Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
DJ-1
Protein-coding gene found in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
DJ1, also known as Parkinson disease protein 7, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PARK7 gene.[5] Its weak glyoxalase activity has been verified by many labs,[6][7] however the reported protein deglycase activity is likely to be an artifact stemming from DJ-1's ability to destroy free methylglyoxal.
Remove ads
Structure
Gene
The gene PARK7, also known as DJ-1, encodes a protein of the peptidase C56 family. The human gene PARK7 has 8 exons and locates at chromosome band 1p36.23.[5]
Protein
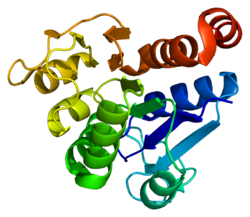
The human protein DJ-1 is 20 kDa in size and composed of 189 amino acids with seven β-strands and nine α-helices in total and is present as a dimer.[8][9][10] It belongs to the peptidase C56 family of proteins.
The protein structures of human protein DJ-1, Escherichia coli chaperone Hsp31, YhbO, and YajL and an Archaea protease are evolutionarily conserved.[11]
Remove ads
Function
Summarize
Perspective
DJ-1 was shown to prevent metabolite and protein damage caused by a glycolytic metabolite.[12] This metabolite has been suggested[12] and confirmed[13] to be cyclic 3-phosphoglycerate (or cyclic 3-phosphoglyceric anhydride). Catalytic efficiency of DJ-1 as a hydrolase of cyclic 3-phosphoglyceric anhydride is 10,000 times higher than other reported enzymatic activities of DJ-1.[13]
Under an oxidative condition, DJ-1 inhibits the aggregation of α-synuclein via its chaperone activity,[14][15] thus functioning as a redox-sensitive chaperone and as a sensor for oxidative stress. Accordingly, DJ-1 apparently protects neurons against oxidative stress and cell death.[5] In parallel, protein DJ-1 acts as a positive regulator of androgen receptor-dependent transcription. DJ-1 is expressed in both the neural retina and retinal pigment epithelium of mammals, where it exerts a neuroprotective role against oxidative stress under both physiological and pathological conditions.[16][17]
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) has been shown to reduce the self-oxidation of the DJ-1 protein, an early step in the onset of some forms of Parkinson's disease.[18]
Functional DJ-1 protein has been shown to bind metals and protect against metal-induced cytotoxicity from copper and mercury.[19]
DJ-1/PARK7 and its bacterial homologs: Hsp31, YhbO, and YajL can repair methylglyoxal and glyoxal glycated nucleotides.[20] Guanine, either in the form of a free nucleotide or as a nucleotide incorporated into nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), if glycated, can be repaired by DJ-1/PARK7.[20] Deglycase-deficient bacterial mutants with reduced ability to repair glycated bases in DNA show strong mutator phenotypes.[20] A follow up study confirmed that DJ-1 reduces levels of reversible adducts of methylglyoxal with guanine and cysteine in vitro. However, since the steady-state kinetics of DJ-1 acting on reversible hemithioacetal substrates are fitted adequately with a computational kinetic model that requires only a DJ-1 glyoxalase activity, it was concluded that deglycation is an apparent rather than a true activity of DJ-1.[21]
DNA repair
DJ-1 is a DNA damage response protein that is recruited to sites of DNA damage where it participates in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks through the processes of non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination.[22] Evidence for a linkage between DNA damage and Parkinson's disease has been reported for decades.[22] Recently evidence has been presented that defective DNA repair is linked specifically to DJ-1 mutation, and thus DJ-1 mutation likely contributes to Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.[22]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
Defects in this gene are the cause of autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinson's disease 7.[5][23]
Interactions
PARK7 has been shown to interact with:
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads