Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Pyomyositis
Medical condition From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Pyomyositis (Myositis tropicans) is a bacterial infection of the skeletal muscles which results in an abscess. Pyomyositis is most common in tropical areas but can also occur in temperate zones.
Pyomyositis can be classified as primary or secondary. Primary pyomyositis is a skeletal muscle infection arising from hematogenous infection, whereas secondary pyomyositis arises from localized penetrating trauma or contiguous spread to the muscle.[1]
Remove ads
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is done via the following manner:[2]
- Pus discharge culture and sensitivity
- X ray of the part to rule out osteomyelitis
- Creatinine phosphokinase (more than 50,000 units)
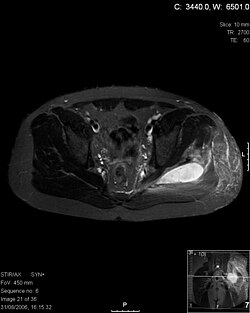
- MRI is useful
- Ultrasound guided aspiration
Bioptates of affected muscle tissues show acute and chronic inflammatory cells, and in one case caused by influenza A infection muscle cells show lack of nuclei.[3]
Symptoms
Pyogenic symptoms usually are present in the following muscles:[4]
- serratus anterior
- pectoralis major
- biceps
- abdominal muscles
- spinal muscles
- glutei
- iliopsoas
- quadriceps
- gastrocnemicus
The course of this disease is divided into three distinct phases. The invasive stage manifests as general muscle soreness and swelling without erythema and low-grade fever and lasts about ten days. The purulent-suppurative stage occurs after about 2–3 weeks and is associated with increased body temperature and muscle tenderness. In the third stage, sepsis occurs that can lead to serious complications, including death.[4]
Remove ads
Treatment
The abscesses within the muscle must be drained surgically (not all patients require surgery if there is no abscess). Antibiotics, such as vancomycin, teicoplanin, tigecycline, daptomycin or linezolid are given for a minimum of three weeks to clear the infection.[5][4] In some cases, co-trimoxazole is sufficient.[4]
Epidemiology
Summarize
Perspective
Pyomyositis is most often caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.[6] The infection can affect any skeletal muscle, but most often infects the large muscle groups such as the quadriceps or gluteal muscles.[5][7][8]
Pyomyositis is mainly a disease of children and was first described by Scriba in 1885. Most patients are aged 2 to 5 years, but infection may occur in any age group.[9][10] Infection often follows minor trauma and is more common in the tropics, where it accounts for 4% of all hospital admissions. In temperate countries such as the US, pyomyositis was a rare condition (accounting for 1 in 3000 pediatric admissions), but has become more common since the appearance of the USA300 strain of MRSA.[5][7][8]
Pyomyositis is inherently related to residency in tropical areas, especially in northern Uganda, where yearly about 400-900 cases are reported.[4] In these regions, the general population affected by this disease is not affected by other concommitant diseases. However, in temperate regions pyomyositis is usually present in immunocompromised indiviiduals or people affected by chronic renal failure or rheumatoid arthritis.[4]
Gonococcal pyomyositis is a rare infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae.[11]
Remove ads
Additional images
- CT with IV contrast showing enlargement and heterogeneous hypodensity in the right pectoralis major muscle. A focal abscess collection with gas within it is present medially. There are enlarged axillary lymph nodes and some extension into the right hemithorax. Note the soft tissue and phlegmon surrounding the right internal mammary artery and vein. The patient was HIV+ and the pyomyositis is believed to be due to direct inoculation of the muscle related to parenteral drug abuse. The patient admitted to being a "pocket shooter"
- CT exam showing a multiloculated fluid collection in the left gluteus minimus muscle found to be a staph aureus pyomyositis in a 12-year-old healthy boy.
- Axial T1 weighted fat suppressed post IV gadolinium contrast enhanced MRI image showing a mutliloculated bacterial abscess in the left gluteal muscle which grew Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin sensitive) thought to be due to tropical pyomyositis.
- Coronal fat suppressed post contrast image showing a multiloculated bacterial abscess in the left gluteus minimus muscle due to tropical pyomyositis.
- Coronal T2 weighted fat suppressed image showing a multiloculated fluid collection in the left gluteal musculature due to tropical pyomositis in a 12-year-old boy.
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads