Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Papilloma
Medical condition From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
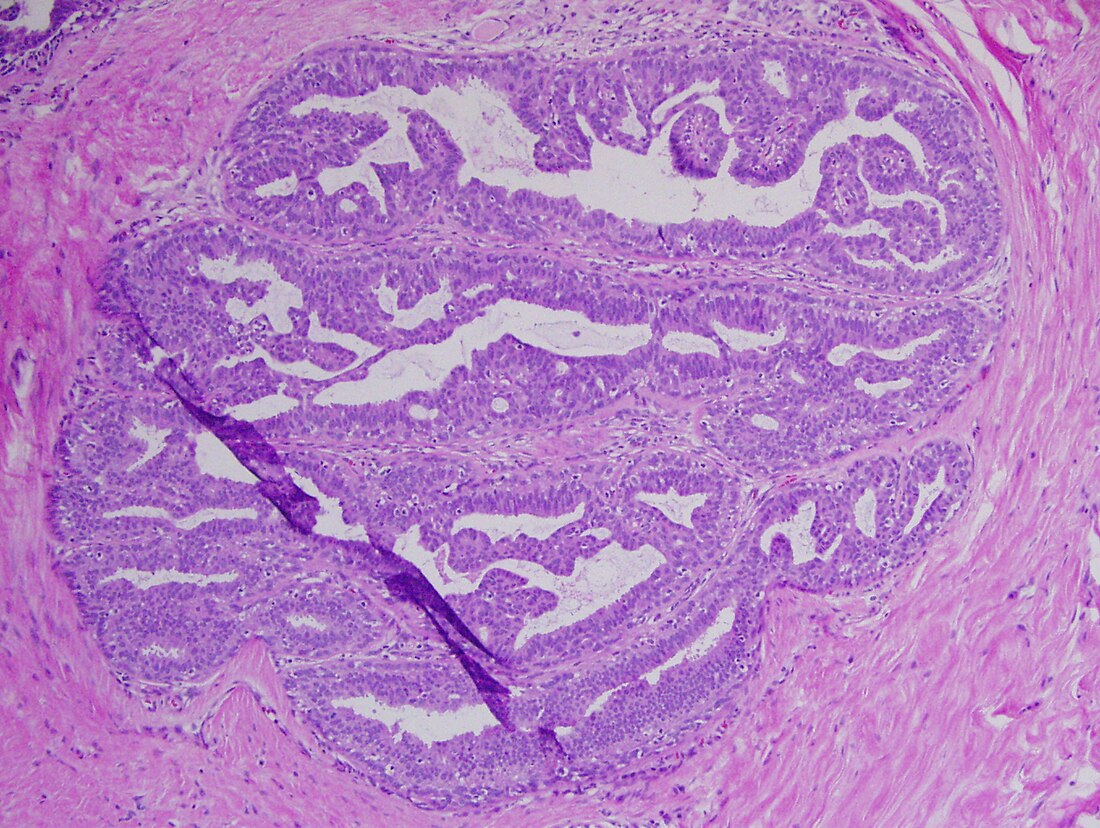
A papilloma (plural papillomas or papillomata) (papillo- + -oma) is a benign epithelial tumor[1] growing exophytically (outwardly projecting) in nipple-like and often finger-like fronds. In this context, papilla refers to the projection created by the tumor, not a tumor on an already existing papilla (such as the nipple).
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2013) |
When used without context, it frequently refers to infections (squamous cell papilloma) caused by a human papillomavirus (HPV), most commonly in the form of warts. Human papillomavirus infections are a major cause of cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer, penile cancer, anal cancer, and HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers.[2][3][4][5][6] Most viral warts are caused by human papillomavirus infection (HPV).[7] There are nearly 200 distinct human papillomaviruses (HPVs),[4] and many types are carcinogenic.[2][3] There are, however, a number of other conditions that cause papillomas, and in many cases the cause may be uncertain.
Remove ads
Signs and symptoms
HPV6 pedunculated papilloma behind the uvula, and HPV6 sessile (flat) papilloma next to the uvula
A benign papillomatous tumor is derived from epithelium, with cauliflower-like projections that arise from the mucosal surface. It may appear white or normal-colored. It may be pedunculated or sessile. The typical size range is 1–5 cm. Neither sex is significantly more likely to develop papillomas. The most common site is the palate–uvula area, followed by tongue and lips. Durations range from weeks to 10 or more years.
Remove ads
Presence of HPV
Immunoperoxidase stains have identified antigens of the human papillomavirus (HPV) types 6 and 11 in approximately 50% of cases of squamous cell papilloma.[8]
Prognosis
There is no evidence that papilloma tissue is itself premalignant, despite HPV's frequent connection to later development of cancers.[citation needed]
Differential diagnosis
Other conditions which may present similar symptoms (and which are also caused by HPV infections) include:
- Intraoral verruca vulgaris (common warts)
- Condyloma acuminatum (genital warts)
- Focal epithelial hyperplasia (oral warts)
Differentiation is done accurately by microscopic examination.
Treatment
With conservative surgical excision, recurrence is rare.[citation needed]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads