Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
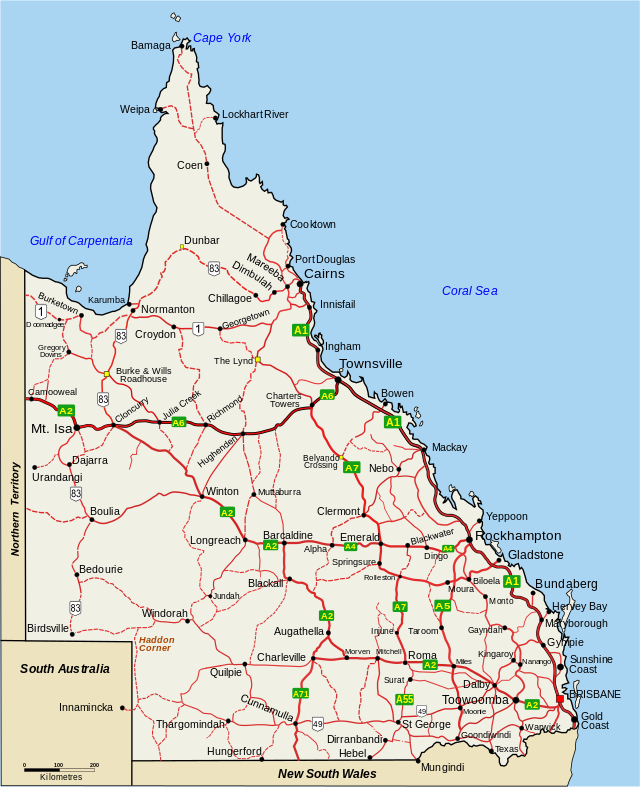
Regions of Queensland
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Regions of Queensland refer to the geographic areas of the Australian state of Queensland. Due to its large size and decentralised population, the state is often divided into regions for statistical and administrative purposes. Each region varies somewhat in terms of its economy, population, climate, geography, flora and fauna. Cultural and official perceptions and definitions of the various regions differ somewhat depending on the government agency or popular group by which they are being applied.

Remove ads
Overview
Various Queensland state government departments adopt different definitions of regions for administrative purposes. The Queensland government Trade and Investment Queensland defines seven regions. These are (roughly from south to north):[citation needed]
- South East Queensland
- Darling Downs
- Wide Bay–Burnett
- Central Queensland
- Mackay, Isaac and Whitsunday
- North Queensland
- Far North Queensland
Smaller regions may also exist within these defined regions, such as the Torres Strait Islands, Whitsunday Islands and South West Queensland.[citation needed]
Remove ads
South East Queensland
Summarize
Perspective


South East Queensland is commonly considered to be a single region. It contains two statistical regions listed above, Brisbane and Moreton. The region has a population of 3,500,000 people, or 72% of the state's population.[1] The area contains Brisbane, the state's capital city, as well as the Logan City, Gold Coast, Sunshine Coast, Ipswich and the Lockyer Valley. The region is the major administrative and commercial centre and focus of tourism within Queensland.[citation needed]
The Brisbane region comprises the greater Brisbane metropolitan area, centred on the City of Brisbane and also including the Logan, Redland, Moreton Bay and Ipswich local government areas. The metropolitan area has a population of 2,360,241 (2016)[2] It is the state's main commercial and administrative centre and contains the state's largest domestic and international airport.[citation needed]
The Gold and Sunshine Coasts, located south and north of Brisbane respectively, are two of the Queensland's most popular tourist regions, containing many hotels and resorts. Each region has an airport which caters primarily to tourists. The remaining parts of the region are located inland, west of Brisbane, and are primarily rural.[3][1]
Remove ads
Darling Downs South West
The Darling Downs South West region is located about 160 kilometres (100 mi) west of Brisbane and borders the states of New South Wales and South Australia. The region consists of the fertile agricultural area west of the Great Dividing Range and south to the New South Wales state border, centred on the city of Toowoomba. It has an area of 410,129 square kilometres (158,352 sq mi) and contains the local government areas of Toowoomba, Goondiwindi, Southern Downs, Western Downs, Maranoa, Balonne, Bulloo, Murweh, Paroo and Quilpie.[citation needed] In 2008, the region had a population of 257,749.[4] Economic activities include cattle grazing, cotton farming, and natural resource extraction such as natural gas and opal mining.[citation needed]
Wide Bay–Burnett

The Wide Bay–Burnett region is located north-east of the Darling Downs and north of the Sunshine Coast, covering a region of 52,377 square kilometres (20,223 sq mi). It consists of the Bundaberg, Fraser Coast, Gympie, North Burnett and South Burnett local government areas. Major centres include Bundaberg, Gympie, Hervey Bay, Kingaroy and Maryborough. The area is rich in sugar cane farms and mills and has a significant tourism industry – it includes Fraser Island, a popular tourist destination and world's largest sand island.[citation needed] Its population in 2008 was 276,752.[4]
Remove ads
Central Queensland and Central West Queensland
The Central Queensland region borders South Australia and the Northern Territory, and contains the major centres of Rockhampton and Gladstone, the coastal areas and popular holiday destinations Yeppoon, Agnes Water and 1770, and well as the areas further west of the Barcaldine, Barcoo, Blackall-Tambo, Boulia, Diamantina, Longreach and Winton local government areas. Despite its vast land area of 497,714 square kilometres (192,168 sq mi), it only had a population of 200,172 (2008). The region's economy is heavily dominated by coal mining, and cattle grazing. A major aluminium smelter is located in Gladstone.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Mackay, Isaac and Whitsunday
The Mackay, Isaac and Whitsunday region is centred on the coastal city of Mackay and extends some 300 km inland. It contains the Whitsunday Islands group and the coastal towns of Bowen, Proserpine, and Sarina. The coastal areas are densely covered in sugar cane farms, while the less densely populated inland areas have several mining communities.[citation needed]
Remove ads
North Queensland
The North Queensland region is a coastal region centred on the city of Townsville and secondary inland city of Mount Isa. Townsville is the location of a major seaport handling exports from mines in Mount Isa and cattle exports from coastal and inland areas. The region also contains a bulk sugar exporting terminal at Lucinda in the region's north. Other inland towns include Charters Towers and Cloncurry, and the coastal towns of Ayr, Home Hill and Ingham.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Far North Queensland

The Far North region is Queensland's largest region covering 22% of the state's area and includes Cape York Peninsula, the Torres Strait, and the Gulf of Carpentaria. The main population and administrative centre of the region is located in Cairns. Other key population centres include Cooktown, the Atherton Tableland, Weipa, Normanton, and Thursday Island. The region also consists of many Aboriginal and farming communities.[citation needed] The region covers an area of 380,748.3 square kilometres (147,008 sq mi) and in 2012 the region's population was 301,256 of which 146,778 lived in Cairns.[4] Significant industries include tourism, cattle grazing, agriculture (sugar cane and tropical fruits) and mining of both sand and bauxite.[citation needed]

Remove ads
Other definitions
Summarize
Perspective
Other names for regions are in popular usage, for example by different government agencies and in various regional maps of Queensland. The state also contains smaller regions within those discussed above which are not necessarily used for statistical purposes, but which are distinct in terms of their geography, economy or demographic characteristics. Such regions in Queensland include:[citation needed]
- Tropical Queensland – the area of the state north of latitude 23.5 degrees South.
- Tropical North Queensland – an area of tropical Queensland that usually includes Far North Queensland, and sometimes also North Queensland.
- The Outback – refers generally to Australian arid inland regions.
- Whitsunday Islands – a group of islands in the Mackay region. A popular tourist destination, the name usually includes the coastal community of Airlie Beach, and sometimes also Proserpine.
- Torres Strait Islands – islands between the northern tip of Queensland and Papua New Guinea
- Atherton Tableland – a fertile agricultural district in the Cairns hinterland, Far North Queensland.
- Granite Belt – an area of south-east Queensland centred on the town of Stanthorpe.
- Border Rivers – an area near the border of New South Wales and Queensland.
- Capricorn Coast – a section of the Central Queensland coastline near the Tropic of Capricorn.
- Maranoa – a district that is sometimes referred to as the Western Darling Downs, in South West Queensland.
- The Marlin Coast – a coastal area centred on Cairns.
- North West Queensland – the area around Mt Isa.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
