Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Main Himalayan Thrust
Geological feature From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
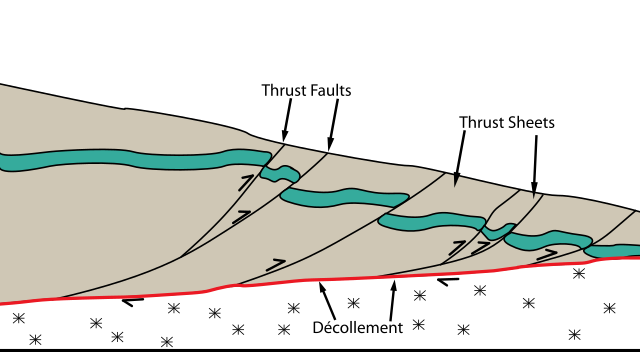
The Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT) is a décollement under the Himalaya Range. This thrust fault follows a northwest-southeast strike, reminiscent of an arc, and gently dips about 10 degrees towards the north, beneath the region. It is the largest active continental megathrust[1] fault in the world.[2]

Remove ads
Overview
Summarize
Perspective
The MHT accommodates crustal shortening of India and Eurasia as a result of the ongoing collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates.[3] The MHT absorbs around 20mm/yr of slip, nearly half of the total convergence rate. This slip can be released from small-scale earthquakes and some plastic deformation, but the MHT still accumulates a deficit of moment of 6.6×1019 Nm/yr. The MHT also remains locked with the overlying Eurasian plate from its surface expression to the front of the higher Himalayas, nearly 100 kilometres away. This locking mechanism combined with the rapid accumulation of deficit of moment are concerning, as some professionals estimate that earthquakes up to the size of 8.9 on the Richter scale could be in order for regions such as western Nepal. Earthquakes of this magnitude are estimated to have a return period of over 1000 years in this region.[4] Deformation of the crust is also accommodated along splay structures including the Main Frontal Thrust (MFT), Main Boundary Thrust (MBT), Main Central Thrust (MCT), and possibly the South Tibetan Detachment. The MHT is the root detachment of these splays. Currently, the MFT and MHT accounts for almost the entire rate of convergence (15–21 mm/yr).[5][6] This fault defines where the Indian subcontinent is underthrust beneath the Himalayan orogenic wedge.
Remove ads
Seismic hazard
The MHT is a known hazard and potential source for large earthquakes of magnitude 8.0 or greater. The MHT is also associated with other large 20th-century earthquakes such as the 1934 Nepal–India earthquake and the 1950 Assam–Tibet earthquake. Within the last thousand years, multiple earthquakes have occurred with magnitudes of at least Mw 8.0 as deduced by paleoseismology. Michel et al. (2021) suggested the maximum magnitude possible on the MHT to be Mw 8.7 with a recurrence interval of 200 years.[7]
In April 2015, a section of the MHT produced a blind rupture earthquake, killing nearly 9,000 people.[8][9] Researchers who published their findings in Nature Geoscience revealed that the Mw 7.8 earthquake failed to rupture towards the surface, thus still leaving the possibility of future large earthquakes. Since the rupture ceased 11 km (6.8 mi) beneath the Kathmandu region, a shallow section of the MHT south of the region remains unruptured and could produce an earthquake of comparable size. The research lead, J. R. Elliott, says such an earthquake could be more devastating because of its shallowness.[10]
Remove ads
Associated seismicity
Summarize
Perspective
The Main Himalayan Thrust and its splay branches has been the source of numerous earthquakes, including some that are indirectly related.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
