Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Prostitution in the United States
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
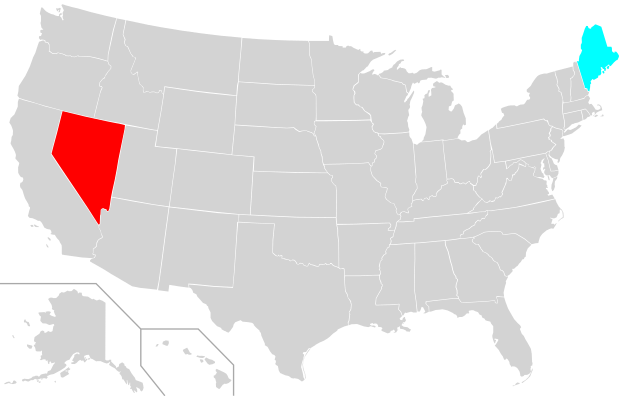
Prostitution is illegal in every US state except Nevada, where licensed brothels are permitted in some counties, and Maine, where selling sex is decriminalized but buying sex is illegal. Prostitution nonetheless occurs in all states. A 2008 report by the National Institute of Justice estimated that 15–20 percent of men in the US have paid for sex.
The Constitution does not grant the federal government a general power to regulate commercial sex, and such regulation is therefore, per the Tenth Amendment, exclusively the domain of the states except as it pertains to interstate commerce, which Congress may regulate with laws such as the Mann Act. In most states, prostitution is considered a misdemeanor in the category of public-order crime. Prostitution was once considered a vagrancy crime.
Nevada is the only state that allows legal prostitution in the form of regulated brothels, the terms of which are stipulated in the Nevada Revised Statutes. As of 2023, there were 19 licensed brothels in Nevada. Of the ten Nevada counties that theoretically allow brothel prostitution, only six contain active licensed brothels; the remaining four have none. Prostitution is illegal in all forms in the remaining seven counties, including Clark (which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area) and Washoe (which contains Reno).
In Maine, prostitution is partially decriminalized following the Nordic model. In 2023, the state enacted a law that decriminalized the act of prostitution (which had previously been a misdemeanor) while elevating the crime of soliciting and purchasing of sex from a misdemeanor to a felony.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
18th century
Some of the women in the American Revolution who followed the Continental Army served the soldiers and officers as sexual partners. Prostitutes were a worrisome presence to army leadership, particularly because of the possible spread of venereal diseases (in modern terms, sexually transmitted infection or STI).
19th century
In the 19th century, parlor house brothels catered to upper class clientele, while bawdy houses catered to the lower class. At concert saloons, men could eat, listen to music, watch a fight, or pay women for sex. Over 200 brothels existed in lower Manhattan. Prostitution was illegal under the vagrancy laws, but was not well-enforced by police and city officials, who were bribed by brothel owners and madams. Attempts to regulate prostitution were struck down on the grounds that regulation would be contrary to the public good.
While official acts of regulation were being struck down, there were those of a more religious perspective who took attempts to reform prostitution into their own hands. The Magdalen Society was an organization in the 1800s that sought to take prostitutes of the streets and turn them into respectable women. Motivated by the concern that Philadelphia was falling into social disorder, the society founded an asylum to take women off of the streets.[1] 138 women sought refuge here in the years between 1807 and 1820, and were placed with religious families who taught them how to read and attempted to convert them into "respectable women". Most of the women who entered the asylum stayed for only two and a half months, using the open doors as a temporary place to live off the street.[1] The biggest success story of the society was that of Elizabeth Ogden, a woman who was deemed reformed and opened a school for children.[2]
The gold rush profits of the 1840s to 1900 attracted gambling, crime, saloons, and prostitution to the mining towns of the wild west. A brothel-keeper, Julia Bulette, who was active in the mining town of Virginia City, Nevada, was murdered in 1867. Thirty years before, in 1836, the New York City courtesan Helen Jewett was murdered by one of her customers, gaining prostitution considerable attention. The Lorette Ordinance of 1857 prohibited prostitution on the first floor of buildings in New Orleans.[3] Nevertheless, prostitution continued to grow rapidly in the U.S. and became a $6.3 million business in 1858, larger than the shipping and brewing industries combined.
Some army officers encouraged the presence of prostitutes during the Civil War to keep troop morale high. On August 20, 1863, U.S. military commander Brig. General Robert S. Granger legalized prostitution in Nashville, Tennessee, in an effort to curb venereal disease among Union soldiers. The move was successful and venereal disease rates fell from forty percent to just four percent due to a stringent program of health checks that required all prostitutes to register and be examined by a board certified physician every two weeks, for which they were charged a five dollar registration fee plus 50 cents per exam.[4]

By the time of the U.S. Civil War, Washington's Pennsylvania Avenue had become a disreputable slum known as Murder Bay, home to an extensive criminal underclass and numerous brothels. So many prostitutes took up residence there to serve the needs of General Joseph Hooker's Army of the Potomac that the area became known as "Hooker's Division". (It is a popular legend that the slang term "hooker" originated from this period. However, the term "hooker" was associated with prostitutes well before General Hooker's rise to popularity.[5]) Two blocks between Pennsylvania and Missouri Avenues became home to such expensive brothels that it was known as "Marble Alley."[6]
In 1873, Anthony Comstock created the New York Society for the Suppression of Vice, an institution dedicated to supervising the morality of the public. Comstock successfully influenced the United States Congress to pass the Comstock Law, which prohibited the delivery or transport of "obscene, lewd, or lascivious" material and birth control information. In 1875, Congress passed the Page Act of 1875, which made it illegal to transport women into the nation to be used as prostitutes.[7]
In the late 19th century, newspapers reported that 65,000 white slaves existed. Around 1890, the term "red-light district" was first recorded in the United States. From 1890 to 1982, the Dumas Brothel in Montana was America's longest-running house of prostitution.

New Orleans city alderman Sidney Story wrote an ordinance in 1897 to regulate and limit prostitution to one small area of the city, "The District", where all prostitutes in New Orleans were required to live and work. The District, which was nicknamed Storyville, became the best known area for prostitution in the nation. Storyville at its peak had some 1,500 prostitutes and 200 brothels.
Japanese girls and women worked as Karayuki-san prostitutes on the west coast of the United States and provided sexual services to Chinese, white, and Japanese men.[8][9] Japanese prostitutes also worked as barmaids.[10] The Issei Japanese American Bunshiro Tazuma said "At the age of 18... I started... work as a dishwasher at a hotel in Spokane. Later I became a [railroad?] cook and went to North Dakota, South Dakota, Idaho, Oregon, Washington, and even as far as to Minnesota and Alaska... To my surprise I found at least two to six Japanese prostitutes in every town where I went between Seattle and St. Paul, a range of two thousand miles. Even when I went to Alaska to... a salmon cannery in 1908, I was surprised to see from two to five or six in such towns as Ketchikan, Juneau, Wrangell, Sitka, and Skagway.”[11]
20th century
Legal measures and morality campaigns

In 1908, the government founded the Bureau of Investigation (BOI; from 1935, the FBI) to investigate "white slavery" by interviewing brothel employees to discover if they had been kidnapped. Out of 1,106 prostitutes interviewed in one city, six said they were victims of white slavery. The White-Slave Traffic Act (Mann Act) of 1910 prohibited so-called white slavery. It also banned the interstate transportation of women for "immoral purposes". Its primary stated intent was to address prostitution and perceived immorality. The Supreme Court later included consensual debauchery, adultery, and polygamy under "immoral purposes". Prior to World War I, there were few laws criminalizing prostitutes or the act of prostitution.[12]
During World War I, the U.S. government developed a public health program called the American Plan that authorized the military to arrest any woman within five miles of a military cantonment. If found infected, a woman could be sentenced to a hospital or a "farm colony" until cured. By the end of the war 15,520 prostitutes had been imprisoned, the majority never being medically hospitalized.[13]
In 1918, the Chamberlain–Kahn Act, which implemented the American Plan,[14] empowered the government to quarantine any woman suspected of having venereal disease. A medical examination was required, and if it revealed the presence of VD, the discovery could be considered proof of prostitution. The purpose of this law was to prevent the spread of venereal diseases among U.S. soldiers.[15] During World War I, Storyville, a district in New Orleans where prostitution was permitted, was shut down to prevent VD transmission to soldiers in nearby army and navy camps.[16]
On January 25, 1917, an anti-prostitution drive in San Francisco attracted huge crowds to public meetings. One meeting was attended by 7,000 people while an additional 20,000 were kept out for lack of room. At a conference with Reverend Paul Smith, an outspoken foe of prostitution, 300 prostitutes made a plea for toleration, explaining that they had been forced into the practice by poverty. When Smith asked if they would take other work at $8 to $10 a week, the ladies laughed derisively, which lost them public sympathy. The police closed about 200 houses of prostitution shortly thereafter.[17]
The National Venereal Disease Control Act, which became effective July 1, 1938, authorized the appropriation of federal funds to assist the states in combating venereal diseases. Appropriations under this act were doubled after the United States entered World War II.
The May Act, which became law in June 1941, was intended to prevent prostitution in restricted zones around military bases. It was invoked chiefly during wartime. See World War II U.S. Military Sex Education.
In Mortensen vs. United States, a 1944 case, the Supreme Court ruled that prostitutes could travel across state lines if the purpose of the travel was not for prostitution.[18]
Later decades
Conditions for sex trade workers changed considerably in the 1960s. The combined oral contraceptive pill was first approved in 1960 for contraceptive use in the United States. "The Pill" helped prostitutes prevent pregnancy.
In 1967, New York City eliminated license requirements for massage parlors. Many massage parlors became brothels.[19] In 1970, Nevada began regulation of houses of prostitution. In 1971, the Mustang Ranch became Nevada's first licensed brothel, eventually leading to the legalization of brothel prostitution in 10 of 17 counties within the state. In time, Mustang Ranch became Nevada's largest brothel, with more revenue than all other legal Nevada brothels combined. By World War II, prostitutes had increasingly begun working as call girls.
In 1971, the New York madam Xaviera Hollander wrote The Happy Hooker: My Own Story, a book that was notable at the time for its frankness and was considered a landmark of positive writing about sex. An early forerunner (1920s-1930s) of Xaviera Hollander's, both as a madam and author, was Polly Adler, whose bestselling book, A House Is Not a Home, was eventually adapted as a film of the same name. Carol Leigh, a prostitute's rights activist known as the "Scarlot Harlot," coined the term "Sex worker" in 1978. That same year, the Broadway musical The Best Little Whorehouse in Texas opened. It was based on the real-life Texas Chicken Ranch brothel. The play was the basis for the 1982 film starring Dolly Parton and Burt Reynolds.
COYOTE, formed in 1973, was the first sex workers' rights group in the country. Other sex workers movements later formed, such as FLOP, HIRE, and PUMA.[20]

In 1997, "Hollywood Madam" Heidi Fleiss was convicted in connection with her prostitution ring on charges including pandering and tax evasion. Her ring had had numerous wealthy clients. Her original three-year sentence prompted widespread outrage at the harshness of the punishment contrasted with the fact that her customers were not punished. Earlier, in the 1980s, a member of Philadelphia's social elite, Sydney Biddle Barrows was revealed as a madam in New York City. She became known as the Mayflower Madam.
In 1990, U.S. Representative Barney Frank (D-MA) admitted to paying for sex in 1989. The House of Representatives voted to reprimand him.[21]
21st century
Ted Haggard, former leader of the National Association of Evangelicals, resigned in 2006 after he was accused of soliciting homosexual sex and methamphetamine.[22]
Randall L. Tobias, former Director of U.S. Foreign Assistance and U.S. Agency for International Development Administrator, resigned in 2007 after being accused of patronizing a Washington escort service.[23]
In 2007, U.S. Senator from Louisiana David Vitter acknowledged past transgressions after his name was listed as a client of "D.C. Madam" Deborah Jeane Palfrey's prostitution service in Washington.[24]
Eliot Spitzer resigned as governor of New York in 2008 amid threats of impeachment after news reports alleged he was a client of an international prostitution ring.[25]
In 2009, Rhode Island signed a bill into law making prostitution a misdemeanor. Prior to the passage of this law, between 1980 and 2009, Rhode Island had been the only U.S. state where prostitution was decriminalized, (though this was limited to prostitution conducted indoors).[26] (See Prostitution in Rhode Island).
In 2014, due Puerto Rico's stagnant economy, the government there considered legalizing prostitution.[27][28] In 2018, economist Robin Hanson suggested that the legalization of prostitution might solve the problem of inceldom, an ideology responsible for numerous outbreaks of violence and mass killings throughout the United States.[29][30][31]
On April 11, 2018, the United States Congress passed the Stop Enabling Sex Traffickers Act, commonly known as FOSTA-SESTA, which imposed severe penalties on online platforms that facilitated illicit sex work. The effectiveness of the bill has come into question as it has purportedly endangered sex workers and has been ineffective in stopping sex traffickers.[32] Prior to the Act's going into effect, the Department of Justice seized the website Backpage and charged its founders with money laundering and promotion of prostitution, contributing to major destabilization in the lives of people who trade sex.
On June 16, 2021, Texas governor Greg Abbott signed HB1540, a law that makes paying for sex in the state of Texas a felony punishable by up to two years in prison for a first-time offense, with enhanced penalties for recruitment from child care or treatment facilities. Texas is the first state in the United States to make the buying of sex a felony. This law represents a shift from the traditional approach, as it targets buyers of sexual services instead of sellers. State representative Senfronia Thompson (D-Houston), the author of the bill, said "We know the demand is the driving force behind human sex trafficking. If we can curb or stamp out the demand end of it, then we can save the lives of numerous persons." The law went into effect on September 1, 2021.[33]
On June 26, 2023, the state of Maine enacted a law that partially decriminalized the act of prostitution, following the Nordic model. The law eliminated Maine's Class E misdemeanor of engaging in prostitution, while elevating the crime of soliciting sex from a child or person with a mental disability from a misdemeanor to a felony punishable by up to five years in prison and a $5,000 fine.[34]
Remove ads
Types of prostitution
Summarize
Perspective
Child prostitution
The prostitution of children in the United States is a serious concern.[35][36] The FBI and National Center for Missing & Exploited Children have estimated that "more than 100,000" children are forced into prostitution every year, though there is limited empirical data to support this.[37][38][39]
Some prostitution laws have led to child prostitution victims being criminalized. In 2007, NYMag writer Jessica Lustig wrote that while the Trafficking Victims Protection Act of 2000 protected immigrant child prostitutes, New York law enforcement arrested prosecuted American-born child prostitutes as criminals.[40] In 2008, New York passed a Safe Harbour For Exploited Children act establishing protections for sexually exploited minors.[41]
Red light districts
Although informal, red light districts can be found in some areas of the country. Since prostitution is illegal everywhere except for a few counties in Nevada, there are no formal brothels in most parts of the country, but massage parlors offering prostitution may be found along with street prostitution. In part because of zoning laws, these areas also typically have other adult-oriented businesses such as strip clubs, sex shops, adult movie theaters, adult video arcades, peep shows, sex shows, and sex clubs.
Street prostitution
Street prostitution is illegal throughout the United States. Street prostitution tends to be clustered in certain areas known for solicitation. For instance, statistics on official arrests from the Chicago Police Department from August 19, 2005, to May 1, 2007, suggest that prostitution activity is highly concentrated: nearly half of all prostitution arrests occur in a tiny one-third of one percent of all blocks in the entire city of Chicago.[42] Street prostitutes who exchange sex for drugs are sometimes known as "strawberries".[43]
A study of violence against women engaged in street prostitution by clinical psychologist and anti-prostitution activist Melissa Farley found that 68% reported having been raped and 82% reported having been physically assaulted.[44]
A variation of street prostitution is that which occurs at truck stops along Interstate highways in rural areas. Called "lot lizards", these prostitutes solicit at truck stop parking lots and may use CB radios to communicate.
In today's society there is a hierarchy among prostitutes, with a substantial distinction between indoor workers and outdoor workers. Indoor prostitutes occupy the top tier, which includes independent call girls and workers in brothels and massage parlors. Outdoor street walkers occupy the lowest level and are more likely to experience abuse.[45] 250 prostitutes, including 150 outdoor workers and 125 indoor workers, were interviewed for a study about victimization. Weitzer, R (2005) noted that indoor workers experienced less harm than outdoor workers:
Outdoor prostitutes or streetwalkers are the most recognized sex workers, but they make up a small percentage of sex workers. Cunningham & Kendall (2011) report that only 20% of prostitutes work on the streets. Indoor workers have more freedom to choose their clients and set boundaries, which contributes to their safety.[46]
Escort or outcall prostitution
In spite of its illegality, escort prostitution exists throughout the United States and includes both independent prostitutes and those employed through escort agencies. Both freelancers and agencies may advertise under the term "bodywork" in the back of alternative newspapers, although some of those advertising bodywork straightforward massage professionals.
Typically, an agency charges its escorts either a flat fee for each client connection or a percentage of the prearranged rate. In San Francisco, it is usual for heterosexual-market agencies to negotiate for as little as $100 up to a full 50% of a woman's reported earnings (not counting any gratuity received). Most transactions occur in cash, and optional tipping of escorts by clients in most major U.S. cities is customary but not compulsory. Credit card processing offered by larger scale agencies is often available for a service charge.[47]
Escorts and escort agencies have historically advertised through classified ads, yellow pages advertising, or word-of-mouth, but in recent years much of the advertising and soliciting of indoor prostitution has shifted to internet sites. Sites may represent individual escorts, agencies, or may run ads for many escorts. There are also a number of sites on which customers discuss and post reviews of the sexual services offered by prostitutes and other sex workers. Many sites allow potential buyers to search for sex workers by physical characteristics and types of services offered.
Internet advertising of sexual services is offered not only by specialty sites, but in many cases by more mainstream advertising sites. Craigslist for many years featured an "adult services" section of this kind. After several years of pressure from law enforcement and anti-prostitution groups, Craigslist closed this section in 2010, first for its U.S. pages and then several months later internationally. In March 2018 the personals section of Craigslist was closed down. In 2017, the "Adult" section of Backpage was closed down.[48] Internet advertising is the most important resource for anyone interested in prostitution. There are websites catering to different clientele, from upscale escorts to budget low end.
Brothel prostitution
With the exception of some rural counties of Nevada, brothels are illegal in the United States.[49] Along with these legal brothels in Nevada, commercial sex also occurs. Due to the topic regarding legal prostitution, the rights of these establishments are neglected. Both participants in establishments such as brothels, are subjected to background checks, cleanliness checks, and working licenses at the government's request.[50] Aside from this, many massage parlors, saunas, spas, and similar otherwise-legal establishments serve as fronts for prostitution, especially in larger cities. They tend to be located in cities or along major highways.[51]
Remove ads
Legal status
Summarize
Perspective

Prostitution permitted, at least one active brothel
Prostitution permitted, no active brothels
Prostitution not permitted at all
Nevada is the only state that allows legal prostitution in the form of regulated brothels, the terms of which are stipulated in the Nevada Revised Statutes. Prostitution outside these licensed brothels is illegal throughout Nevada. Prostitution is illegal in the major metropolitan areas of Las Vegas, Reno, and Carson City, where most of the population lives; more than 90% of Nevada citizens live in a county in which prostitution is illegal. As of 2023, there were 19 licensed brothels in Nevada. Of the ten Nevada counties that theoretically allow brothel prostitution, only six (Elko, Lyon, Nye, White Pine, Lander, Storey) contain active licensed brothels; the remaining four (Churchill, Esmeralda, Humboldt, and Mineral) have none.[52]
In addition, it is decriminalized to sell sex but illegal to buy sex in Maine.
Prostitution in Rhode Island was outlawed in 2009. On November 3, governor Donald Carcieri signed into law a bill which makes the buying and selling of sexual services a crime.[26] Prostitution had been legal in Rhode Island between 1980 and 2009 because there was no specific statute to define the act and outlaw it, although associated activities such as street solicitation, running a brothel, and pimping were illegal.
Louisiana is the only state where convicted prostitutes are required to register as sex offenders. The State's crime against nature by solicitation law is used when a person is accused of engaging in oral or anal sex in exchange for money. Only prostitutes prosecuted under this law are required to be registered. This has led to a lawsuit filed by the Center for Constitutional Rights.[53]
The federal government also prosecutes some prostitution offenses. One man who forced women into prostitution received a 40-year sentence in federal court.[54] Another was prosecuted for income tax evasion.[55] Another man pleaded guilty to federal charges of harboring a 15-year-old girl and having her work as a prostitute.[56] Another federal defendant was sentenced to life imprisonment for sex trafficking of a child by force.[57]
The ban on prostitution in the US has been criticized from a variety of viewpoints.[58]
Push for legalization in New York
In 2020, some New York elected officials introduced bills to legalize prostitution in the state, but those bills have not received widespread support.[59] The state did, however, repeal an anti-loitering law that critics argued discouraged street prostitution and targeted transgender people.[60][61]
Local district attorneys have significant discretion over how to enforce existing prostitution laws. In New York City, District Attorneys often dismiss cases after community service is complete.[62] In January 2021, the Brooklyn DA office stated that it would dismiss over a 1,000 warrants based on prostitution in the past 50 years, and erase prostitution in the criminal history of over 25,000 people who had been convicted of prostitution.[63] Despite this, the issue often comes up in District Attorney elections, such as most recently in Manhattan, where prominent attorneys for the city, notably P. A. Potter, the assistant DA for the borough, included an amnesty for sex workers as part of his successful campaign.[64] Some New York District Attorneys have stated their support for the Nordic Model, however this support engendered a backlash from sex worker advocates who oppose the prosecution of buyers.[65]
Remove ads
Statistics on prostitutes and customers
Summarize
Perspective
One 1990 study estimated the annual prevalence of full-time equivalent prostitutes in the United States to be 23 per 100,000 population based on a capture–recapture study of prostitutes found in Colorado Springs, CO, police and sexually transmitted diseases clinic records between 1970 and 1988.[66]
A continuation of the Colorado Springs study[67] found a death rate among active prostitutes of 459 per 100,000 person-years, 5.9 times that of the (age and race adjusted) general population. Many people view prostitution as a victimless crime, as usually both sides are in agreement. However, many statistics show that it is physically dangerous. The death rate per 100,000 of prostitutes in the U.S. is nearly double that of Alaskan fishermen.[68]
Among voluntary substance abuse program participants, 41.4% of women and 11.2% of men reported selling sexual services during the preceding year (March 2008).[69] In Newark, New Jersey, one report claimed in 2000 that 57 percent of prostitutes were HIV-positive, while in Atlanta, 12 percent of were possibly HIV-positive.[70]
A 2004 TNS poll reported that 15 percent of all men had paid for sex and 30 percent of single men over age 30 had done so.[71] Over 200 men answered ads placed in Chicago area sex service classifieds for in depth interviews. Of these self-admitted "johns", 83% viewed buying sex as a form of addiction, 57% suspected that the women they paid had been abused as children, and 40% said they were usually intoxicated when they purchase sex.[72] A 2008 report by the National Institute of Justice estimated that 15-20 percent of men in the US had paid for sex.[73]
The prostitution trade in the United States is estimated to generate $14 billion per year.[74] A 2012 report by Fondation Scelles indicated that there were an estimated 1 million prostitutes in the U.S.[75]
Remove ads
John schools
Summarize
Perspective
John schools are programs whose mission is the rehabilitation of purchasers of prostitution.[76] A mandated program that is used as treatment for men who have been detained for soliciting sex from prostitutes. This program consists of several therapy sessions and informational meeting regarding legal actions, the dangers, and lasting outcomes that may take place as a result of soliciting sex from a prostitute.[76] In the first 12 years of the ongoing program, now denominated the "First Offender Prostitution Program", the recidivism rate of offenders was reduced from 8% to less than 5%. Since 1995, similar programs have been implemented in more than 40 communities in the US, including Washington, D.C.; West Palm Beach, Florida; Buffalo and Brooklyn, New York; and Los Angeles, California. An audit in 2009 of the first john school in San Francisco, California by the budget analysts of the City faulted the program with poorly defined objectives and absence of a method to determine its efficacy. Despite being touted as a national model for which taxpayers pay nothing, the audit stated that the program did not fully cover its expenses in each of the preceding 5 years, which resulted in a deficit of $270,000.[77]
Remove ads
Sex trafficking
Sex trafficking includes the transportation of persons by means of coercion, deception, or force into exploitative and slavery-like conditions,[78] and is commonly associated with organized crime.[79][80]
It has been estimated that two-thirds of trafficking victims in the United States are US citizens. Most victims who are foreign-born entered the US legally, on various visas.[81] The State Department has estimated that between 15,000 and 50,000 women and girls are trafficked into the United States each year.[citation needed]
Measures against trafficking of women focus on harsher criminal legislation and punishments and improving international police cooperation. Extensive press campaigns are designed to reach the public as well as to policy makers and potential victims.[79][82][83]
Remove ads
See also
- Prostitution in American Samoa
- Prostitution in California
- Prostitution in Guam
- Prostitution in Hawaii
- Prostitution in Nevada
- Prostitution in Rhode Island
- Trafficking of Korean women in the United States
- Contemporary slavery in the United States
- Human trafficking in the United States
- Sexuality in the United States
- Sex Worker's Rights Movement
- Male prostitution#United States
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
