Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
ORF9b
Gene From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
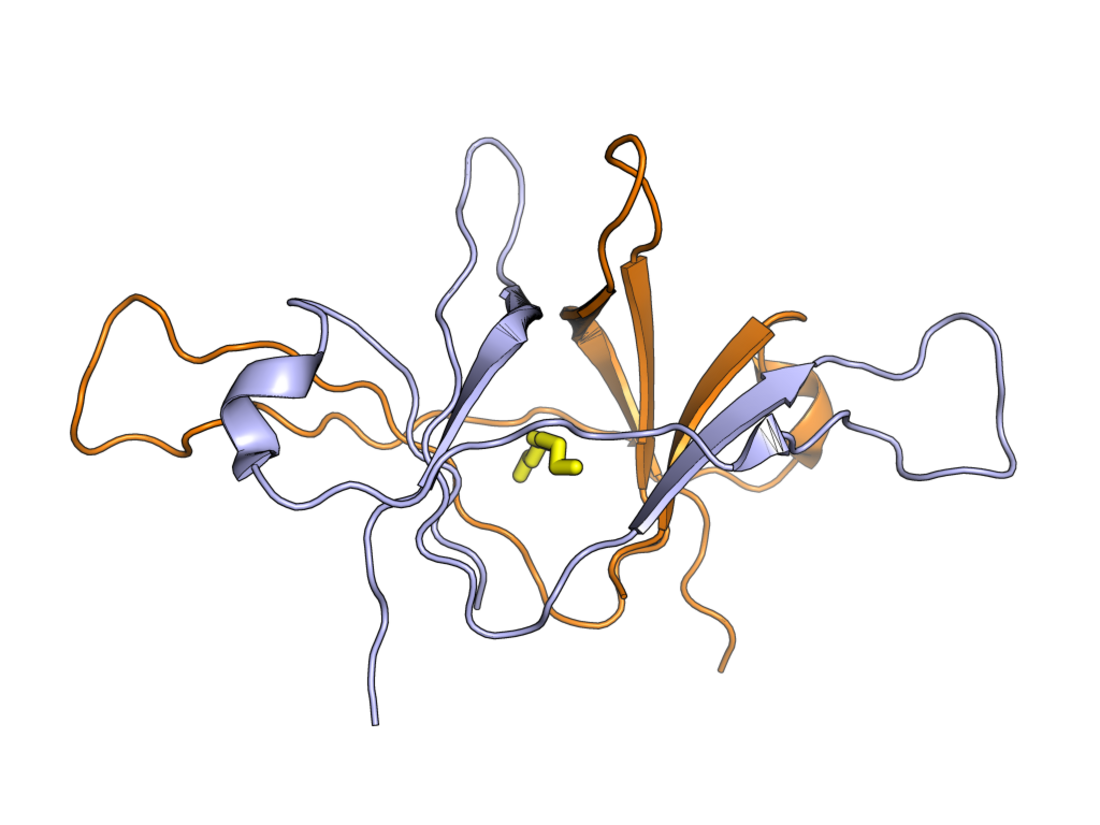
ORF9b (formerly sometimes called ORF13) is a gene that encodes a viral accessory protein in coronaviruses of the subgenus Sarbecovirus, including SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. It is an overlapping gene whose open reading frame is entirely contained within the N gene, which encodes coronavirus nucleocapsid protein.[2][3][4] The encoded protein is 97 amino acid residues long in SARS-CoV[2][3] and 98 in SARS-CoV-2,[4] in both cases forming a protein dimer.
Remove ads
Nomenclature
There has been inconsistency in the nomenclature used for this gene in the scientific literature. In some work on SARS-CoV, it has been referred to as ORF13. It has also sometimes been referred to as ORF9a, resulting in a downstream ORF of 76 codons in SARS-CoV, also overlapping with the N gene, being designated ORF9b. The recommended nomenclature refers to the longer ORF as 9b and the downstream, shorter ORF as ORF9c.[5]
Remove ads
Structure
The ORF9b protein is 97 amino acid residues long in SARS-CoV[2][3] and 98 in SARS-CoV-2.[4] It forms a beta sheet-rich homodimer with a hydrophobic cavity in the center that binds lipids.[2][3][4] The lipid-binding cavity may serve as an unusual mechanism for anchoring the protein to membranes.[1]
A fragment of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF9b protein has been structurally characterized in a protein complex with Tom70 in which ORF9b forms an alpha helix rather than the beta-sheet structure observed in isolation.[6] This fold switching behavior is also consistent with bioinformatics predictions and may also occur for the SARS-CoV homolog.[7]
Remove ads
Expression and localization
ORF9b is one of two overlapping genes fully contained within the open reading frame of the N gene encoding coronavirus nucleocapsid protein, the other being ORF9c. ORF9b is expressed by ribosome leaky scanning from its bicistronic subgenomic RNA.[2][3][8] Unlike its neighbor ORF9c, its length is well conserved in sarbecoviruses and there is strong evidence it is a functional protein-coding gene.[9]
In SARS-CoV, the protein is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)[3] and to intracellular vesicles.[2][1] It does not have a nuclear localization sequence but can enter the cell nucleus by passive diffusion; it does however have a nuclear export sequence for exit from the nucleus.[2][3] In SARS-CoV-2, it is reportedly associated with the mitochondrial membrane.[4]
Function
The function of the ORF9b protein is not well characterized. It is not essential for viral replication.[2]
Viral protein interactions
The ORF9b protein has been reported to interact with a number of other viral proteins, including ORF6, non-structural protein 5, non-structural protein 14, and coronavirus envelope protein.[2] It has been detected in mature SARS-CoV virions and thus may be a minor viral structural protein.[2][3][8]
Host cell effects
The ORF9b protein may be involved in modulating the host's immune system response. The SARS-CoV-2 protein has been reported to suppress interferon response via its interactions with Tom70, a component of the mitochondrial translocase of the outer membrane (TOM) complex.[6][10]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads