Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Nesher Ramla Homo
Extinct population of archaic humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Nesher Ramla Homo group are an extinct population of archaic humans who lived during the Middle Pleistocene in what is now Israel. In 2010, evidence of a tool industry had been discovered during a year of archaeological excavations at the Nesher Ramla site. In 2021, the first Nesher Ramla Homo individual was identified from remains discovered during further excavations.


Remove ads
Taxonomy
Summarize
Perspective
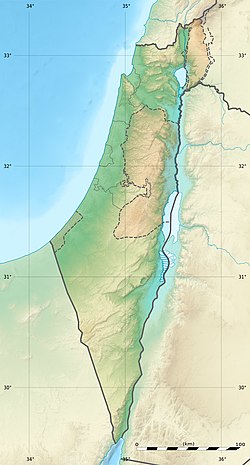
Locations of the Nesher Ramla remains, alongside locations of previously discovered human fossils that a team led by Zaidner in 2021 hypothesised as representing the same group [1]
The Nesher Ramla site was discovered in a karst depression following quarrying from a nearby cement factory. The site was excavated by archaeologists between 2010–2011 and yielded artefacts in archaeological deposits from the Middle Paleolithic that were reported by D. Friesem, Y. Zaidner, and R. Shahack-Gross.[2] Evidence of a lithic industry was found during the excavation. The artefacts from the site contained Levallois tools and lithic cores.[3]
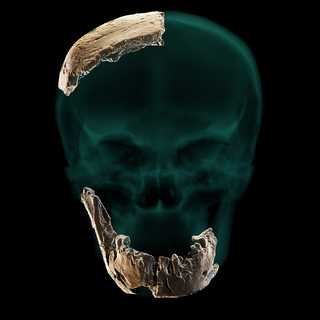
Later excavations led by anthropologist Israel Hershkovitz in 2021 led to the discovery of five pieces of a braincase and a nearly-complete lower jaw. The remains were dated to 140–120 kya, during the Middle Pleistocene.
Hershkovitz speculated that the specimen might be categorised as among the last survivors of a population that would contribute to the Neanderthals and East Asian Homo.[4] Philip Rightmire of Harvard University did not agree with the findings, believing instead that properly, the skull should be categorised as among early Neanderthals. Rightmire also discussed the possibility of a Neanderthal population having migrated to the area from Europe.[5] Yoel Rak of Tel Aviv University stated that the mandible bore characteristics typical of a Neanderthal, and that the specimen itself should be classified as a Neanderthal.[6]
Remove ads
Artefacts
More than 6,000 stone tools were excavated in the fossil-bearing sediment of the site. The Nesher Ramla Homo population mastered stone tool production technologies previously known among Neanderthals and Homo sapiens. The team led by Zaidner interpreted the presence of this tool industry as evidence of cultural interactions between Nesher Ramla populations and Homo sapiens populations.[1]
Gallery
- Video showing the location on a skull of the skullcap fragment dubbed "Nesher Ramla 1"
- Mandible (lower jaw
- Scan of the mandible (lower jaw)
- Levallois flake found at Nesher Ramla
See also
- Denisovan – Extinct species of archaic human from Asia
- Homo longi – Archaic human from China, 146,000 BP
- Homo luzonensis – Archaic human from Luzon, Philippines
- Homo naledi – South African archaic human species
- Homo floresiensis – Extinct small human species found in Flores
- Ayalon Cave from the same area, with unique ecosystem home to food chain based on chemosynthesising bacteria
- Nesher-Ramla hiding complex (1st century BCE-1st c. CE) also discovered within the Nesher quarry
Remove ads
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads