Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
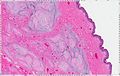
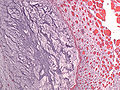
Myxoma
Myxoid tumor of primitive connective tissue From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A myxoma (New Latin from Greek muxa 'mucus') is a myxoid tumor of primitive connective tissue.[1] It is most commonly found in the heart (and is the most common primary tumor of the heart in adults) but can also occur in other locations.
Remove ads
Types
Summarize
Perspective
Table below:[2]
1.^ SMA, smooth muscle actin. 2.^ MSA, muscle-specific actin. 3.^ EMA, epithelial membrane antigen.
Remove ads
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms associated with cardiac myxomas are typically due to the effect of the mass of the tumor obstructing the normal flow of blood within the chambers of the heart. Because pedunculated myxomas are somewhat mobile, symptoms may only occur when the patient is in a particular position.
Some symptoms of myxoma may be associated with the release of interleukin 6 (IL-6) by the myxoma.[3][4] High levels of IL-6 may be associated with a higher risk of embolism of the myxoma.[5]
Symptoms of a cardiac myxoma include:[6]
- Dyspnea on exertion
- Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
- Fever
- Weight loss (see cachexia)
- Lightheadedness or syncope (Loss of consciousness)
- Hemoptysis
- Sudden death
- Tachycardia or milder heartrate, i.e. 75–100 cycl/min
Remove ads
Location
Summarize
Perspective

Ocular myxoma
Myxoma is a rare, benign stromal tumor of mesenchymal origin often confused with other conjunctival stromal tumors. Conjunctival myxomas are thought to originate in Tenon's capsule and can masquerade as conjunctival lymphoma, lymphangioma, ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN), or amelanotic melanoma.[7]

Atrial myxoma
Myxomas are usually located in either the left or right atrium of the heart; about 86 percent occur in the left atrium.[8]
Myxomas are typically pedunculated, with a stalk that is attached to the interatrial septum. The most common location for attachment of the stalk is the fossa ovalis region of the interatrial septum.[9]
An atrial myxoma may create an extra heart sound, audible to auscultation just after S2. It is most seen on echocardiography, as a pedunculated mass that is heterogeneous in appearance. A left atrial myxoma will cause an increase in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure.[citation needed]
The differential diagnosis include other cardiac tumors such as lipomas and rhabdomyomas (and rarely teratomas). These other tumors of the heart are typically not pedunculated, however, and are more likely to infiltrate the muscle of the heart. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help non-invasively diagnose cardiac tumors. However, diagnosis usually requires examination of a tissue sample by a pathologist.[citation needed]
Treatment
Myxomas are usually removed surgically. The surgeon removes the myxoma, along with at least 5 surrounding millimeters of atrial septum. The septum is then repaired, using material from the pericardium.[citation needed]
Epidemiology
Cardiac myxomas predominantly appear in females in their 30s to 40s. Myxomas are the most common primary cardiac tumor affecting adults,[9] accounting for one quarter to half of primary cardiac tumors seen in clinical practice.[10]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads