Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Russian Empire
Eurasian empire (1721–1917) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Russian Empire[d][e] was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about 22,800,000 km2 (8,800,000 sq mi), roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the third-largest empire in history, behind only the British and Mongol empires. It also colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity.
From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (r. 1462–1505), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured independence against the Tatars. His grandson, Ivan IV (r. 1533–1584), became in 1547 the first Russian monarch to be crowned tsar of all Russia. Between 1550 and 1700, the Russian state grew by an average of 35,000 km2 (14,000 sq mi) per year. Peter I transformed the tsardom into an empire, and fought numerous wars that turned a vast realm into a major European power. He moved the Russian capital from Moscow to the new model city of Saint Petersburg, and led a cultural revolution that introduced a modern, scientific, rationalist, and Western-oriented system. Catherine the Great (r. 1762–1796) presided over further expansion of the Russian state by conquest, colonization, and diplomacy, while continuing Peter's policy of modernization. Alexander I (r. 1801–1825) helped defeat the militaristic ambitions of Napoleon and subsequently constituted the Holy Alliance, which aimed to restrain the rise of secularism and liberalism across Europe. Russia further expanded to the west, south, and east, strengthening its position as a European power. Its victories in the Russo-Turkish Wars were later checked by defeat in the Crimean War (1853–1856), leading to a period of reform and conquests in Central Asia.[10] Alexander II (r. 1855–1881) initiated numerous reforms, most notably the 1861 emancipation of all 23 million serfs.
By the start of the 19th century, Russian territory extended from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Black Sea in the south, and from the Baltic Sea in the west to Alaska, Hawaii, and California in the east. By the end of the 19th century, Russia had expanded its control over the Caucasus, most of Central Asia and parts of Northeast Asia. Notwithstanding its extensive territorial gains and great power status, the empire entered the 20th century in a perilous state. The devastating Russian famine of 1891–1892 killed hundreds of thousands and led to popular discontent. As the last remaining absolute monarchy in Europe, the empire saw rapid political radicalization and the growing popularity of revolutionary ideas such as communism.[11] After the Russian Revolution of 1905, Tsar Nicholas II authorized the creation of a national parliament, the State Duma, although he still retained absolute political power.
When Russia entered the First World War on the side of the Allies, it suffered a series of defeats that further galvanized the population against the emperor. In 1917, mass unrest among the population and mutinies in the army culminated in the February Revolution, which led to the abdication of Nicholas II, the formation of the Russian Provisional Government, and the proclamation of the first Russian Republic. Political dysfunction, continued involvement in the widely unpopular war, and widespread food shortages resulted in mass demonstrations against the government in July.[12] The republic was overthrown in the October Revolution by the Bolsheviks, who proclaimed the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and whose Treaty of Brest-Litovsk ended Russia's involvement in the war, but who nevertheless were opposed by various factions known collectively as the Whites.[13][14] After emerging victorious in the Russian Civil War, the Bolsheviks established the Soviet Union across most of the Russian territory; Russia was one of four continental European empires to collapse as a result of World War I, along with Germany, Austria–Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire.[15]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
The foundations of a unified Russian state were laid in the 15th century under Ivan III.[16][17] Moscow came to dominate the region known as Great Russia, and by the early 16th century, the Russian states were united with Moscow.[17][18] The subjects of the Muscovite ruler were overwhelmingly Great Russian in ethnicity and Orthodox in religion.[17] As Moscow was the only independent Orthodox power following the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, its rulers had already taken symbolic steps toward becoming an empire by marrying into the Byzantine imperial dynasty, adopting the double-headed eagle as their symbol, and the title of tsar (caesar).[17]
During the reign of Ivan IV, the khanates of Kazan and Astrakhan were conquered by Russia in the mid-16th century, marking the beginning of the transformation from an almost mono-ethnic realm into a multi-ethnic empire.[19][20] The Russians began to expand into Siberia, initially in pursuit of the region's profitable furs.[19] Following the Time of Troubles in the early 17th century, the traditional alliance of autocratic monarchy, church, and aristocracy was seen as the only basis for preserving social order and Russian statehood, which legitimized the rule of the Romanov dynasty.[19]
Peter the Great (1682–1725)



The foundations of the Russian Empire were laid during Peter I's reforms, which altered Russia's political and social structure,[21] and as a result of the Great Northern War which strengthened Russia's world standing.[22][23] Peter I (r. 1682–1725), played a major role in introducing the European state system into Russia. While Russia's vast lands had a population of 14 million, grain yields trailed behind those in the West.[24] Nearly the entire population was devoted to agriculture, with only a small percentage living in towns. The class of kholops, whose status was close to that of slaves, remained a major institution in Russia until 1723, when Peter converted household kholops into house serfs, thus counting them for poll taxation. Agricultural kholops had been converted into serfs in 1679. They were largely tied to the land, in a feudal sense, until the late 19th century.
Peter's first military efforts were directed against the Ottoman Empire. His attention then turned north; Russia lacked a secure northern seaport, except at Arkhangelsk on the White Sea, where the harbor was frozen for nine months a year. Access to the Baltic Sea was blocked by Sweden, whose territory enclosed it on three sides. Peter's ambitions for a "window to the sea" led him, in 1699, to make a secret alliance with Saxony, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and Denmark-Norway against Sweden; they conducted the Great Northern War, which ended in 1721 when an exhausted Sweden asked for peace with Russia. On 2 November [O.S. 22 October] 1721, the day of the announcement of the Treaty of Nystad, the Governing Senate and Synod invested the tsar with the titles of Peter the Great,[25] Pater Patriae (father of the fatherland),[f] and Imperator of all Russia.[g][26][27] The adoption of the title of imperator by Peter I is seen as the beginning of "imperial" Russia.[h][30]
As a result of the war with Sweden, Peter acquired four provinces situated south and east of the Gulf of Finland, securing access to the sea. There he built Russia's new capital, Saint Petersburg, on the Neva river in 1703, to replace Moscow, which had long been Russia's cultural center. This relocation expressed his intent to adopt European elements for his empire. Many of the government and other major buildings were designed under Italianate influence.
Peter reorganized his government based on the latest political models, molding Russia into an absolutist state. The Military Regulations recognised the autocratic nature of the regime.[31] Peter replaced the old Boyar Duma (council of nobles) with a nine-member Senate, in effect a supreme council of state. The vestiges of the independence of the boyars were lost. The countryside was divided into new provinces and districts. Peter informed the Senate that its mission was to collect taxes, and tax revenues tripled over his reign. Peter continued and intensified his predecessors' requirement of state service from all nobles, in the Table of Ranks and equated the votchina with an estate. Russia's modern fleet was built by Peter, along with an army reformed in a European style and educational institutions (the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences). Civil lettering was adopted during Peter I's reign, and the first Russian newspaper, Vedomosti, was published. Peter I promoted science, particularly geography and geology, trade, and industry,[32] including shipbuilding, as well as the growth of the educational system. Every tenth Russian acquired an education during his reign, when there were 15 million Russians.[33]
As part of Peter's reorganization, he enacted a church reform. The Russian Orthodox Church was partially incorporated into the country's administrative structure, in effect making it a tool of the state. Peter abolished the patriarchate and replaced it with a collective body, the Most Holy Synod, which was led by a government official.[34]
The concept of the triune of the Russian people, composed of the Great Russians, the Little Russians, and the White Russians, was introduced under Peter I, and it was associated with the name of Archimandrite Zacharias Kopystensky (1621), the Archimandrite of the Kiev Pechersk Lavra and expanded upon in the writings of an associate of Peter I, Archbishop Professor Theophan Prokopovich. Several of Peter I's associates include Alexander Menshikov, Jacob Bruce, Mikhail Golitsyn and Anikita Repnin. During Peter's reign serf labor played a significant role in the growth of industry, reinforcing traditional socioeconomic structures. International trade increased as a result of Peter I's industrial reforms. However, imports of goods overtook exports, strengthening the role of foreigners in Russian trade, particularly the British.[35]
In 1722, Peter turned his aspirations toward increasing Russian influence in the Caucasus and the Caspian Sea at the expense of the weakened Safavid Persians. He made Astrakhan the base of military efforts against Persia, and waged the first full-scale war against them in 1722–23.[36] Peter the Great temporarily annexed areas of Iran to Russia, which after his death were returned in the 1732 Treaty of Resht and 1735 Treaty of Ganja as a deal to oppose the Ottomans.[37]
Peter died in 1725, leaving an unsettled succession. After a short reign by his widow, Catherine I, the crown passed to Empress Anna. She slowed reforms and led a successful war against the Ottoman Empire. This resulted in a significant weakening of the Crimean Khanate, an Ottoman vassal and long-term Russian adversary. The next emperor, the infant Ivan VI was deposed and killed. The discontent over the dominant positions of Baltic Germans in Russian politics resulted in Peter I's daughter Elizabeth being put on the Russian throne. Elizabeth supported the arts, architecture, and the sciences (for example, the founding of Moscow University). But she did not carry out significant structural reforms. Her reign, which lasted nearly 20 years, is also known for Russia's involvement in the Seven Years' War, where it was successful militarily, but gained little politically.[38]
Catherine the Great (1762–1796)



Catherine the Great was a German princess who married Peter III, the German heir to the Russian crown. After the death of Empress Elizabeth, Catherine came to power after she effected a coup d'état against her very unpopular husband. She contributed to the resurgence of the Russian nobility that began after the death of Peter the Great, abolishing State service and granting them control of most state functions in the provinces. She also removed the Beard tax instituted by Peter the Great.[39]
Catherine extended Russian political control over the lands of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, supporting the Targowica Confederation. However, the cost of these campaigns further burdened the already oppressive social system, under which serfs were required to spend almost all of their time laboring on their owners' land. A major peasant uprising took place in 1773, after Catherine legalized the selling of serfs separate from land. Inspired by a Cossack named Yemelyan Pugachev and proclaiming "Hang all the landlords!", the rebels threatened to take Moscow before they were ruthlessly suppressed. Instead of imposing the traditional punishment of drawing and quartering, Catherine issued secret instructions that the executioners should execute death sentences quickly and with minimal suffering, as part of her effort to introduce compassion into the law.[40]
She furthered these efforts by ordering the public trial of Darya Nikolayevna Saltykova, a high-ranking noblewoman, on charges of torturing and murdering serfs. Whilst these gestures garnered Catherine much positive attention from Europe during the Enlightenment, the specter of revolution and disorder continued to haunt her and her successors. Indeed, her son Paul introduced a number of increasingly erratic decrees in his short reign aimed directly against the spread of French culture in response to their revolution.
In order to ensure the continued support of the nobility, which was essential to her reign, Catherine was obliged to strengthen their authority and power at the expense of the serfs and other lower classes. Nevertheless, Catherine realized that serfdom must eventually be ended, going so far in her Nakaz ("Instruction") to say that serfs were "just as good as we are" – a comment received with disgust by the nobility. Catherine advanced Russia's southern and western frontiers, successfully waging war against the Ottoman Empire for territory near the Black Sea, and incorporating territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Partitions of Poland, alongside Austria and Prussia. As part of the Treaty of Georgievsk, signed with the Georgian Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti, and her own political aspirations, Catherine waged a new war against Persia in 1796 after they had invaded eastern Georgia. Upon achieving victory, she established Russian rule over it and expelled the newly established Persian garrisons in the Caucasus.
Catherine's expansionist policy caused Russia to develop into a major European power,[41] as did the Enlightenment era and the Golden age in Russia. But after Catherine died in 1796, she was succeeded by her son, Paul. He brought Russia into a major coalition war against the new-revolutionary French Republic in 1798. Russian commander Field Marshal Suvorov led the Italian and Swiss expedition,—he inflicted a series of defeats on the French; in particular, the Battle of the Trebbia in 1799.
State budget

Russia was in a continuous state of financial crisis. While revenue rose from 9 million rubles in 1724 to 40 million in 1794, expenses grew more rapidly, reaching 49 million in 1794. The budget allocated 46 percent to the military, 20 percent to government economic activities, 12 percent to administration, and nine percent for the Imperial Court in St. Petersburg. The deficit required borrowing, primarily from bankers in Amsterdam; five percent of the budget was allocated to debt payments. Paper money was issued to pay for expensive wars, thus causing inflation. As a result of its spending, Russia developed a large and well-equipped army, a very large and complex bureaucracy, and a court that rivaled those of Versailles and London. But the government was living far beyond its means, and 18th-century Russia remained "a poor, backward, overwhelmingly agricultural, and illiterate country".[43]
Population
Much of Russia's expansion occurred in the 17th century, culminating in the first Russian colonization of the Pacific, the Russo-Polish War (1654–1667) which led to the incorporation of left-bank Ukraine, and the Russian conquest of Siberia. Poland was partitioned by its rivals in 1772–1815, most of its land and population taken under Russian rule. Most of the empire's growth in the 19th century came from gaining territory in central and eastern Asia south of Siberia.[44] By 1795, after the Partitions of Poland, Russia became the most populous state in Europe, ahead of France.
First half of the 19th century

In 1801, over four years after Paul became the emperor of Russia, he was killed in Saint Michael's Castle in a coup. Paul was succeeded by his 23-year-old son, Alexander. Russia was in a state of war with the French Republic under the leadership of the Corsica-born First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte. After he became the emperor, Napoleon defeated Russia at Austerlitz in 1805, Eylau and Friedland in 1807. After Alexander was defeated in Friedland, he agreed to negotiate and sued for peace with France; the Treaties of Tilsit led to the Franco-Russian alliance against the Coalition and joined the Continental System.[46] By 1812, Russia had occupied many territories in Eastern Europe, holding some of Eastern Galicia from Austria and Bessarabia from the Ottoman Empire;[47] from Northern Europe, it had gained Finland from the war against a weakened Sweden; it also gained some territory in the Caucasus.
Following a dispute with Emperor Alexander I, in 1812, Napoleon launched an invasion of Russia. It was catastrophic for France, whose army was decimated during the Russian winter. Although Napoleon's Grande Armée reached Moscow, the Russians' scorched earth strategy prevented the invaders from living off the country. In the harsh and bitter winter, thousands of French troops were ambushed and killed by peasant guerrilla fighters.[48] Russian troops then pursued Napoleon's troops to the gates of Paris, presiding over the redrawing of the map of Europe at the Congress of Vienna (1815), which ultimately made Alexander the monarch of Congress Poland.[49] The "Holy Alliance" was proclaimed, linking the monarchist great powers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia.

Although the Russian Empire played a leading political role in the next century, thanks to its role in defeating Napoleonic France, its retention of serfdom precluded economic progress to any significant degree. As Western European economic growth accelerated during the Industrial Revolution, Russia began to lag ever farther behind, creating new weaknesses for the empire seeking to play a role as a great power. Russia's status as a great power concealed the inefficiency of its government, the isolation of its people, and its economic and social backwardness. Following the defeat of Napoleon, Alexander I had been ready to discuss constitutional reforms, but though a few were introduced, no major changes were attempted.[50]

The liberal Alexander I was replaced by his younger brother Nicholas I (1825–1855), who at the beginning of his reign was confronted with an uprising. The background of this revolt lay in the Napoleonic Wars, when a number of well-educated Russian officers travelled in Europe in the course of military campaigns, where their exposure to the liberalism of Western Europe encouraged them to seek change on their return to autocratic Russia. The result was the Decembrist revolt (December 1825), which was the work of a small circle of liberal nobles and army officers who wanted to install Nicholas' brother Constantine as a constitutional monarch. The revolt was easily crushed, but it caused Nicholas to turn away from the modernization program begun by Peter the Great and champion the doctrine of Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality.[51]
In order to repress further revolts, censorship was intensified, including the constant surveillance of schools and universities. Textbooks were strictly regulated by the government. Police spies were planted everywhere. Under Nicholas I, would-be revolutionaries were sent off to Siberia, with hundreds of thousands sent to katorga camps.[52] The retaliation for the revolt made "December Fourteenth" a day long remembered by later revolutionary movements.[citation needed]
The question of Russia's direction had been gaining attention ever since Peter the Great's program of modernization. Some favored imitating Western Europe while others were against this and called for a return to the traditions of the past. The latter path was advocated by Slavophiles, who held the "decadent" West in contempt. The Slavophiles were opponents of bureaucracy, who preferred the collectivism of the medieval Russian obshchina or mir over the individualism of the West.[53] More extreme social doctrines were elaborated by such Russian radicals on the left, such as Alexander Herzen, Mikhail Bakunin, and Peter Kropotkin.
Foreign policy (1800–1864)


After Russian armies liberated the Eastern Georgian Kingdom (allied since the 1783 Treaty of Georgievsk) from the Qajar dynasty's occupation of 1802,[citation needed] during the Russo-Persian War (1804–1813), they clashed with Persia over control and consolidation of Georgia, and also became involved in the Caucasian War against the Caucasian Imamate. At the conclusion of the war, Persia irrevocably ceded what is now Dagestan, eastern Georgia, and most of Azerbaijan to Russia, under the Treaty of Gulistan.[54] Russia attempted to expand to the southwest, at the expense of the Ottoman Empire, using recently acquired Georgia at its base for its Caucasus and Anatolian front. The late 1820s were successful years militarily. Despite losing almost all recently consolidated territories in the first year of the Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828, Russia managed to favorably bring an end to the war with the Treaty of Turkmenchay, including the formal acquisition of what are now Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iğdır Province.[55] In the 1828–1829 Russo-Turkish War, Russia invaded northeastern Anatolia and occupied the strategic Ottoman towns of Karin and Gümüşhane (Argiroupoli) and, posing as protector of the Greek Orthodox population, received extensive support from the region's Pontic Greeks. Following a brief occupation, the Russian imperial army withdrew back into Georgia.[56]
Russian emperors quelled two uprisings in their newly acquired Polish territories: the November Uprising in 1830 and the January Uprising in 1863. In 1863, the Russian autocracy had given the Polish artisans and gentry reason to rebel, by assailing national core values of language, religion, and culture.[57] France, Britain, and Austria tried to intervene in the crisis but were unable to do so. The Russian press and state propaganda used the Polish uprising to justify the need for unity in the empire.[58] The semi-autonomous polity of Congress Poland subsequently lost its distinctive political and judicial rights, with Russification being imposed on its schools and courts.[59] However, Russification policies in Poland, Finland and among the Germans in the Baltics largely failed and only strengthened political opposition.[58]
Second half of the 19th century



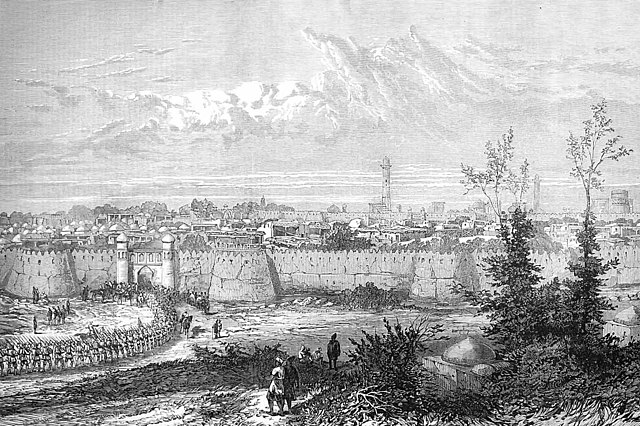

In 1854–1855, Russia fought Britain, France and the Ottoman Empire in the Crimean War, which Russia lost. The war was fought primarily in the Crimean peninsula, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic during the related Åland War. Since playing a major role in the defeat of Napoleon, Russia had been regarded as militarily invincible, but against a coalition of the great powers of Europe, the reverses it suffered on land and sea exposed the weakness of Emperor Nicholas I's regime.
When Emperor Alexander II ascended the throne in 1855, the desire for reform was widespread. A growing humanitarian movement attacked serfdom as inefficient. In 1859, there were more than 23 million serfs in usually poor living conditions. Alexander II decided to abolish serfdom from above, with ample provision for the landowners, rather than wait for it to be abolished from below by revolution.[60]
The Emancipation Reform of 1861, which freed the serfs, was the single most important event in 19th-century Russian history, and the beginning of the end of the landed aristocracy's monopoly on power. The 1860s saw further socioeconomic reforms to clarify the position of the Russian government with regard to property rights.[61] Emancipation brought a supply of free labor to the cities, stimulating industry, while the middle class grew in number and influence. However, instead of receiving their lands as a gift, the freed peasants had to pay a special lifetime tax to the government, which in turn paid the landlords a generous price for the land that they had lost. In numerous cases the peasants ended up with relatively small amounts of the least productive land. All the property turned over to the peasants was owned collectively by the mir, the village community, which divided the land among the peasants and supervised the various holdings. Although serfdom was abolished, its abolition was achieved on terms unfavorable to peasants; thus, revolutionary tensions remained. Revolutionaries believed that the newly freed serfs were merely being sold into wage slavery in the onset of the industrial revolution, and that the urban bourgeoisie had effectively replaced the landowners.[62]
Seeking more territories, Russia obtained Priamurye (Outer Manchuria) from the weakened Manchu-led Qing China, which had been occupied fighting against the Taiping Rebellion. In 1858, the Treaty of Aigun ceded much of the Manchu homeland to the Russian Empire, and in 1860, the Treaty of Peking also ceded the modern Primorsky Krai, which provided the land for the establishment of the outpost of the future Vladivostok.[63] Meanwhile, Russia under Alexander II decided to sell what it saw as the indefensible Russian America to the United States for 11 million rubles (7.2 million dollars) in 1867 to Andrew Johnson's government in the Alaska Purchase.[64][65] Initially, many Americans considered this newly gained territory to be a wasteland and useless, and saw the government wasting money, whereupon the transaction was sometimes called "Seward's Folly" through the eponymous Secretary of State William H. Seward who brokered the deal,[66][67] but later, much gold and petroleum were discovered.[68]
In the late 1870s, Russia and the Ottoman Empire again clashed in the Balkans. From 1875 to 1877, the Balkan crisis intensified, with rebellions against Ottoman rule by various Slavic nationalities,[69] which the Ottoman Turks had dominated since the 15th century. This was seen as a political risk in Russia, which similarly suppressed its Muslims in Central Asia and Caucasia. Russian nationalist opinion became a major domestic factor with its support for liberating Balkan Christians from Ottoman rule and making Bulgaria and Serbia independent. In early 1877, Russia intervened on behalf of Serbian and Russian volunteer forces,[70] leading to the Russo-Turkish War (1877–78).[71] Within one year, Russian troops were nearing Constantinople and the Ottomans surrendered. Russia's nationalist diplomats and generals persuaded Alexander II to force the Ottomans to sign the Treaty of San Stefano in March 1878, creating an enlarged, independent Bulgaria that stretched into the southwestern Balkans.[70] When Britain threatened to declare war over the terms of the treaty, an exhausted Russia backed down. At the Congress of Berlin in July 1878, Russia agreed to the creation of a smaller Bulgaria and Eastern Rumelia, as a vassal state and an autonomous principality inside the Ottoman Empire, respectively.[72][73] As a result, Pan-Slavists were left with a legacy of bitterness against Austria-Hungary and Germany for failing to back Russia. Disappointment at the results of the war stimulated revolutionary tensions, and helped Serbia, Romania, and Montenegro gain independence from, and strengthen themselves against, the Ottomans.[74]

Another significant result of the war was the acquisition from the Ottomans of the provinces of Batumi, Ardahan, and Kars in Transcaucasia, which were transformed into the militarily administered regions of Batum Oblast and Kars Oblast. To replace Muslim refugees who had fled across the new frontier into Ottoman territory, the Russian authorities settled large numbers of Christians from ethnically diverse communities in Kars Oblast, particularly Georgians, Caucasus Greeks, and Armenians, each of whom hoped to achieve protection and advance their own regional ambitions.
Alexander III
In 1881, Alexander II was assassinated by the Narodnaya Volya, a Nihilist terrorist organization. The throne passed to Alexander III (1881–1894), a reactionary who revived the maxim of "Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality" of Nicholas I. A committed Slavophile, Alexander III believed that Russia could be saved from turmoil only by shutting itself off from the subversive influences of Western Europe. During his reign, Russia formed the Franco-Russian Alliance, to contain the growing power of Germany; completed the conquest of Central Asia; and demanded important territorial and commercial concessions from China. The emperor's most influential adviser was Konstantin Pobedonostsev, tutor to Alexander III and his son Nicholas, and procurator of the Holy Synod from 1880 to 1895. Pobedonostsev taught his imperial pupils to fear freedom of speech and the press, as well as dislike democracy, constitutions, and the parliamentary system. Under Pobedonostsev, revolutionaries were persecuted—by the imperial secret police, with thousands being exiled to Siberia—and a policy of Russification was carried out throughout the empire.[75]
Foreign policy (1864–1907)
Russia had little difficulty expanding to the south, including conquering Turkestan,[76] until Britain became alarmed when Russia threatened Afghanistan, with the implicit threat to India; and decades of diplomatic maneuvering resulted, called the Great Game.[77] That rivalry between the two empires has been considered to have included far-flung territories such as Outer Mongolia and Tibet. The maneuvering largely ended with the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907.[78]
Expansion into the vast stretches of Siberia was slow and expensive, but finally became possible with the building of the Trans-Siberian Railway, 1890 to 1904. This opened up East Asia; and Russian interests focused on Mongolia, Manchuria, and Korea. China was too weak to resist, and was pulled increasingly into the Russian sphere. Russia obtained treaty ports such as Dalian/Port Arthur. In 1900, the Russian Empire invaded Manchuria as part of the Eight-Nation Alliance's intervention against the Boxer Rebellion. Japan strongly opposed Russian expansion, and defeated Russia in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. Japan took over Korea, and Manchuria remained a contested area.[79]
Meanwhile, France, looking for allies against Germany after 1871, formed a military alliance in 1894, with large-scale loans to Russia, sales of arms, and warships, as well as diplomatic support. Once Afghanistan was informally partitioned by the Anglo-Russian Convention in 1907, Britain, France, and Russia came increasingly close together in opposition to Germany and Austria-Hungary. The three would later comprise the Triple Entente alliance in the First World War.[80]
Early 20th century

In 1894, Alexander III was succeeded by his son, Nicholas II, who was committed to retaining the autocracy that his father had left him. Nicholas II proved as an ineffective ruler, and in the end his dynasty was overthrown by the Russian Revolution.[82] The Industrial Revolution began to show significant influence in Russia, but the country remained rural and poor.
Economic conditions steadily improved after 1890, thanks to new crops such as sugar beets, and new access to railway transportation. Total grain production increased, as well as exports, even with rising domestic demand from population growth. As a result, there was a slow improvement in the living standards of Russian peasants in the empire's last two decades before 1914. Recent research into the physical stature of Army recruits shows they were bigger and stronger. There were regional variations, with more poverty in the heavily populated central black earth region; and there were temporary downturns in 1891–93 and 1905–1908.[83]
By the end of the 19th century, the Russian Empire had reached its greatest territorial extent, covering a surface area of 22,800,000 km2, and ranking as the third-largest empire in world history.
On the political right, the reactionary elements of the aristocracy strongly favored the large landholders, who, however, were slowly selling their land to the peasants through the Peasants' Land Bank. The Octobrist party was a conservative force, with a base of landowners and businessmen. They accepted land reform but insisted that property owners be fully paid. They favored far-reaching reforms, and hoped the landlord class would fade away, while agreeing they should be paid for their land. Liberal elements among industrial capitalists and nobility, who believed in peaceful social reform and a constitutional monarchy, formed the Constitutional Democratic Party or Kadets.[84]
On the left, the Socialist Revolutionaries (SRs) and the Marxist Social Democrats wanted to expropriate the land, without payment, but debated whether to distribute the land among the peasants (the Narodnik solution), or to put it into collective local ownership.[85] The Socialist Revolutionaries also differed from the Social Democrats in that the SRs believed a revolution must rely on urban workers, not the peasantry.[86]
In 1903, at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, in London, the party split into two wings: the gradualist Mensheviks and the more radical Bolsheviks. The Mensheviks believed that the Russian working class was insufficiently developed and that socialism could be achieved only after a period of bourgeois democratic rule. They thus tended to ally themselves with the forces of bourgeois liberalism. The Bolsheviks, under Vladimir Lenin, supported the idea of forming a small elite of professional revolutionists, subject to strong party discipline, to act as the vanguard of the proletariat, in order to seize power by force.[87]

Defeat in the Russo-Japanese War (1904–1905) was a major blow to the tsarist regime and further increased the potential for unrest. In January 1905, an incident known as "Bloody Sunday" occurred when Father Georgy Gapon led an enormous crowd to the Winter Palace in Saint Petersburg to present a petition to the emperor. When the procession reached the palace, soldiers opened fire on the crowd, killing hundreds. The Russian masses were so furious over the massacre that a general strike was declared, which demanded a democratic republic. This marked the beginning of the Revolution of 1905. Soviets (councils of workers) appeared in most cities to direct revolutionary activity. Russia was paralyzed, and the government was desperate.[88]
In October 1905, Nicholas reluctantly issued the October Manifesto, which conceded the creation of a national Duma (legislature) to be called without delay. The right to vote was extended and no law was to become final without confirmation by the Duma. The moderate groups were satisfied, but the socialists rejected the concessions as insufficient and tried to organise new strikes. By the end of 1905, there was disunity among the reformers, and the emperor's position was strengthened, allowing him to roll back some of the concessions with the new Russian Constitution of 1906.
War, revolution, and collapse
Origins of causes
Russia, along with France and Britain, was a member of the Entente in antecedent to World War I; these three powers were formed up in response to Germany's rival[89] Triple Alliance, comprising itself, Austria-Hungary and Italy. The relations with Britain were in disquietude from the Great Game in Central Asia until the 1907 Anglo-Russian Convention, when both agreed to settle their differences and joined to oppose the new rising power of Germany.[90] Russia and France's relations remained isolated before the 1890s when both sides agreed to ally when peace was threatened.[91]
The relations between Russia and the Triple Alliance, especially Germany and Austria, were like those of the League of the Three Emperors. Russia's relations with Germany were deteriorating,[92] and tensions over the Eastern question had reached a breaking point with Austria-Hungary.[93] The 1908 Bosnian Crisis had nearly led to war and in 1912–13 relations between Saint Petersburg and Vienna were tense during the Balkan Wars.[94]
The assassination of the Austro-Hungarian heir, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, raised Europe's tensions, which led to the confrontation between Austria and Russia.[95] Serbia rejected an Austrian ultimatum that demanded an obligation for the heir's death, and Austria-Hungary cut all diplomatic ties and declared war on 28 July 1914. Russia supported Serbia because it was a fellow Slavic state, and two days later, Emperor Nicholas II ordered a mobilization to attempt to force Austria-Hungary to back down.[96]
Declaration of War

As a result of Vienna's declaration of war on Serbia, Nicholas II ordered the mobilization of 4.9 million men. Germany, Austria-Hungary's ally, saw the call to arms as a threat,[97] and declared war on 1 August 1914.[98] The Russians were imbued with patriotic earnestness and Germanophobic sentiment, including the name of the capital, Saint Petersburg, which sounded too German and was renamed Petrograd.[99]
The Russian entry into the First World War was followed by France.[100] The German General Staff had devised the Schlieffen Plan, which first eliminated France via nonaligned Belgium before moving east to attack Russia, whose massive army was much slower to mobilise.[101]
Theaters of operations
German front

By August 1914, Russia had invaded with unexpected speed the German province of East Prussia, ending with a humiliating defeat at Tannenberg, owing to a message sent without wiring and coding,[102] causing the destruction of the entire second army. Russia suffered a massive defeat at the Masurian Lakes twice, the first ending with a hundred thousand casualties;[103] and the second suffering 200,000.[104] By October, the German Ninth Army was near Warsaw, and the newly-formed Tenth Army had retreated from the frontier in East Prussia. Grand Duke Nicholas, the Russian commander-in-chief, now had the order to invade Silesia with his Fifth, Fourth, and Ninth armies.[105] The Ninth Army, led by Mackensen, retreated from the frontline in Galicia and concentrated between the cities of Posen and Thorn. The advance took place on 11 November against the main army's right flank and rear; the First and Second armies were severely mauled, and the Second army was nearly surrounded in Łódź on 17 November.
Exhausted Russian troops began to withdraw from Russian-held Poland, allowing the Germans to capture many cities, including the kingdom's capital Warsaw on 5 August 1915.[106] In the same month, the emperor dismissed Grand Duke Nicholas and took personal command;[107] this was a turning point for the Russian army and the beginning of the worst disaster.[108] Russia lost the entire territory of Poland and Lithuania,[109] part of the Baltic states and Grodno, and partly of Volhynia and Podolia in Ukraine; thereafter the front with Germany was stable until 1917.
Austrian front
Austria-Hungary went to war with Russia on 6 August. The Russians started to invade Galicia, held by Austrian Cisleithania on 20 August, and annihilated the Austro-Hungarian Army at Lemberg, leading to the occupation of Galicia.[110] While the fortress of Premissel was besieged, the first attempt to capture the fortress failed, but the second attempt seized the redoubt in March 1915.[111] On 2 May, the Russian army was broken through by joint Austro-German forces, retreating from the Gorlice to Tarnów line and losing Premissel.
On 4 June 1916, General Aleksei Brusilov carried out an offensive by targeting Kovel. His offensive was a great success, taking 76,000 prisoners from the main attack and 1,500 from the Austrian bridgehead. But the offensive was halted by inadequate ammunition and a lack of supplies.[112] The eponymous offensive was the most successful allied strike of World War I,[113] practically destroying the Austro-Hungarian army as an independent force, but the slaughter of many casualties (approximately one million men) forced the Russian forces not to rebuild or launch any further attacks.
Turkish front
On 29 October 1914, a prelude to the Russo-Turkish front, the Turkish fleet, with German support, began to raid Russian coastal cities in Odessa, Sevastopol, Novorossiysk, Feodosia, Kerch, and Yalta[114] This led Russia to declare war on the Ottoman Empire on 2 November.[115] In December 1914, Russia obtained success at Sarikamish, where the Russian General Nikolai Yudenich routed Enver Pasha.[116] Yudenich captured Köprüköy in January 1916 and captured Erzurum about one month later in February.[117]
The Russian Navy's Black Sea Fleet was on the defensive in 1914, but this changed in the spring of 1915, when the high command ordered the fleet to attack the Turkish coast to assist the Western Entente landings in Gallipoli.[118] The Russian naval raids did make any difference for the Gallipoli campaign, but they were very successful in disrupting coal shipments to Constantinople from other parts of Anatolia. The coal shortage caused by Russian submarine and destroyer attacks threatened the Ottoman Empire's continued participation in the war.[119]
Problems in the empire

By the middle of 1915, the impact of the war was demoralizing. Food and fuel were in short supply, casualties were increasing, and inflation was mounting. Strikes rose among low-paid factory workers, and there were reports that peasants, who wanted reforms of land ownership, were restless. The emperor eventually decided to take personal command of the army and moved to the front, leaving his wife, the Empress Alexandra, in charge in the capital. She fell under the spell of a monk, Grigori Rasputin (1869–1916). His assassination in late 1916 by a clique of nobles could not restore the emperor's lost prestige.[120]
End of imperial rule
On 3 March 1917, International Women's Day, a strike was organized at a factory in the capital, followed by thousands of people took to the streets in Petrograd to protest food shortages. A day later, protesters rose to two hundred thousand, demanding that Russia withdraw from the war and the emperor be deposed. Eighty thousand Russian troops, half of the men sent to restore order, had gone on strike and refused the senior officers' orders.[121] Any imperial symbols were destroyed and burned. The capital was out of control and gripped by protest and strife.[122]
In the city of Pskov, 262 km (163 mi) southwest from the capital, many generals and politicians advised the Emperor to abdicate in favor of the Tsarevich; Nicholas accepted, but he bequeathed the throne to Grand Duke Michael as his legitimate successor.[123] Michael stated that he would only accept the throne if it would be offered by a constituent assembly.[124] The form of political organization that emerged has been described as "dual power", with the Russian Provisional Government co-existing with the soviets.[124] The constitutional framework of Russia remained in limbo until Alexander Kerensky finally confirmed Russia's status as a republic on 1 September.[124] In July 1918, following the October Revolution, the Romanov family was executed by the Bolsheviks in Yekaterinburg.
Remove ads
Territory
Summarize
Perspective


By the end of the 19th century the area of the empire was about 22,400,000 square kilometers (8,600,000 sq mi), or almost one-sixth of the Earth's landmass; its only rival in size at the time was the British Empire. The majority of the population lived in European Russia. More than 100 different ethnic groups lived in the Russian Empire, with ethnic Russians composing about 45% of the population.[125]
Geography
The administrative boundaries of European Russia, apart from Finland and its portion of Poland, coincided approximately with the natural limits of the East-European plains. To the north was the Arctic Ocean. Novaya Zemlya and the Kolguyev and Vaygach Islands were considered part of European Russia, but the Kara Sea was part of Siberia. To the east were the Asiatic territories of the empire: Siberia and the Kyrgyz steppes, which were separated from European Russia by the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, and the Caspian Sea. The administrative boundary, however, partly extended into Asia on the Siberian slope of the Urals. To the south were the Black Sea and the Caucasus, being separated from the rest of European Russia by the Manych River depression, which in post-Pliocene times connected the Sea of Azov with the Caspian. The western boundary was purely arbitrary: it crossed the Kola Peninsula from the Varangerfjord to the Gulf of Bothnia. It then ran to the Curonian Lagoon in the southern Baltic Sea, and then to the mouth of the Danube, taking a great circular sweep to the west to embrace east-central Poland, and separating Russia from Prussia, Austrian Galicia, and Romania.
An important feature of Russia is its few free outlets to the open sea, outside the ice-bound shores of the Arctic Ocean. The deep indentations of the Gulfs of Bothnia and Finland were surrounded by what is ethnically Finnish territory, and it is only at the very head of the latter gulf that the Russians had taken firm foothold by erecting their capital at the mouth of the Neva river. The Gulf of Riga and the Baltic belong also to territory that was not inhabited by Slavs, but by Baltic and Finnic peoples, and by Germans. The east coast of the Black Sea belonged to Transcaucasia, a great chain of mountains separating it from Russia. But even this sheet of water is an inland sea, the only outlet of which, the Bosphorus, was in foreign hands, while the Caspian Sea, an immense shallow lake, mostly bordered by deserts, possessed more importance as a link between Russia and its Asiatic settlements than as a channel for intercourse with other countries.
Territorial development
From 1860 to 1905, the Russian Empire occupied all territories of the present-day Russian Federation, with the exception of the present-day Kaliningrad Oblast, Kuril Islands and Tuva. In 1905 Russia lost southern Sakhalin to Japan, but gained Tuva as a protectorate in 1914. Prior to 1917 the Russian Empire included most of Dnieper Ukraine, Belarus, Bessarabia, the Grand Duchy of Finland, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Central Asian states of Russian Turkestan, most of the Baltic governorates, a significant part of Poland, and the former Ottoman provinces of Ardahan, Artvin, Iğdır, Kars, and the northeastern part of Erzurum Province.
Henry Kissinger noted that the methodological procedure of how the Russian Empire started to expand their territory was comparable to that of how the United States had done the same. Russian statesman Alexander Gorchakov justified the Russian expansion in consonance of the Manifest destiny of the United States; thereafter, the Russian territorial expansion only encountered nomadic or feudal societies which is strikingly similar to the Westward Expansion of the United States.[126]
Between 1742 and 1867, the Russian-American Company administered Alaska as a colony. The company also established settlements in Hawaii, including Fort Elizabeth (1817), and as far south in North America as Fort Ross Colony (established in 1812) in Sonoma County, California just north of San Francisco. Both Fort Ross and the Russian River in California got their names from Russian settlers, who had staked claims in a region claimed until 1821 by the Spanish as part of New Spain.
Following the Swedish defeat in the Finnish War of 1808–1809 and the signing of the Treaty of Fredrikshamn on 17 September 1809, the eastern half of Sweden, the area that then became Finland, was incorporated into the Russian Empire as an autonomous grand duchy. The emperor eventually ended up ruling Finland as a semi-constitutional monarch through the Governor-General of Finland and a native Senate appointed by him. The emperor never explicitly recognized Finland as a constitutional state in its own right, although his Finnish subjects came to consider the grand duchy as such.

In the aftermath of the Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812), and the ensuing Treaty of Bucharest (1812), the eastern parts of the Principality of Moldavia, an Ottoman vassal state, along with some areas formerly under direct Ottoman rule, came under the rule of the empire. This area (Bessarabia) was among the Russian Empire's last territorial acquisitions in Europe. At the Congress of Vienna (1815), Russia gained sovereignty over Congress Poland, which on paper was an autonomous kingdom in personal union with Russia. However, this autonomy was eroded after the November Uprising in 1831, and was finally abolished in 1867.
Saint Petersburg gradually extended and consolidated its control over the Caucasus in the course of the 19th century, at the expense of Persia through the Russo-Persian War (1804–13) and Russo-Persian War (1826–28) and the respectively ensuing treaties of Gulistan and Turkmenchay,[127] as well as through the Caucasian War (1817–1864).
The Russian Empire expanded its influence and possessions in Central Asia, especially in the later 19th century, conquering much of Russian Turkestan in 1865 and continuing to add territory as late as 1885.
Newly discovered Arctic islands became part of the Russian Empire: the New Siberian Islands from the early 18th century; Severnaya Zemlya ("Emperor Nicholas II Land") first mapped and claimed as late as 1913.
During World War I, Russia briefly occupied a small part of East Prussia, then a part of Germany; a significant portion of Austrian Galicia; and significant portions of Ottoman Armenia. While the modern Russian Federation currently controls the Kaliningrad Oblast, which comprised the northern part of East Prussia, this differs from the area captured by the empire in 1914, though there was some overlap: Gusev (Gumbinnen in German) was the site of the initial Russian victory.
Imperial territories

According to the 1st article of the Organic Law, the Russian Empire was one indivisible state. In addition, the 26th article stated that "With the Imperial Russian throne are indivisible the Kingdom of Poland and Grand Principality of Finland". Relations with the Grand Principality of Finland were also regulated by the 2nd article, "The Grand Principality of Finland, constituted an indivisible part of the Russian state, in its internal affairs governed by special regulations at the base of special laws", and by the law of 10 June 1910.
Between 1744 and 1867, the empire also controlled Russian America. With the exception of this territory – modern-day Alaska – the Russian Empire was a contiguous mass of land spanning Europe and Asia. In this it differed from contemporary colonial-style empires. The result of this was that, while the British and French empires declined in the 20th century, a large portion of the Russian Empire's territory remained together, first within the Soviet Union, and after 1991 in the smaller Russian Federation.
Furthermore, the empire at times controlled concession territories, notably the Kwantung Leased Territory and the Chinese Eastern Railway, both conceded by Qing China, as well as the Russian concession of Tianjin.
In 1815, Georg Anton Schäffer, a Russian entrepreneur, went to Kauai and negotiated a treaty of protection with the island's governor Kaumualii, vassal of King Kamehameha I of Hawaii, but the Russian emperor refused to ratify the treaty. See also Orthodox Church in Hawaii and Russian Fort Elizabeth.
In 1889, a Russian adventurer, Nikolay Ivanovitch Achinov, tried to establish a Russian colony in Africa, Sagallo, situated on the Gulf of Tadjoura in present-day Djibouti. However this attempt angered the French, who dispatched two gunboats against the colony. After a brief resistance, the colony surrendered and the Russian settlers were deported to Odessa.
Remove ads
Government and administration
Summarize
Perspective
From its initial creation until the 1905 Revolution, the Russian Empire was led by the emperor (also referred to as tsar) who ruled as an absolute monarch. After the Revolution of 1905, Russia developed a new type of government, which became difficult to categorize. In the Almanach de Gotha for 1910, Russia was described as "a constitutional monarchy under an autocratic Tsar". This contradiction in terms demonstrated the difficulty of precisely defining the system, transitional and sui generis, established in the Russian Empire after October 1905. Before this date, the fundamental laws of Russia described the power of the emperor as "autocratic and unlimited". After October 1905, while the imperial style was still "Emperor and Autocrat of All the Russias", the fundamental laws were changed by removing the word unlimited. While the emperor retained many of his old prerogatives, including an absolute veto over all legislation, he equally agreed to the establishment of an elected parliament, without whose consent no laws were to be enacted in Russia. Not that the regime in Russia had become in any true sense constitutional, far less parliamentary. But the "unlimited autocracy" had given way to a "self-limited autocracy". Whether this autocracy was to be permanently limited by the new changes, or only at the continuing discretion of the autocrat, became a subject of heated controversy between conflicting parties in the state. Provisionally, then, the Russian governmental system may perhaps be best defined as "a limited monarchy under an autocratic emperor".
Conservatism was the ideology of most of the Russian leadership, albeit with some reformist activities from time to time. The structure of conservative thought was based upon anti-rationalism of the intellectuals, religiosity rooted in the Russian Orthodox Church, traditionalism rooted in the landed estates worked by serfs, and militarism rooted in the army officer corps.[128] Regarding irrationality, Russia avoided the full force of the European Enlightenment, which gave priority to rationalism, preferring the romanticism of an idealized nation state that reflected the beliefs, values, and behavior of the distinctive people.[129] The distinctly liberal notion of "progress" was replaced by a conservative notion of modernization based on the incorporation of modern technology to serve the established system. The promise of modernization in the service of autocracy frightened the socialist intellectual Alexander Herzen, who warned of a Russia governed by "Genghis Khan with a telegraph".[130]
Emperor

Peter the Great changed his title from tsar to emperor in order to secure Russia's position in the European states system.[131] While later rulers did not discard the new title, the Russian monarch was commonly known as the tsar or tsaritsa until the imperial system was abolished during the February Revolution of 1917. Prior to the issuance of the October Manifesto, the emperor ruled as an absolute monarch, subject to only two limitations on his authority, both of which were intended to protect the existing system: the emperor and his consort must both belong to the Russian Orthodox Church, and he must obey the Pauline Laws of succession established by Paul I. Beyond this, the power of the Russian autocrat was virtually limitless.
On 17 October 1905, the situation changed: the ruler voluntarily limited his legislative power by decreeing that no measure was to become law without the consent of the Imperial Duma, a freely elected national assembly established by the Organic Law issued on 28 April 1906. However, he retained the right to disband the newly established Duma, and he exercised this right more than once. He also retained an absolute veto over all legislation, and only he could initiate any changes to the Organic Law itself. His ministers were responsible solely to him, and not to the Duma or any other authority, which could question but not remove them. Thus, while the emperor's personal powers were limited in scope after 28 April 1906, they remained formidable.
Imperial Council


Under Russia's revised Fundamental Law of 20 February 1906, the State Council was associated with the Duma as a legislative Upper House; from this time the legislative power was exercised normally by the emperor only in concert with the two chambers.[132] The Council of the Empire, or Imperial Council, as reconstituted for this purpose, consisted of 196 members, of whom 98 were nominated by the emperor, while 98 were elective. The ministers, also nominated, were ex officio members. Of the elected members, 3 were returned by the "black" clergy (the monks), 3 by the "white" clergy (secular), 18 by the corporations of nobles, 6 by the academy of sciences and the universities, 6 by the chambers of commerce, 6 by the industrial councils, 34 by local governmental zemstvos, 16 by local governments having no zemstvos, and 6 by Poland. As a legislative body the powers of the council were coordinate with those of the Duma; in practice, however, it has seldom if ever initiated legislation.
State Duma
The Duma of the Empire or Imperial Duma (Gosudarstvennaya Duma), which formed the lower house of the Russian parliament, consisted (since the ukaz of 2 June 1907) of 442 members, elected by an exceedingly complicated process. The membership was manipulated as to secure an overwhelming majority of the wealthy (especially the landed classes) and also for the representatives of the Russian peoples at the expense of the subject nations. Each province of the empire, except Central Asia, returned a certain number of members; added to which were those returned by several large cities. The members of the Duma were chosen by electoral colleges and these, in their turn, were elected by assemblies of the three classes: landed proprietors, citizens, and peasants. In these assemblies the wealthiest proprietors sat in person while the lesser proprietors were represented by delegates. The urban population was divided into two categories according to taxable wealth and elected delegates directly to the college of the governorates. The peasants were represented by delegates selected by the regional subdivisions called volosts. Workmen were treated in a special manner, with every industrial concern employing fifty hands electing one or more delegates to the electoral college.
In the college itself, the voting for the Duma was by secret ballot and a simple majority carried the day. Since the majority consisted of conservative elements (the landowners and urban delegates), the progressives had little chance of representation at all, save for the curious provision that one member at least in each government was to be chosen from each of the five classes represented in the college. That the Duma had any radical elements was mainly due to the peculiar franchise enjoyed by the seven largest towns — Saint Petersburg, Moscow, Kiev, Odessa, Riga, and the Polish cities of Warsaw and Łódź. These elected their delegates to the Duma directly, and though their votes were divided (on the basis of taxable property) in such a way as to give the advantage to wealth, each returned the same number of delegates.
Council of Ministers
In 1905, a Council of Ministers (Sovyet Ministrov) was created, under a minister president, the first appearance of a prime minister in Russia. This council consisted of all the ministers and of the heads of other principal departments. The ministries were as follows:
- Ministry of the Imperial Court
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs;
- Ministry of War;
- Ministry of the Navy;
- Ministry of Finance;
- Ministry of Commerce and Industry (created in 1905);
- Ministry of Internal Affairs (including police, health, censorship and press, posts and telegraphs, foreign religions, statistics);
- Ministry of Agriculture and State Assets;
- Ministry of Ways of Communications;
- Ministry of Justice;
- Ministry of National Education.
Most Holy Synod

The Most Holy Synod (established in 1721) was the supreme organ of government of the Orthodox Church in Russia. It was presided over by a lay Procurator, representing the emperor, and consisted of the three metropolitans of Moscow, Saint Petersburg, and Kiev, the Archbishop of Georgia, and a number of bishops sitting in rotation.
Senate
The Senate (Pravitelstvuyushchi Senat, i.e. directing or governing senate), originally established during the Government reform of Peter the Great, consisted of members nominated by the emperor. Its wide variety of functions were carried out by the different departments into which it was divided. It was the supreme court of cassation; an audit office; a high court of justice for all political offences; and one of its departments fulfilled the functions of a heralds' college. It also had supreme jurisdiction in all disputes arising out of the administration of the empire, notably in differences between representatives of the central power and the elected organs of local self-government. Lastly, it promulgated new laws, a function which theoretically gave it a power akin to that of the Supreme Court of the United States, of rejecting measures not in accordance with fundamental laws.
Administrative divisions


As of 1914, Russia was divided into 81 governorates (guberniyas), 20 oblasts, and 1 okrug. Vassals and protectorates of the Russian Empire included the Emirate of Bukhara, the Khanate of Khiva, and, after 1914, Tuva (Uriankhai). Of these, 11 Governorates, 17 oblasts, and 1 okrug (Sakhalin) belonged to Asian Russia. Of the rest, 8 Governorates were in Finland and 10 in Congress Poland. European Russia thus embraced 59 governorates and 1 oblast (that of the Don). The Don Oblast was under the direct jurisdiction of the ministry of war; the rest each had a governor and deputy-governor, the latter presiding over the administrative council. In addition, there were governors-general, generally placed over several governorates and armed with more extensive powers, usually including the command of the troops within the limits of their jurisdiction. In 1906, there were governors-general in Finland, Warsaw, Vilna, Kiev, Moscow, and Riga. The larger cities (Saint Petersburg, Moscow, Odessa, Sevastopol, Kerch, Nikolayev, and Rostov) had administrative systems of their own, independent of the governorates; in these the chief of police acted as governor.
Remove ads
Judicial system
Summarize
Perspective
The judicial system of the Russian Empire was established by the statute of 20 November 1864 of Alexander II. This system – based partly on English and French law – was predicated on the separation of judicial and administrative functions, the independence of the judges and courts, public trials and oral procedure, and the equality of all classes before the law. Moreover, a democratic element was introduced by the adoption of the jury system and the election of judges. This system was disliked by the bureaucracy, due to its putting the administration of justice outside of the executive sphere. During the latter years of Alexander II and the reign of Alexander III, power that had been given was gradually taken back, and that takeback was fully reversed by the third Duma after the 1905 Revolution.[j]
The system established by the law of 1864 had two wholly separate tribunals, each having their own courts of appeal and coming in contact with each other only in the Senate, which acted as the supreme court of cassation. The first tribunal, based on the English model, were the courts of the elected justices of the peace, with jurisdiction over petty causes, whether civil or criminal; the second, based on the French model, were the ordinary tribunals of nominated judges, sitting with or without a jury to hear important cases.
Remove ads
Local administration
Summarize
Perspective
Alongside the local organs of the central government in Russia there are three classes of local elected bodies charged with administrative functions:
- the peasant assemblies in the mirs and the volosts;
- the zemstvos in the 34 governorates of Russia;
- the municipal dumas.
Municipal dumas

Since 1870, the municipalities in European Russia had institutions like those of the zemstvos. All owners of houses, tax-paying merchants, artisans, and workmen were enrolled on lists, in descending order according to their assessed wealth. The total valuation was then divided into three equal parts, representing three groups of electors very unequal in number, each of which would elect an equal number of delegates to the municipal duma. The executive was in the hands of an elected mayor and an uprava, which consisted of several members elected by the municipal duma. Under Alexander III, however, bylaws promulgated in 1892 and 1894, the municipal dumas were subordinated to the governors in the same way as the zemstvos. In 1894, municipal institutions, with still more restricted powers, were granted to several towns in Siberia, and in 1895 to some in the Caucasus.
Baltic provinces
The formerly Swedish-controlled Baltic provinces of Livonia and Estonia and later Duchy of Courland, a vassal of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, were incorporated into the Russian Empire after the defeat of Sweden in the Great Northern War. Under the Treaty of Nystad of 1721, the Baltic German nobility retained considerable powers of self-government and numerous privileges in matters affecting education, police, and the local administration of justice. After 167 years of German language administration and education, in 1888 and 1889 laws were passed transferring administration of the police and manorial justice from Baltic German control to officials of the central government. About the same time, a process of Russification was being carried out in the same provinces, in all departments of administration, in the higher schools, and in the Imperial University of Dorpat, the name of which was altered to Yuriev. In 1893, district committees for the management of the peasants' affairs, similar to those in purely Russian governments, were introduced into this part of the empire.
Remove ads
Economy
Summarize
Perspective

Before the abolition of serfdom in 1861, Russia's economy mainly depended on agriculture.[133] By the census of 1897, 95% of the Russian population lived in the countryside.[134] Nicholas I attempted to modernise his country, and have it not been so dependent on a single economic sector.[135] During the reign of Alexander III, many reforms occurred. The Peasants' Land Bank was founded in 1883 to provide loans for Russian peasants, both as individuals and in communes. The Nobles' Land Bank, in 1885, made loans at nominal interest rates to the landed nobility. The poll tax was abolished in 1886.[136]
When Ivan Vyshnegradsky was appointed as the new minister of finance in 1886, he increased the pressure on peasants by increasing taxes on land and prescribing how they harvested grain. These policies led to the severe Russian famine of 1891–1892, with four hundred thousand perishing from starvation. Vyshnegradsky was succeeded by Count Sergei Witte in 1892. Witte began by raising revenues through a monopoly on alcohol, which brought in 300 million rubles in 1894. These reforms returned the peasants to essentially being serfs again.[137] In 1900, a wealthy peasant class (kulaks) had emerged, representing less than 20% of the population.[138] An income tax was introduced in 1916.
Agriculture
Russia had a longstanding economic bargain on fundamental agriculture on large estates worked by Russian peasants (also known as serfs), who did not get any rights from slave masters under the system of "barshchina".[k] Another system was called obrok,[l] in which serfs worked in exchange for cash or goods from the master, allowing them to work outside the estate.[139] These systems were based on a legal code called the Sobornoye Ulozheniye, which was introduced by Alexis I in 1649.
From 1891 to 1892, peasants were faced with new policies carried out by Ivan Vyshnegradsky, causing a famine and disease that took the lives of four hundred thousand people,[140][141] especially in the Volga region, eliciting the greatest decline in grain production.[142]
Mining and heavy industry


Remove ads
Infrastructure
Rail

After 1860, the expansion of Russian rail had far-reaching effects on the economy, culture, and ordinary life of Russia. The central authorities and the imperial elite made most of the key decisions, but local elites made demands for rail linkages. Local nobles, merchants, and entrepreneurs imagined a future of promoting their regional interests, from "locality" to "empire". Often, they had to compete with other cities. By envisioning their own role in a rail network they came to understand how important they were to the empire's economy.[143]
During the 1880s, the Russian army built two major rail lines in Central Asia. The Transcaucasus Railway connected the city of Batum on the Black Sea and the oil center of Baku on the Caspian Sea. The Trans-Caspian Railway began at Krasnovodsk on the Caspian Sea and reached Bukhara, Samarkand, and Tashkent. Both lines served the commercial and strategic needs of the empire and facilitated migration.[144]
Remove ads
Religion
Summarize
Perspective


The Russian Empire's state religion was Orthodox Christianity.[145] The emperor was not allowed to "profess any faith other than the Orthodox" (Article 62 of the 1906 Fundamental Laws) and was deemed "the Supreme Defender and Guardian of the dogmas of the predominant Faith and is the Keeper of the purity of the Faith and all good order within the Holy Church" (Article 64 ex supra). Although he made and annulled all senior ecclesiastical appointments, he did not settle questions of dogma or church teaching. The principal ecclesiastical authority of the Russian Church—which extended its jurisdiction over the entire territory of the empire, including the ex-Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti—was the Most Holy Synod, the civilian Over Procurator of the Holy Synod being one of the council of ministers with wide de facto powers in ecclesiastical matters.
The ecclesiastical heads of the national Russian Orthodox Church consisted of three metropolitans (Saint Petersburg, Moscow, Kiev), fourteen archbishops and fifty bishops, all drawn from the ranks of the monastic (celibate) clergy. The parochial clergy had to be married when appointed, but if left widowers were not allowed to marry again; this rule continues to apply today.
Religious policy
All non-Orthodox religions were formally forbidden from proselytizing within the empire.[146] In a policy influenced by Catherine II but solidified in the 19th century, Tsarist Russia exhibited increasing "confessionalization", pursuing top-down reorganization of the empire's faiths,[146] also referred to as the "confessional state".[147] The tsarist administration sought to arrange "orthodoxies" within Islam, Buddhism, and the Protestant faiths, which was performed by creating spiritual assemblies (in the case of Islam, Judaism, and Lutheranism), banning and declaring bishoprics (in the case of Roman Catholicism), and arbitrating doctrinal disputes.[146] When the state lacked resources to provide a secular bureaucracy across its entire territory, guided 'reformation' of faiths provided elements of social control.[146][147]
Anti-semitism
After Catherine II annexed eastern Poland in the Polish Partitions,[148] there were restrictions placed against Jews known as the Pale of Settlement, an area of Tsarist Russia inside which Jews were authorized to settle, and outside of which were deprived of various rights such as freedom of movement or commerce.[149] Particularly repressive was Emperor Nicholas I, who sought the forced assimilation of Jews,[150] from 1827 conscripted Jewish children as Cantonists in military institutions in the east aiming to compel them to convert to Christianity,[151] attempted to stratify Jews into "useful" and "not useful" based on wealth[150] and further restricted religious and commercial rights within the Pale of Settlement.[149][152] Emperor Alexander II ceased this harsh treatment and pursued a more bureaucratic type of assimilation,[150] such as compensating the Cantonists for their previous military service, including those who remained Jewish,[149] although certain military ranks were still limited to Christians.[150] In contrast, Emperor Alexander III resumed an atmosphere of oppression, including the May Laws, which further restricted Jewish settlements and rights to own property, as well as limiting the types of professions available,[149][153] and the expulsion of Jews from Kiev in 1886 and Moscow in 1891. The overall anti-Jewish policy of the Russian Empire led to significant sustained emigration.[149]
Persecution of Muslims
Islam had a "sheltered but precarious" place in the Russian Empire.[154] Initially, sporadic forced conversions were demanded against Muslims in the early Russian Empire. In the 18th century, Catherine II issued an edict of toleration that gave legal status to Islam and allowed Muslims to fulfill religious obligations.[155] Catherine also established the Orenburg Muslim Spiritual Assembly, which had a degree of imperial jurisdiction over the organization of Islamic practice in the country.[156] As the Russian Empire expanded, tsarist administrators found it expedient to draw on existing Islamic religious institutions that were already in place.[157][156]

In the 19th century, the restrictive policies became much more oppressive during the Russo-Turkish Wars, and the Russian Empire perpetrated persecutions such as the Circassian genocide during the 1860s.[155][159] Following its conquest of Circassia, around 1 to 1.5 million Circassians – almost half of the total population – were killed or forcibly deported.[160] Many of those who fled persecution also died en route to other countries. Today, the vast majority of Circassians live in diaspora communities.[161] Throughout the late 19th century, the term "Circassian" became a common adage for "highwayman" across the Balkan and Anatolian regions, due to the prevalence of homeless Circassian refugees.[162]
Many groups of Muslims such as Crimean Tatars were forced to emigrate to the Ottoman Empire following the Russian defeat in the Crimean War.[163] During the latter portion of the 19th century, the status of Islam in the Russian Empire became associated with the tsarist regime's ideological principles of Official Nationality requiring Russian Orthodoxy.[157] Nonetheless, in certain areas Islamic institutions were allowed to operate, such as the Orenburg Assembly, but were designated with a lower status.[156]
Policy towards non-Eastern Orthodox Christian sects

Despite the predominance of Orthodoxy, several Christian denominations were professed.[164] Lutherans were particularly tolerated with the invited settlement of Volga Germans and the presence of Baltic German nobility.[165] During the reign of Catherine II, the Jesuit suppression was not promulgated, so Jesuits survived in Russian Empire, and this "Russian Society" played a role in re-establishing the Jesuits in the west.[166] Overall, Roman Catholicism was strictly controlled during Catherine II's reign, which was considered an epoch of relative tolerance for Catholicism.[146][167] Catholics were distrusted by the Russian Empire as elements of Polish nationalism, a perception which especially increased following the January Uprising.[168] After this Russification policies intensified and Orthodox churches such as Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, Warsaw were built across Congress Poland, but no forced conversion was attempted.
Tsarist religious policy was focused on punishing Orthodox dissenters, such as uniates and sectarians.[146] Old Believers were seen as dangerous elements and persecuted heavily.[169][22] Various minor sects such as Spiritual Christians and Molokan were banished in internal exile to Transcaucasia and Central Asia, with some further emigrating to the Americas.[170] Doukhobors came to settle primarily in Canada.[171]
In 1905, Emperor Nicholas II issued a religious toleration edict that gave legal status to non-Orthodox religions.[172] This created a "Golden Age of Old Faith" for the previously persecuted Old Believers until the emergence of the Soviet Union.[22] In the early 20th century, some of the restrictions of the Pale of Settlement were reversed, though were not formally abolished until the February Revolution.[149] However, some historians evaluate Tsar Nicholas II as having given tacit approval to the antisemitic pogroms that resulted from reactionary riots.[152][173] Edward Radzinsky suggested that many pogroms were incited by authorities and supported by the Tsarist Russian secret police, the Okhrana, even if some happened spontaneously.[174] According to Radzinsky, Sergei Witte (appointed Prime Minister in 1905) remarked in his Memoirs that he found that some proclamations inciting pogroms were printed and distributed by imperial Police.[174]: 69
Remove ads
Demography
Summarize
Perspective



Imperial census of 1897
According to returns published in 1905, based on the Russian Empire census of 1897, adherents of the different religious communities in the empire numbered approximately as follows.
Russian Central Asia
Russian Central Asia was also called Turkestan. As of the 1897 census, Russian Central Asia's five oblasts contained 5,260,300 inhabitants, 13.9 percent of them urban. The largest towns were Tashkent (156,400), Kokand (82,100), Namangan (61,900), and Samarkand (54,900). By 1911, 17 percent of Semireche's population and half of its urban residents were Russians, four-fifths of them agricultural colonists. In the other four oblasts in the same year, Russians constituted only 4 percent of the population, and the overwhelming majority lived in European-style settlements alongside the native quarters in the major towns.[176]
Military
Summarize
Perspective


The armed forces of the Russian Empire consisted of the Imperial Russian Army and the Imperial Russian Navy. The Emperor of Russia was the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and implemented out his military policies through the Ministry of War and the Ministry of the Navy, which were tasked with administering their respective branches. There was no joint staff, but joint commissions were formed to work on specific tasks that involved both services.[177][178] The Main Staff of the War Ministry administered the Army's organization, training, and mobilization, as well as coordinating the different branches of the Army, while the General Staff was tasked with operational planning. This structure developed in the 1860s after the Crimean War.[179] The Navy Ministry had a similar structure, including a Main Staff tasked with administration and a Naval Technological Committee, and after the Russo-Japanese War a Naval General Staff was added for operational planning and war preparation.[180][181]
Peter the Great transformed Russia's mix of irregular, feudal, and modernized forces into a standing army and navy to meet the demands posed by the Great Northern War against Sweden and the conflicts with the Ottoman Empire. His reign also accelerated changes that had already started earlier. Peter issued a decree in 1699 that formed the basis for army recruitment,[182] founded an artillery school in 1701 and an engineer school in 1709, put together military regulations for the organization of the army in 1716,[183] created administrative organs to oversee the land and naval forces in 1718 (the College of War and the Admiralty),[182] and oversaw the building of a new navy from scratch.[182] These reforms were done with the help of foreign experts, though before the end of Peter's reign these experts were being increasingly replaced by Russian officers.[182]
Most of the enlisted soldiers and sailors were peasant conscripts, though by the late 19th century Imperial Navy preferred to draft members of the urban working class to fill its more technical roles. Both the army and navy had a shortage of non-commissioned officers, who were promoted from the enlisted ranks and tended to leave the military at the end of their mandatory service.[184][185] Except for a few special units,[186] almost no one voluntarily joined the military without the intention of becoming an officer.[187] After the post-Crimean War reforms, there were three main commissioning sources of army officers: the Page Corps, the cadet corps, and the junker or military schools.[188] The cadet corps, among which the Page Corps was considered the most elite,[189] provided a military boarding school education to the sons of the high nobility as teenagers.[190] The junker schools provided the largest number of officers, and had a two-year education program for older enlisted soldiers that served for at least one year, and these were most often either lesser nobility or commoners.[191] The majority of army officers were nobles, though this changed by the end of the 19th century, with non-nobles being almost half of the officer corps in the 1890s.[192] The source of naval officers was the Naval Cadet Corps.[193] The majority of naval officers were also from the nobility, and many of them were descended from Baltic German or Swedish families with a history of naval service.[194]
The Russian military budget declined in the late 19th century as the government prioritized spending for civilian purposes, paying interest on foreign loans, and building railways.[194] Russia maintained a large peacetime standing army of over one million men in the decades after the Napoleonic Wars,[195] and at the outbreak of World War I it was the largest in Europe.[196] During the war the Russian Army was unable to match the German Army in tactical and operational proficiency, but its performance against the Austro-Hungarian Army and the Ottoman Army was credible.[197] The Russo-Japanese War took Russia from having the third largest navy in the world to the sixth largest.[198] A reconstruction program approved by the State Duma in 1912, but it was not completed before World War I.[199] Russia's Baltic Fleet stayed on the defensive against the German High Seas Fleet,[200] but its Black Sea Fleet had success in raiding Ottoman merchant shipping and threatened the ability of the Ottoman Empire to continue the war.[119]
Remove ads
Society
Summarize
Perspective
The Russian Empire was predominantly a rural society spread over vast spaces. In 1913, 80% of the people were peasants. Soviet historiography proclaimed that the Russian Empire of the 19th century was characterized by systemic crisis, which impoverished the workers and peasants and culminated in the revolutions of the early 20th century. Recent research by Russian scholars disputes this interpretation. Boris Mironov assesses the effects of the reforms of latter 19th-century, especially in terms of the 1861 emancipation of the serfs, agricultural output trends, various standard of living indicators, and taxation of peasants. He argues that those reforms brought about measurable improvements in social welfare. More generally, he finds that the well-being of the Russian people declined during most of the 18th century but increased slowly from the end of the 18th century to 1914.[201]
Estates
Subjects of the Russian Empire were segregated into sosloviyes, or social estates (classes) such as nobility (dvoryanstvo), clergy, merchants, cossacks, and peasants. Native people of the Caucasus, non-ethnic Russian areas such as Tatarstan, Bashkortostan, Siberia and Central Asia were officially registered as a category called inorodtsy ('non-Slavic', lit. 'people of another origin').
A majority of the population, 81.6%, belonged to the peasant order. The other classes were the nobility, 0.6%; clergy, 0.1%; the burghers and merchants, 9.3%; and military, 6.1%. More than 88 million Russians were peasants, some of whom were former serfs (10,447,149 males in 1858) – the remainder being "state peasants" (9,194,891 males in 1858, exclusive of the Archangel governorate) and "domain peasants" (842,740 males the same year).
- Other status
Serfdom


The serfdom that had developed in Russia in the 16th century, and had become enshrined in law in 1649, was abolished in 1861.[202][203]
Household servants or dependents attached to personal service were merely set free, while the landed peasants received their houses and orchards, and allotments of arable land. These allotments were given over to the rural commune, the mir, which was responsible for the payment of taxes for the allotments. For these allotments the peasants had to pay a fixed rent, which could be fulfilled by personal labor. The allotments could be redeemed by peasants with the help of the Crown, and then they were freed from all obligations to the landlord. The Crown paid the landlord and the peasants had to repay the Crown, for forty-nine years at 6% interest. The financial redemption to the landlord was not calculated on the value of the allotments but was considered as compensation for the loss of the compulsory serf labor. Many proprietors contrived to curtail the allotments that the peasants had occupied under serfdom, and frequently deprived them of precisely that land of which they were most in need: pasture lands around their houses. The result was to compel the peasants to rent land from their former masters.[204][205]
Serfs lived in deplorable conditions, working in the fields for nearly seven days a week and being exiled to the harsh land of Siberia or sent to military service. Owners had the right to sell slaves, depending on whether they were targeting land or accused (i.e., had escaped from working). Children of serfs received less education. These serfs were heavily taxed, making them the poorest of any Russians.[139] In 1861, Emperor Alexander II saw serfs as a problem that held back Russia's development, so he liberated 23 million serfs to become free,[206] but they remained indigent throughout the former enslaved population despite their rights. The zemstvo system was introduced in 1865 as a rural assembly with administrative authority over the local population, including education and welfare, which ex-serfs were unable to acquire.
- Exceptional status
Peasants


The former serfs became peasants, joining the millions of farmers who already had peasant status.[205][203] Most peasants lived in tens of thousands of small villages under a highly patriarchal system. Hundreds of thousands moved to cities to work in factories, but they typically retained their village connections.[207]
After Emancipation reform, one-quarter of peasants received allotments of only 1.2 hectares (2.9 acres) per male, and one-half received less than 3.4 to 4.6 hectares (8.5 to 11.4 acres); the normal size of the allotment necessary for the subsistence of a family under the three-fields system is estimated at 11 to 17 hectares (28 to 42 acres). This land was of necessity rented from the landlords. The aggregate value of the redemption and land taxes often reached 185 to 275% of the normal rental value of the allotments, not to speak of taxes for recruiting purposes, the church, roads, local administration, and so on, chiefly levied on the peasants. This burden increased every year; consequently, one-fifth of the inhabitants left their houses and cattle disappeared. Every year more than half the adult males (in some districts three-quarters of the men and one-third of the women) quit their homes and wandered throughout Russia in search of work. In the governments of the Black Earth Area the state of matters was hardly better. Many peasants took "gratuitous allotments", whose amount was about one-eighth of the normal allotments.[208]
The average allotment in Kherson was only 0.36 hectares (0.90 acres), and for allotments from 1.2 to 2.3 hectares (2.9 to 5.8 acres) the peasants paid 5 to 10 rubles in redemption tax. The state peasants were better off; but they, too, were emigrating in masses. It was only in the steppe that the situation was more hopeful. In Ukraine, where the allotments were personal (the mir existing only among state peasants), the state of affairs was not better, on account of high redemption taxes. In the western provinces, where the land was more cheaply valued and the allotments somewhat increased after the Polish insurrection, the situation was better. Finally, in the Baltic provinces nearly all the land belonged to the German landlords, who either farmed the land themselves, with hired laborers, or let it in small farms. Only one-quarter of the peasants were farmers; the remainder were mere laborers.[209]
Landowners
The situation of the former serf-proprietors was also unsatisfactory. Accustomed to the use of compulsory labor, they failed to adapt to the new conditions. The millions of rubles of redemption money received from the crown was spent without any real or lasting agricultural improvements having been effected. The forests were sold, and the only prosperous landlords were those who exacted rack-rents for the land allotted to peasants. There was an increase of wealth among the few, but along with this a general impoverishment of the mass of the people. Added to this, the peculiar institution of the mir—framed on the principle of community ownership and occupation of the land—the overall effect was not encouraging of individual effort.
During the years 1861 to 1892 the land owned by the nobles decreased 30%, or from 850,000 to 610,000 km2 (210,000,000 to 150,000,000 acres); during the following four years an additional 8,577 km2 (2,119,500 acres) were sold; and since then the sales went on at an accelerated rate, until in 1903 alone close to 8,000 km2 (2,000,000 acres) passed out of their hands. On the other hand, since 1861, and more especially since 1882, when the Peasant Land Bank was founded for making advances to peasants who were desirous of purchasing land, the former serfs, or rather their descendants, had between 1883 and 1904 bought about 78,900 km2 (19,500,000 acres) from their former masters.
In November 1906, however, Emperor Nicholas II promulgated a provisional order permitting the peasants to become freeholders of allotments made at the time of emancipation, all redemption dues being remitted. This measure, which was endorsed by the third Duma in an act passed on 21 December 1908, was calculated to have far-reaching and profound effects on the rural economy of Russia. Thirteen years previously the government had endeavored to secure greater fixity and permanence of tenure by providing that at least twelve years must elapse between every two redistributions of the land belonging to a mir amongst those entitled to share in it. The order of November 1906 provided that the various strips of land held by each peasant should be merged into a single holding; the Duma, however, on the advice of the government, left its implementation to the future, regarding it as an ideal that could only gradually be realized.[209]
Media
Censorship was heavy-handed until the reign of Alexander II, but it never went away.[210] Newspapers were strictly limited in what they could publish, and intellectuals favored literary magazines for their publishing outlets. Fyodor Dostoyevsky, for example, ridiculed the St. Petersburg newspapers, such as Golos and Peterburgskii Listok, accusing them of publishing trifles and distracting readers from the pressing social concerns of contemporary Russia through their obsession with spectacle and European popular culture.[211]
Education

Educational standards were very low in the Russian Empire, though they slowly increased in its last century of existence. By 1800, the level of literacy among male peasants ranged from 1 to 12 percent and from 20 to 25 percent for urban men. Literacy among women was very low. Literacy rates were highest for the nobility (84 to 87 percent), followed by merchants (over 75 percent), and then the workers and peasants. Serfs were the least literate. In every group, women were far less literate than men. By contrast, in Western Europe, urban men had about a 50 percent literacy rate. The Orthodox hierarchy was suspicious of education, seeing no religious need for literacy whatsoever. Peasants did not need to be literate, and those who did — such as artisans, businessmen, and professionals — were few in number. As late as 1851, only 8% of Russians lived in cities.[212]
The accession in 1801 of Alexander I (1801–1825) was widely welcomed as an opening to fresh liberal ideas from the European Enlightenment. Many reforms were promised, but few were implemented before 1820, when the emperor shifted his focus to foreign affairs and personal religious matters, neglecting issues of reform. In sharp contrast to Western Europe, the entire empire had a very small bureaucracy – about 17,000 public officials, most of whom lived in two of the largest cities, Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Modernization of government required much larger numbers; but that, in turn, required an educational system that could provide suitable training. Russia lacked that, and for university education, young men went to Western Europe. The army and the church had their own training programs, narrowly focused on their particular needs. The most important successful reform under Alexander I was the creation of a national system of education.[213]

The Ministry of Education was established in 1802, and the country was divided into six educational regions. The long-term plan was for a university in every region, a secondary school in every major city, upgraded primary schools, and – serving the largest number of students – a parish school for every two parishes. By 1825, the national government operated six universities, forty-eight secondary state schools, and 337 improved primary schools. Highly qualified teachers arrived from France, fleeing the revolution there. Exiled Jesuits set up elite boarding schools until their order was expelled in 1815. At the highest level, universities were based on the German model—in Kazan, Kharkov, St. Petersburg, Vilna (refounded as the Imperial University in 1803) and Dorpat—while the relatively young Imperial Moscow University was expanded. The higher forms of education were reserved for a very small elite, with only a few hundred students at the universities by 1825 and 5500 in the secondary schools. There were no schools open to girls. Most rich families still depended on private tutors.[214]
Emperor Nicholas I was a reactionary who wanted to neutralize foreign ideas, especially those he ridiculed as "pseudo-knowledge". Nevertheless, his Minister of Education, Sergey Uvarov, promoted greater academic freedom at the university level for faculty members, who were under suspicion by reactionary church officials. Uvarov raised academic standards, improved facilities, and opened the admission doors a bit wider. Nicholas tolerated Uvarov's achievements until 1848, after which he reversed these innovations.[215] For the rest of the century, the national government continued to focus on universities, and generally ignored elementary and secondary educational needs. By 1900 there were 17,000 university students, and over 30,000 were enrolled in specialized technical institutes. The students were conspicuous in Moscow and Saint Petersburg as a political force typically at the forefront of demonstrations and disturbances.[216] The majority of tertiary institutions in the empire used Russian, while some used other languages but later underwent Russification.[217] Other educational institutions in the empire included the Nersisian School in Tiflis.
Remove ads
See also
Notes
- In 1914, the city was renamed Petrograd to reflect anti-German sentiments of Russia during World War I.[1]
- As Chairman of the Committee of Ministers.
- Russian: Россійская Имперія, romanized: Rossíyskaya Impériya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijskəjə ɪmˈpʲerʲɪjə] ⓘ; Российская Империя in modern Russian spelling.
- Also known as Imperial Russia, and in some contexts may be imprecisely referred to as Tsarist Russia, or simply Russia. Also, pre-revolutionary Russia may refer to the Russian Empire either before the Russian Revolution of 1905 or before the Russian Revolution of 1917.
- Russian: Отец отечества, romanized: Otets otechestva, IPA: [ɐˈtʲet͡s ɐˈtʲet͡ɕɪstvə]
- Originally there was no distinction between the titles tsar and imperator. However, tsar was also used to refer to other monarchs below the rank of "emperor" (according to the Western European view), and thus Westerners began to translate tsar as rex ("king"). By adopting the title imperator, Peter claimed equality to the Holy Roman Emperor.[28][29]
- A ukaz of 1879 gave the governors the right to report secretly on the qualifications of candidates for the office of justice of the peace. In 1889, Alexander III abolished the election of justices of the peace, except in certain large towns and some outlying parts of the Empire, and greatly restricted the right of trial by jury. The combining of judicial and administrative functions was introduced again by the appointment of officials as judges. In 1909, the third Duma restored the election of justices of the peace.
- Russian: барщина, IPA: [ˈbarɕːɪnə]
- Russian: оброк, IPA: [ɐˈbrok]
- The Lutheran Church was the dominant faith of the Baltic Provinces, of Ingria, and of the Grand Duchy of Finland
References
Works cited
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads






