Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
N Scorpii
Star in the constellation of Scorpius From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
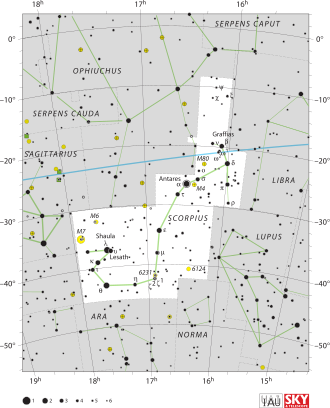
N Scorpii, also known as HD 148703, is a solitary,[14] bluish-white hued star located in the southern constellation Scorpius. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.23, making it readily visible to the naked eye. N Scorpii was initially given the Bayer designation Alpha Normae by Lacaille but it was later moved from Norma to Scorpius.[15] N Scorpii is currently located 550 light years away based on parallax measurements from the Hipparcos satellite and is part of the Upper Scorpius–Centaurus region of the Scorpius–Centaurus association.[16]
N Scorpii has been given several stellar classifications over the years. It has been given the luminosity class of a main sequence star (V),[17] a subgiant (IV),[18] an evolved giant star (III),[19] or a blend between the last two classes (III-IV).[3] It is generally classified as either a B2 or B3 star several times hotter than the Sun. HD 148703 is a candidate β Cephei variable[4] and its variability was first noticed in 1983 by C. Sterken.[20] Further observations were made by Abt et al. (2002) by observing its projected rotational velocity.[21] It was identified as a candidate in 2002 in a survey for non-radial pulsations in B-type stars.[22]
The object has two generally accepted classes: B2 III-IV and B2 IV. It has 7.8 times the mass of the Sun[7] and 6.25 times its size.[8] It has a bolometric luminosity 6,918 times greater than the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 21,877 K.[9] N Scorpii is estimated to be 22 million years old,[7] which is twice the average age of the aforementioned association. Like most hot stars, N Scorpii spins rapidly, having a projected rotational velocity of 70 km/s.[11]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads