Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
P-Hydroxynorephedrine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
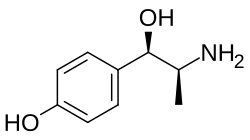
p-Hydroxynorephedrine (PHN or 4-hydroxynorephedrine) is the para-hydroxy analog of norephedrine and an active sympathomimetic metabolite of amphetamine in humans.[1][2] When it occurs as a metabolite of amphetamine, it is produced from both p-hydroxyamphetamine and norephedrine.[2][3][4]
Remove ads
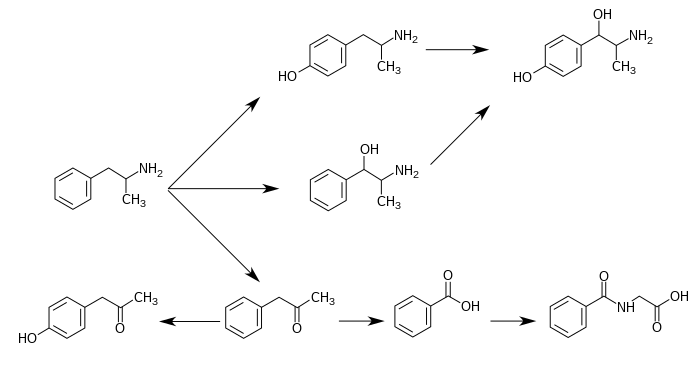
Amphetamine metabolism
Metabolic pathways of amphetamine in humans[sources 1]
|
Remove ads
Notes
- 4-Hydroxyamphetamine has been shown to be metabolized into 4-hydroxynorephedrine by dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH) in vitro and it is presumed to be metabolized similarly in vivo.[6][11] Evidence from studies that measured the effect of serum DBH concentrations on 4-hydroxyamphetamine metabolism in humans suggests that a different enzyme may mediate the conversion of 4-hydroxyamphetamine to 4-hydroxynorephedrine;[11][13] however, other evidence from animal studies suggests that this reaction is catalyzed by DBH in synaptic vesicles within noradrenergic neurons in the brain.[14][15]
Remove ads
See also
References
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads