Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Scheduled Banks (India)
Banks holding reserves above a specific level From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Scheduled Banks in India refer to those banks which have been included in the Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.[1] Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in turn includes only those banks in this Schedule which satisfy all the criteria laid down via section 42(6)(a) of the said Act. Banks not under this Schedule are called Non-Scheduled Banks.
Remove ads
Facilities
Every scheduled bank enjoys two types of principal facilities: it becomes eligible for debts/loans at the bank rate from the RBI; and, it automatically acquires the membership of clearing house.[2]
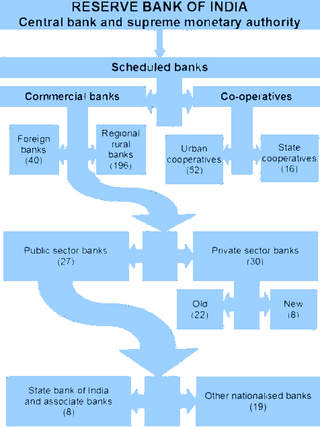
Types of banks
There are two main categories of Scheduled Banks in India, namely:
- Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Scheduled Co-operative Banks
Scheduled Commercial Banks are further divided into six types, as below:
- Scheduled Public Sector Banks
- Scheduled Private Sector Banks
- Scheduled Small Finance Banks
- Scheduled Regional Rural Banks
- Foreign Banks
- Scheduled Payments Banks[3][4]
Scheduled Co-operative Banks are further divided into two types, as below:
- Scheduled State Co-operative Banks
- Scheduled Urban Co-operative Banks
Remove ads
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
