDMA ("ecstasy").[2]
Remove ads
Use and effects
According to Alexander Shulgin in his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved), MDPEA was inactive at doses of up to 300 mg orally.[2] This is likely because of extensive first-pass metabolism by the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO).[2] However, if MDPEA were either used in high enough of doses (e.g., 1–2 grams), or in combination with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), it is probable that it would become active, though it would likely have a relatively short duration.[citation needed] This idea is similar in concept to the use of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) inhibitors to augment dimethyltryptamine (DMT) as in ayahuasca[3] and of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitors to potentiate phenethylamine (PEA).[4][5]
Besides being evaluated by Shulgin, MDPEA was studied at Edgewood Arsenal in the 1950s and was administered to humans at doses of up to 5.0 mg/kg (350 mg for a 70-kg person) by intravenous injection, although the results of these tests do not seem to have been released.[6]
Remove ads
Interactions
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
MDPEA produces sympathomimetic effects when administered intravenously at sufficiently high doses in dogs.[7][8] It was about half as potent in this regard as PEA.[7][8] The effects and toxicity of MDPEA in various animal species via intravenous injection have been studied and described.[6]
Chemistry
Properties
Analogues
Analogues of MDPEA include 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylphenethylamine (MDMPEA), lophophine (5-methoxy-MDPEA), mescaline (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine), 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), and 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine (MDMA), among others.[2]
History
MDPEA was first described in the scientific literature by Gordon Alles by 1959.[7][8] It was studied at Edgewood Arsenal under the code name EA-1297 in the 1950s, being administered by humans in 1952.[2][6] The drug was described by Alexander Shulgin in his 1991 book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved).[2]
Society and culture
Legal status
Poland
MDPEA is a controlled substance in Poland.[1]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads